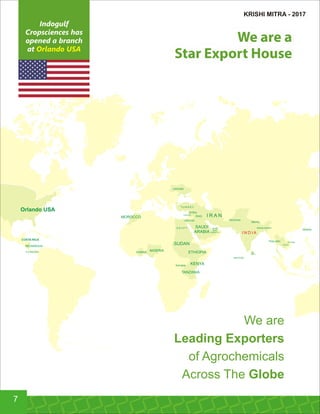
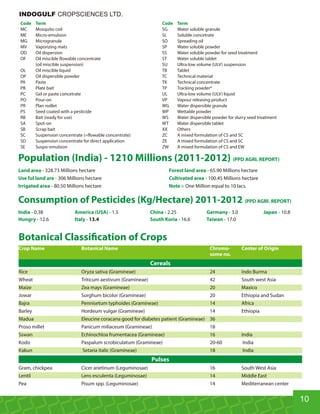
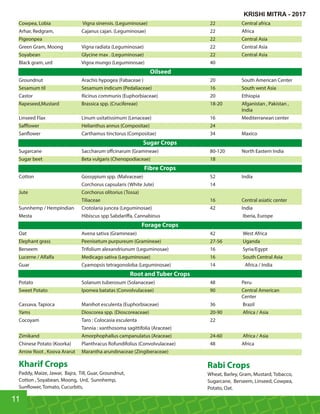
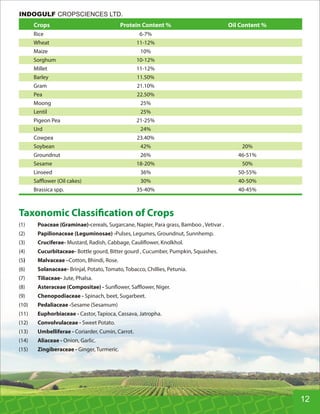
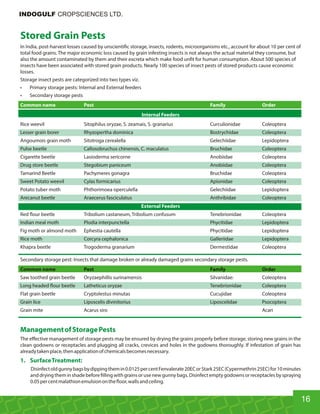
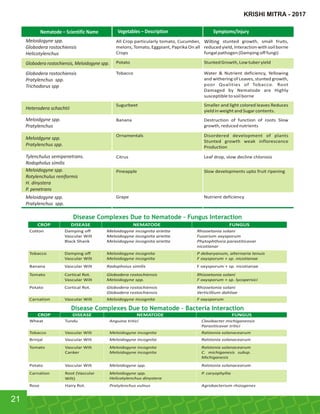
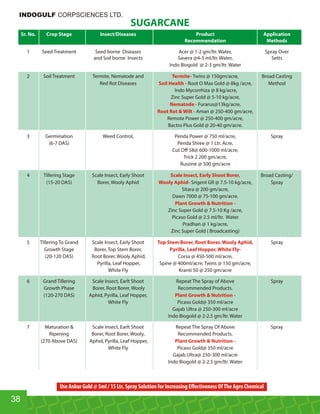
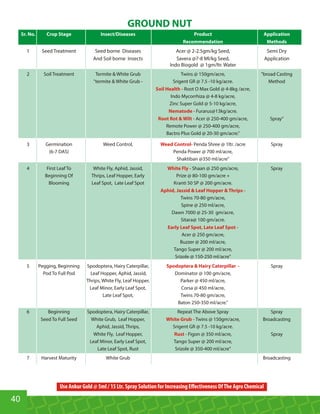
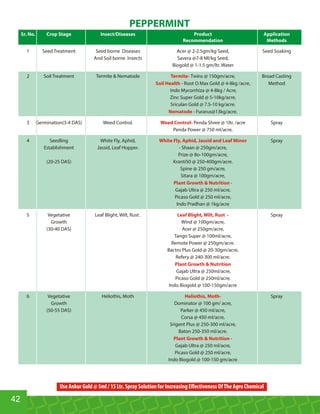
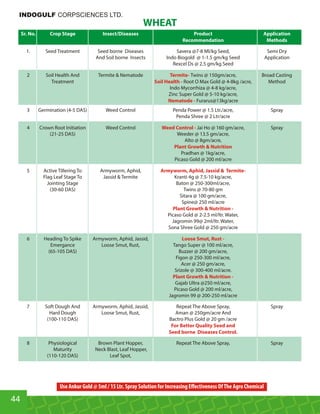
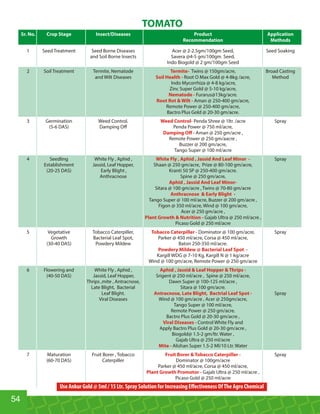
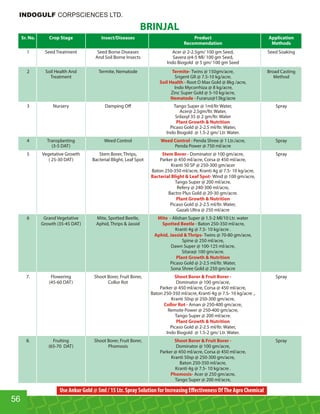
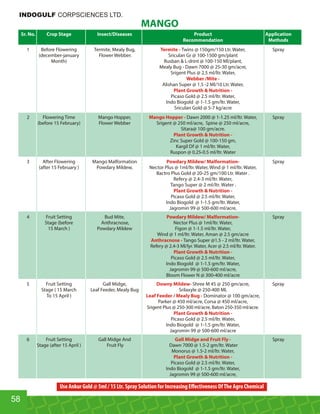
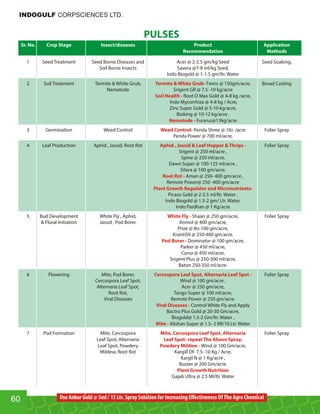
This document provides an overview of Indogulf Cropsciences Ltd., an agrochemical company. It discusses the company's founding in 1972, research and development efforts including facilities and certifications, product portfolio including formulations and target pests. It also includes sections on crop classification, losses caused by pests, and abbreviations commonly used in pesticide names. The document aims to be a friendly guide for farmers on modern agricultural practices.