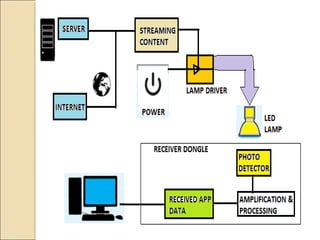
Li-Fi is a technology that uses light from LED bulbs to transmit data wirelessly. It provides high-speed connectivity and is seen as a supplement to Wi-Fi networks. The document traces the history of Li-Fi from experiments in the 1990s to recent demonstrations of speeds over 100Mbps. It describes how Li-Fi works by switching LED bulbs on and off very fast to transmit binary code. Potential applications include use in vehicles, airplanes, hospitals and underwater. While Li-Fi has limitations like inability to pass through walls, it could provide connectivity through devices like street lamps at a low cost.