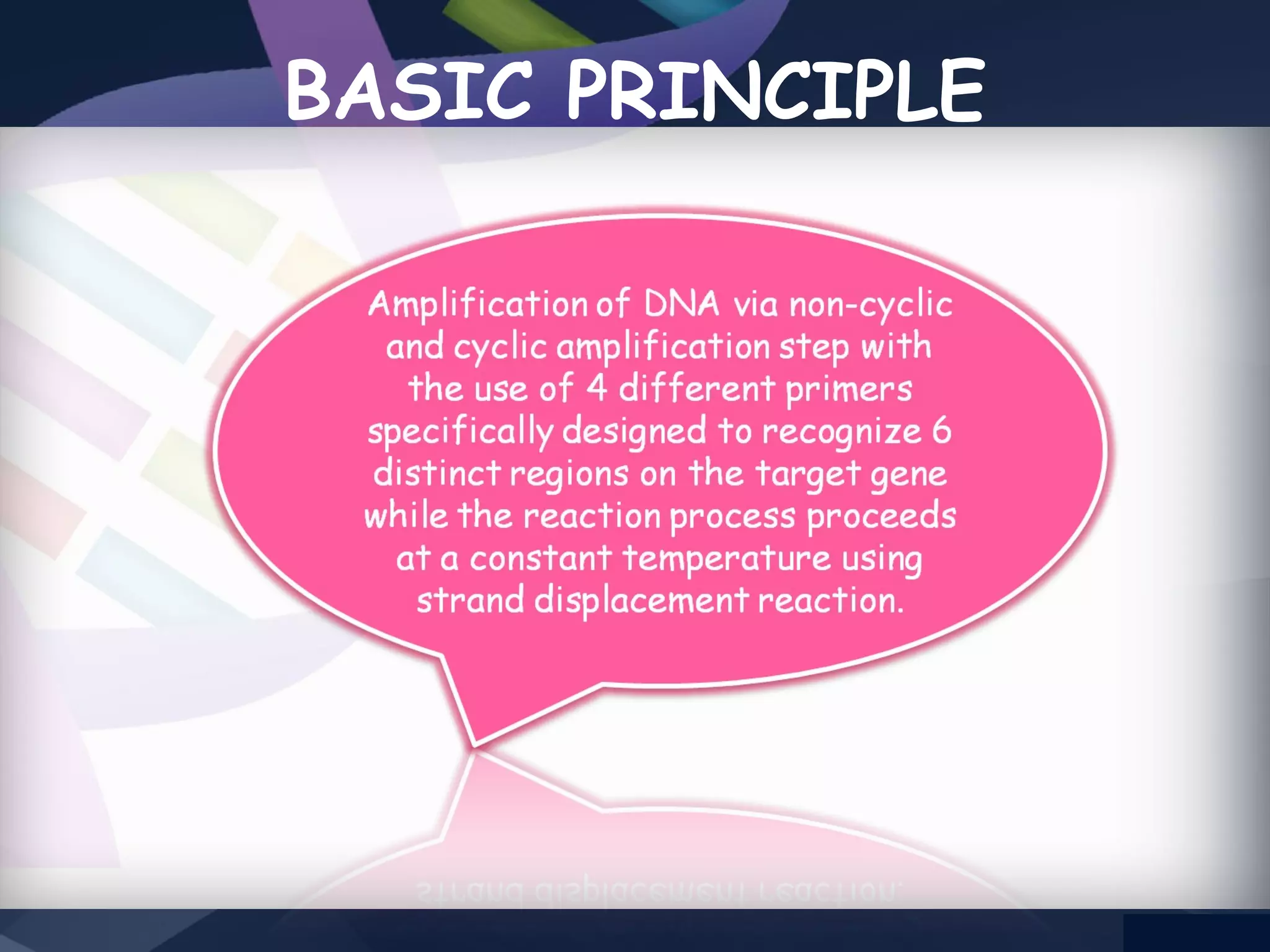
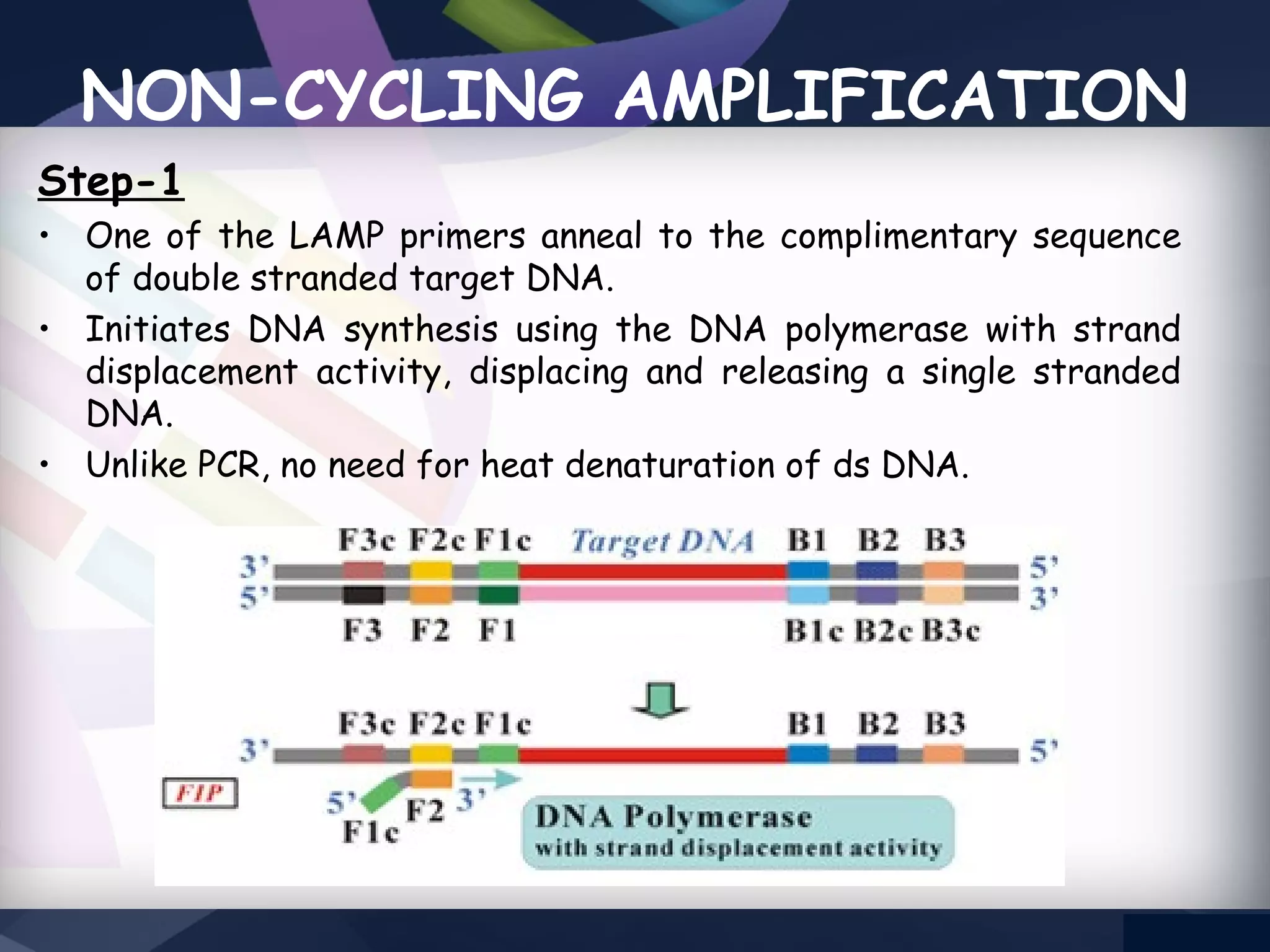
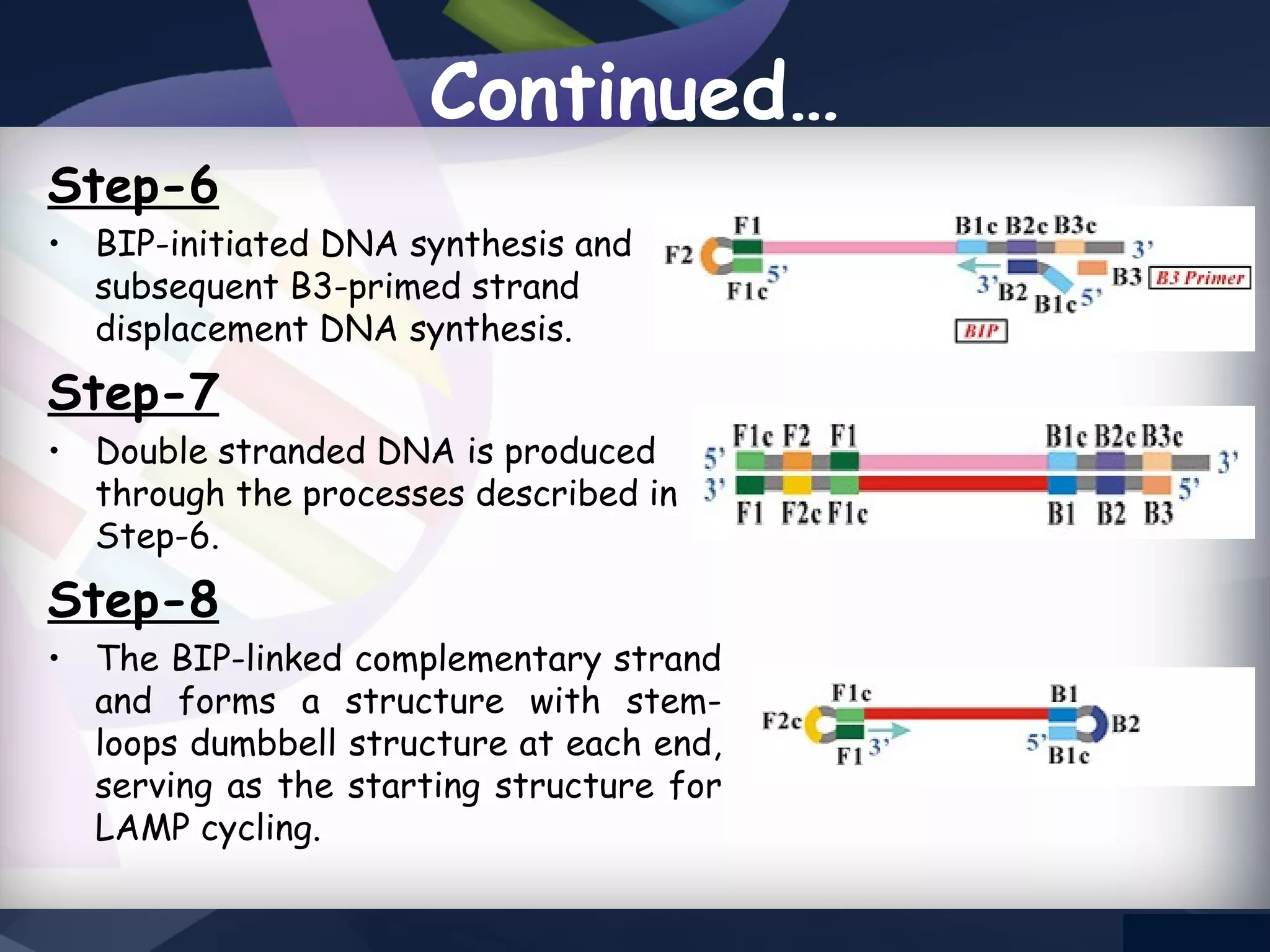
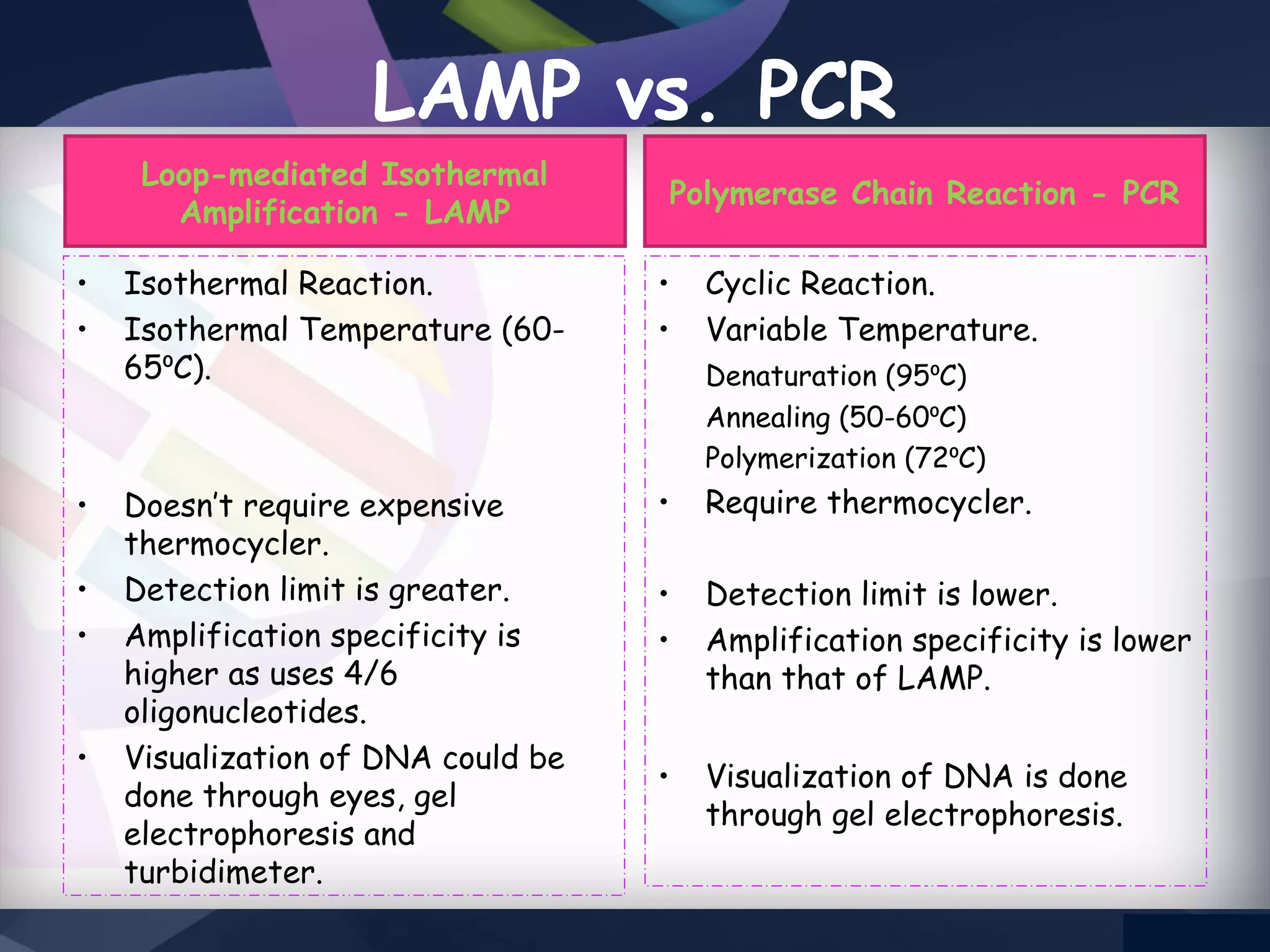
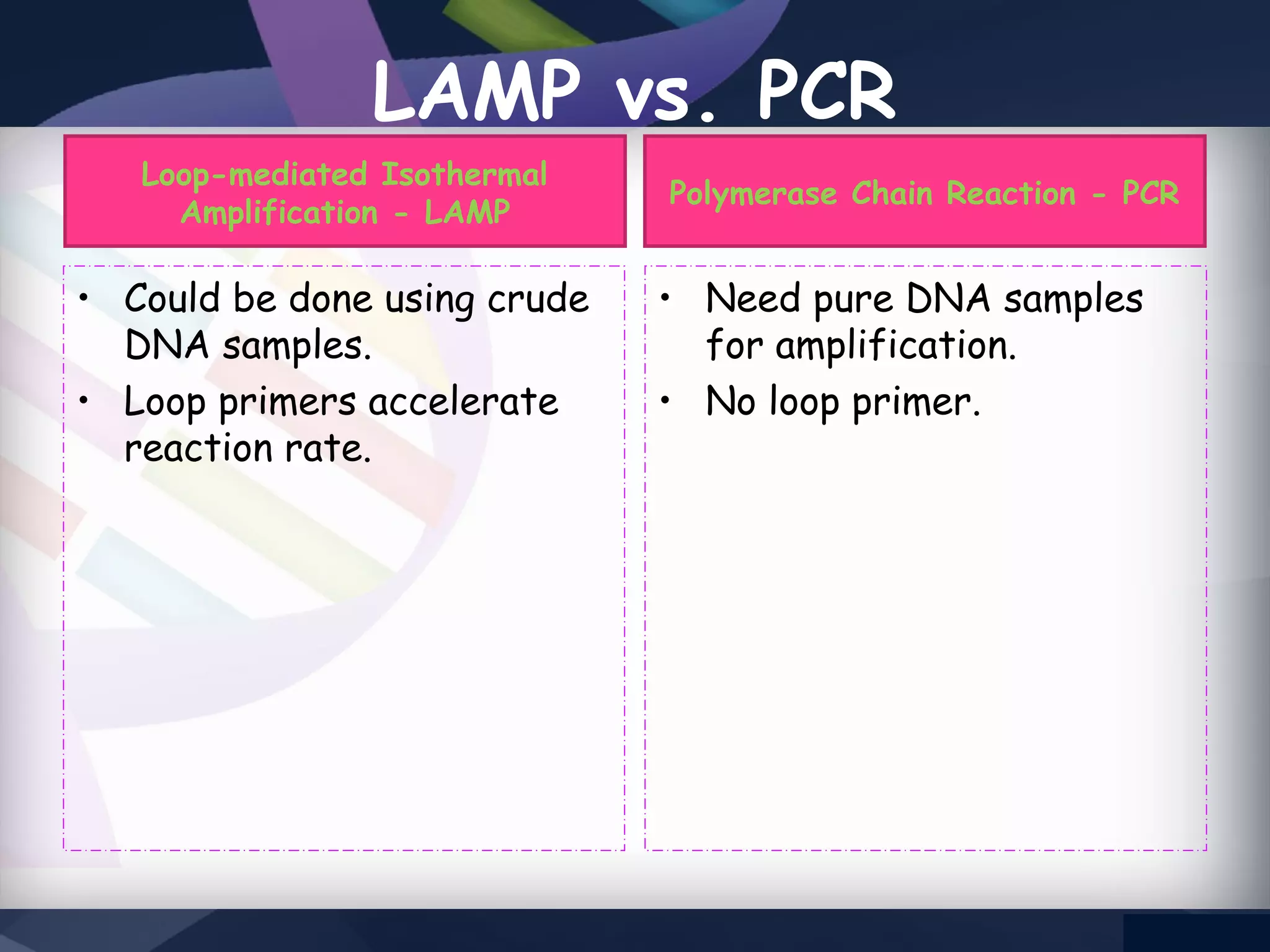
LAMP PCR is a nucleic acid amplification technique that uses a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity. It requires 4-6 designed primers that recognize 6 distinct regions on the target gene. Amplification occurs isothermally without temperature cycling. It produces stem-loop DNA structures with dumbbell ends that are amplified quickly using loop primers. LAMP has advantages over PCR like higher specificity, greater detection limit, simpler operation without expensive equipment, and ability to use crude samples. It is a sensitive, specific and cost-effective technique used for diagnosing infectious diseases.