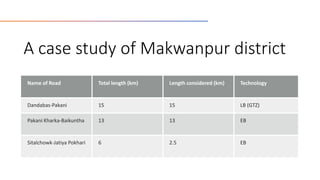
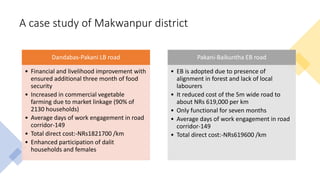
This document compares labor-based and equipment-based rural road construction technologies in Nepal. Labor-based technology uses local labor and hand tools, while equipment-based uses mechanized tools. Labor-based has longer duration but lower capital costs, is suitable for agricultural off-seasons, and provides more local employment. Equipment-based has shorter duration but higher capital costs and requires repair/maintenance services. A case study in Makwanpur district found labor-based roads improved livelihoods and food security more than equipment-based roads. The conclusion is that labor-based technology is more appropriate for rural road construction in Nepal due to sustainability, local employment benefits, and support for agricultural markets.