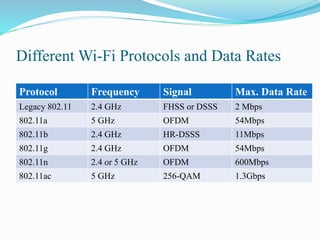
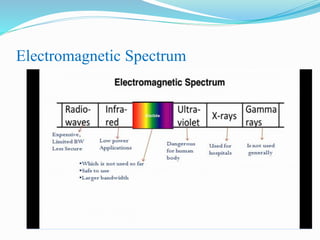
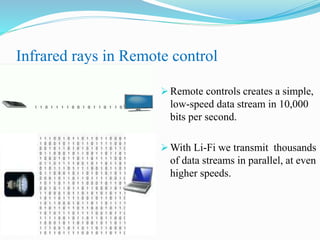
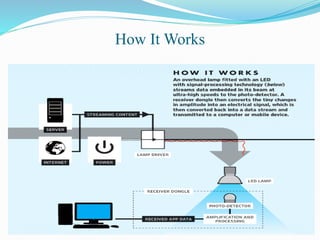
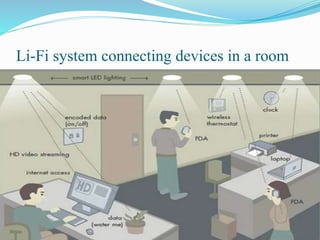
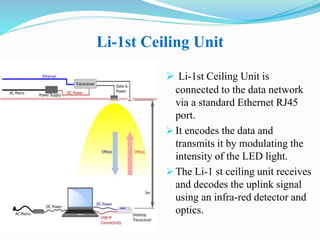
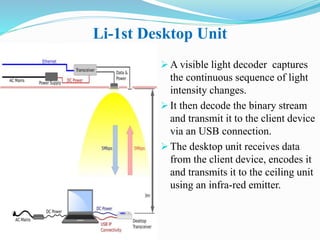
Li-Fi is a wireless optical networking technology that uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for data transmission. It was coined by Harald Haas at the University of Edinburgh in 2011. Li-Fi provides higher speeds and more bandwidth than Wi-Fi, with the added benefit of not interfering with other wireless networks. Li-Fi works by varying the rate at which an LED light flickers on and off, which encodes data. Products like Li-Fi 1st and Li-Flame have been developed to transmit data through LED lights at speeds up to 5Mbps downlink and 5Mbps uplink within a range of 3 meters. Solar Li-Fi uses existing LED lights and solar panels to transmit