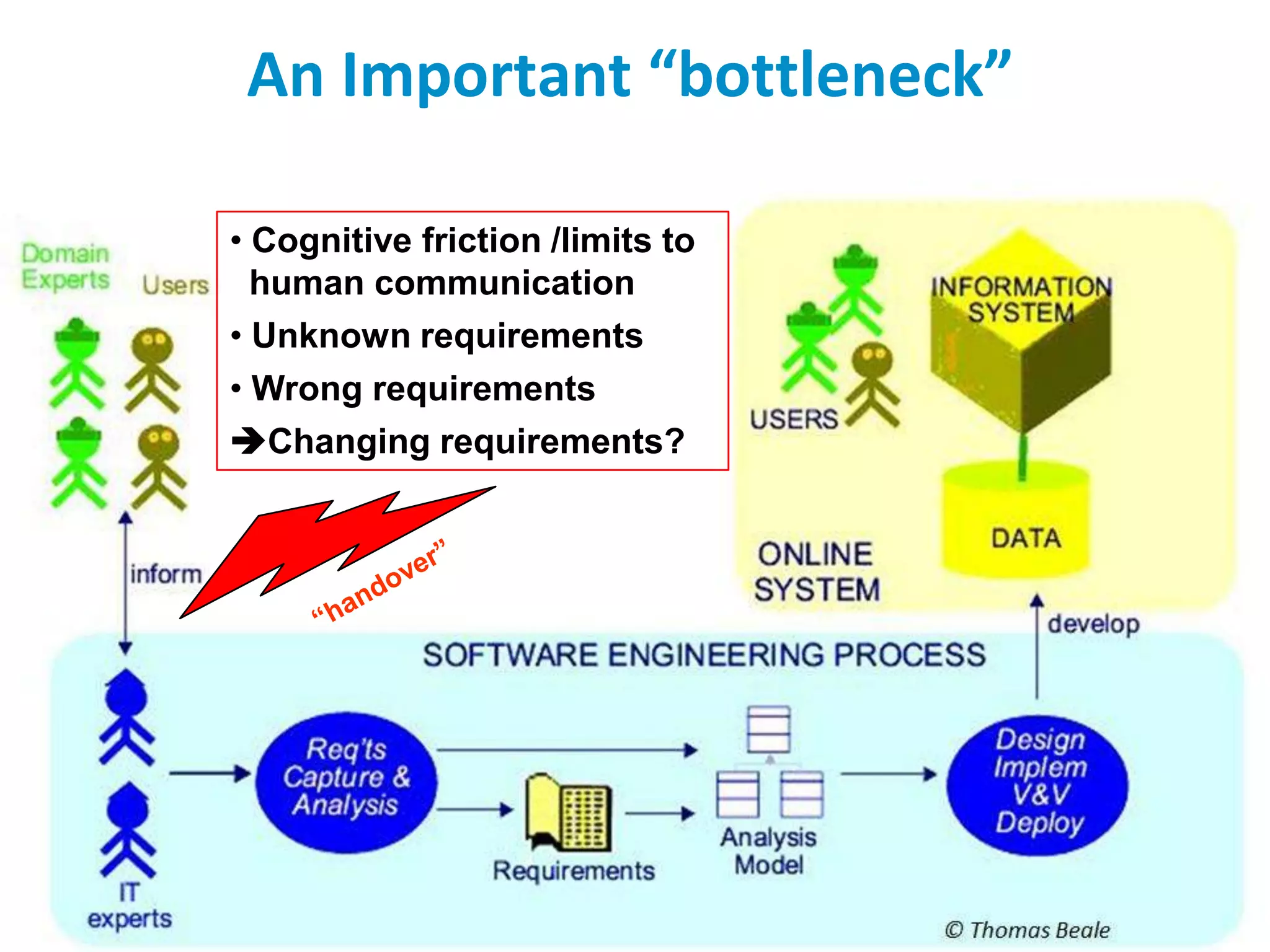
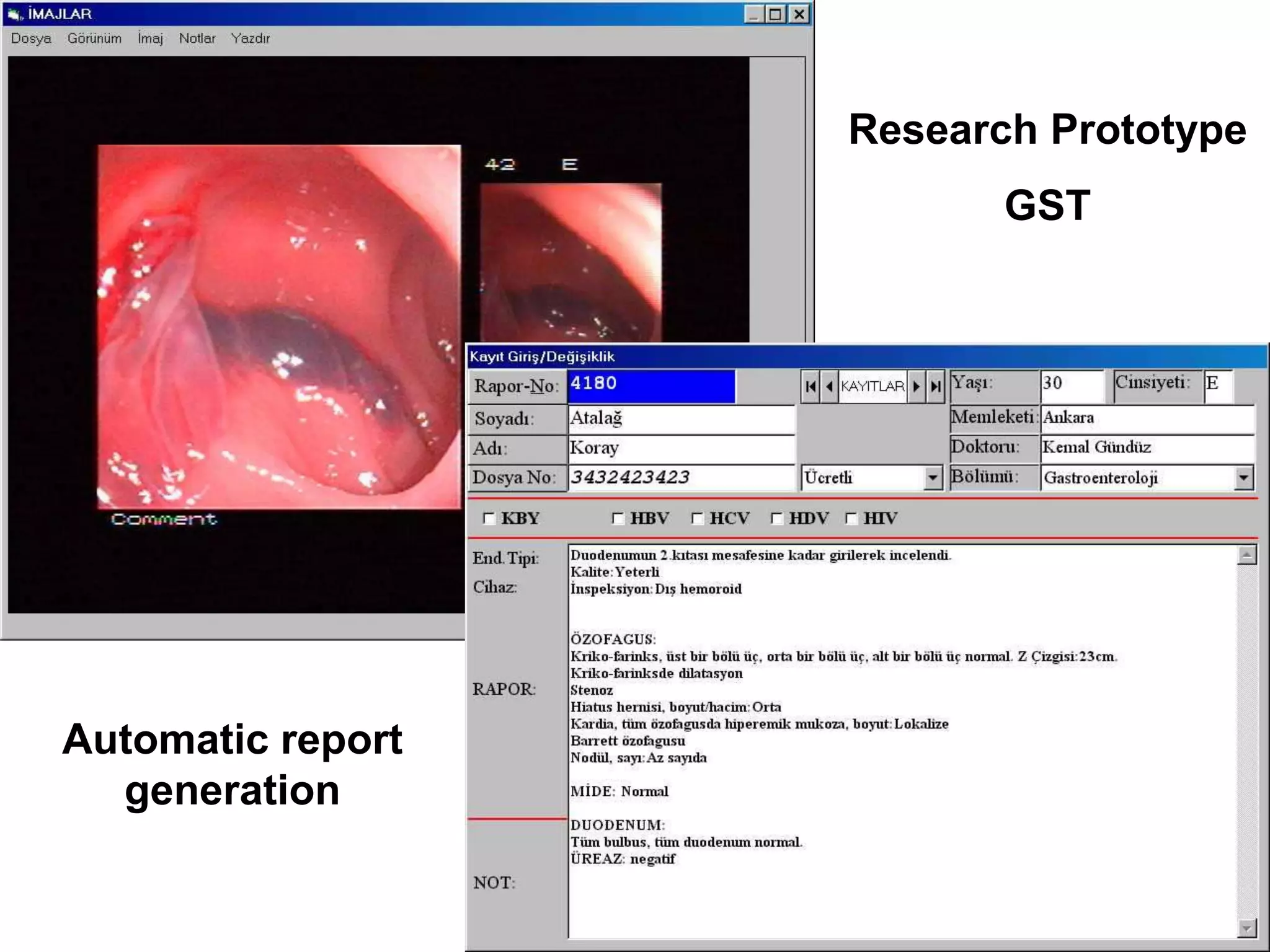
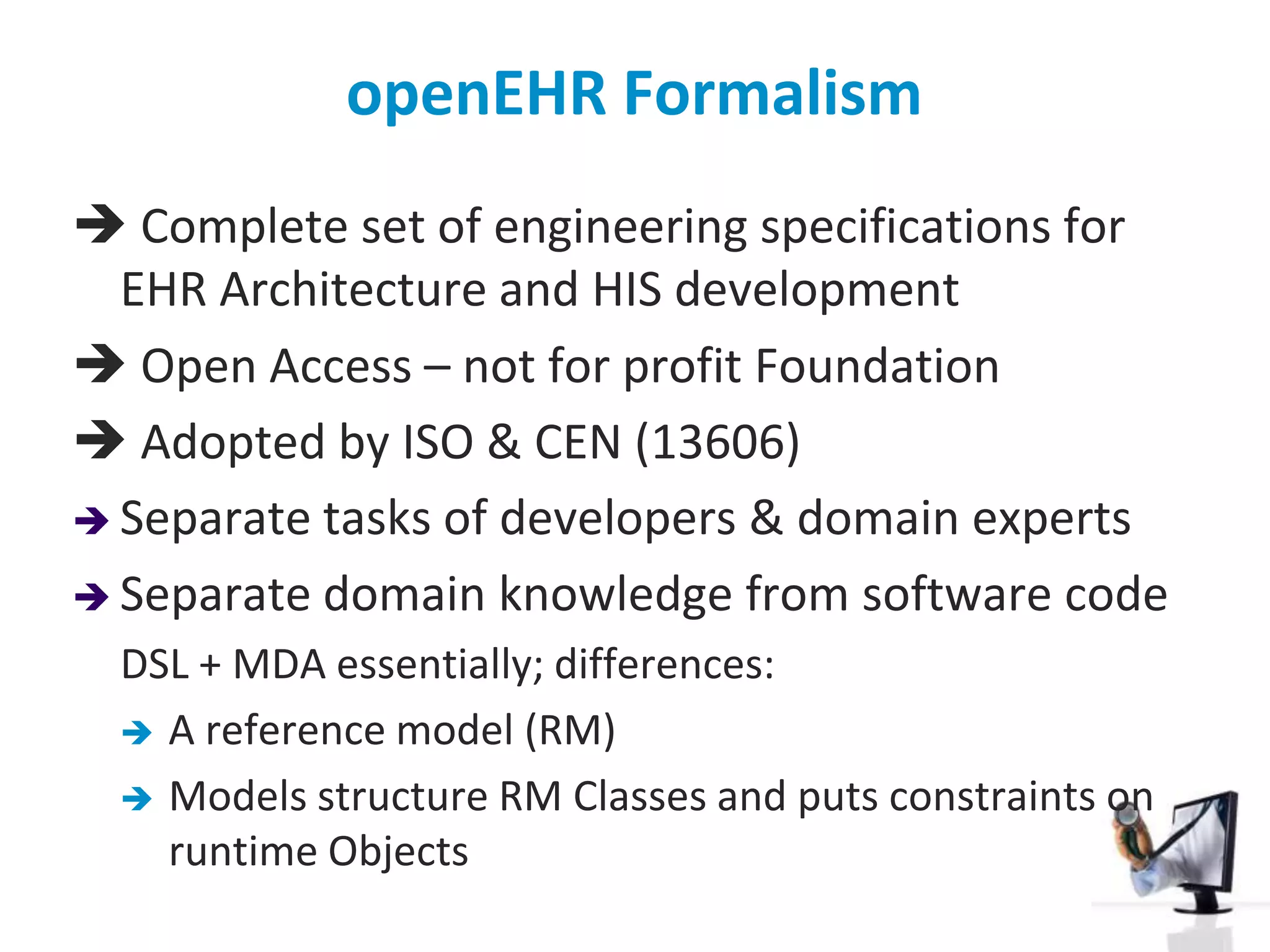
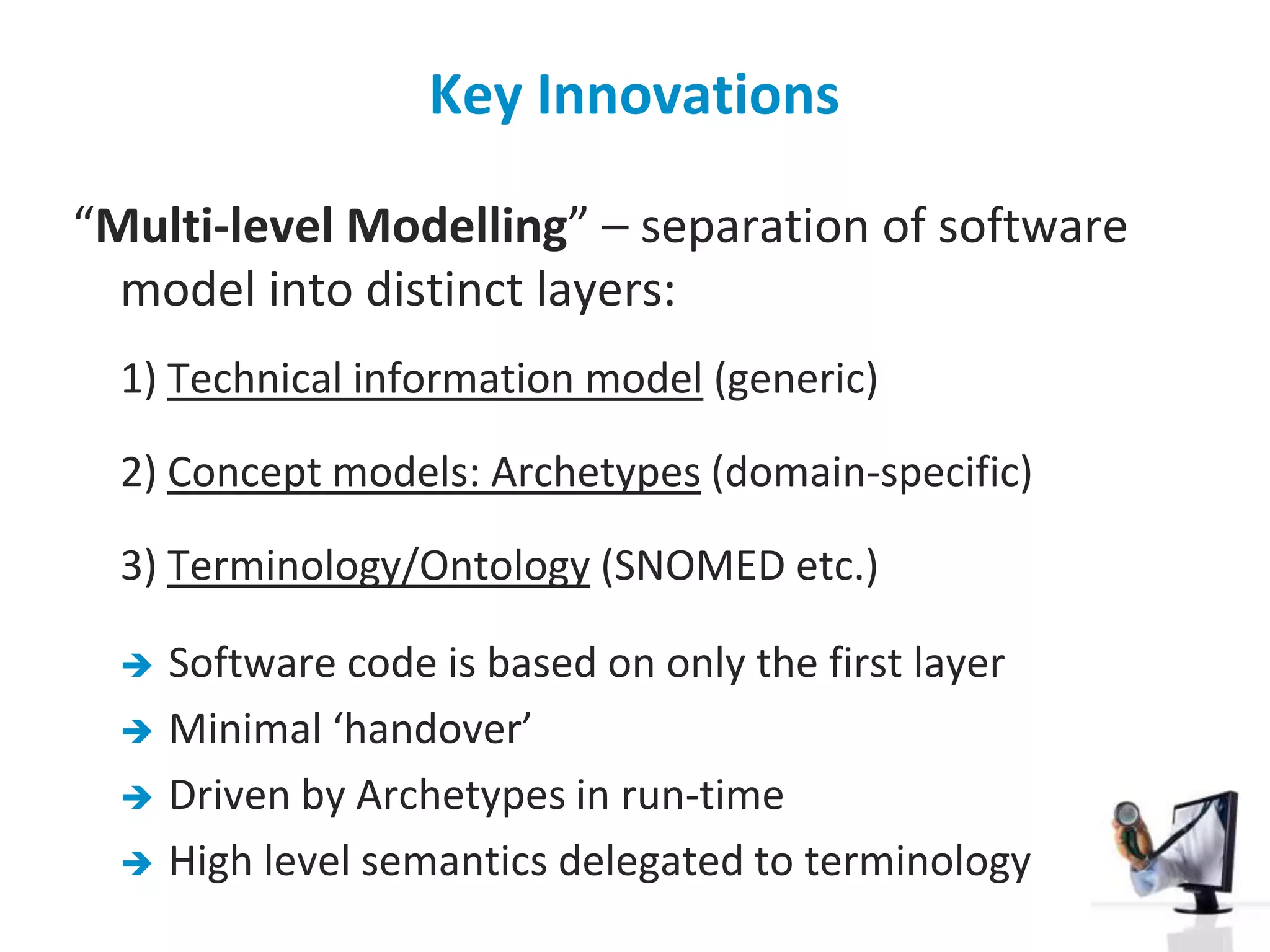
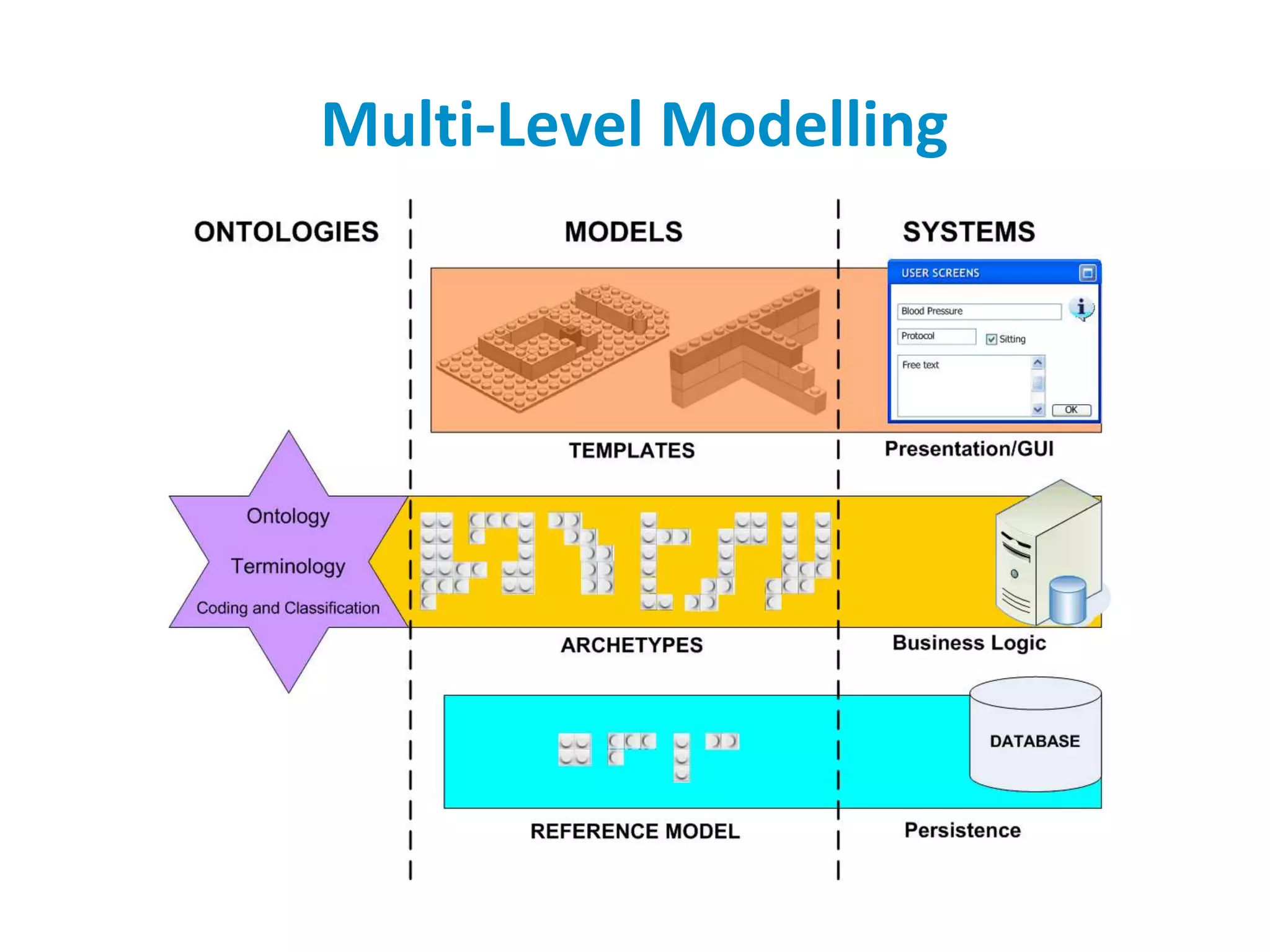
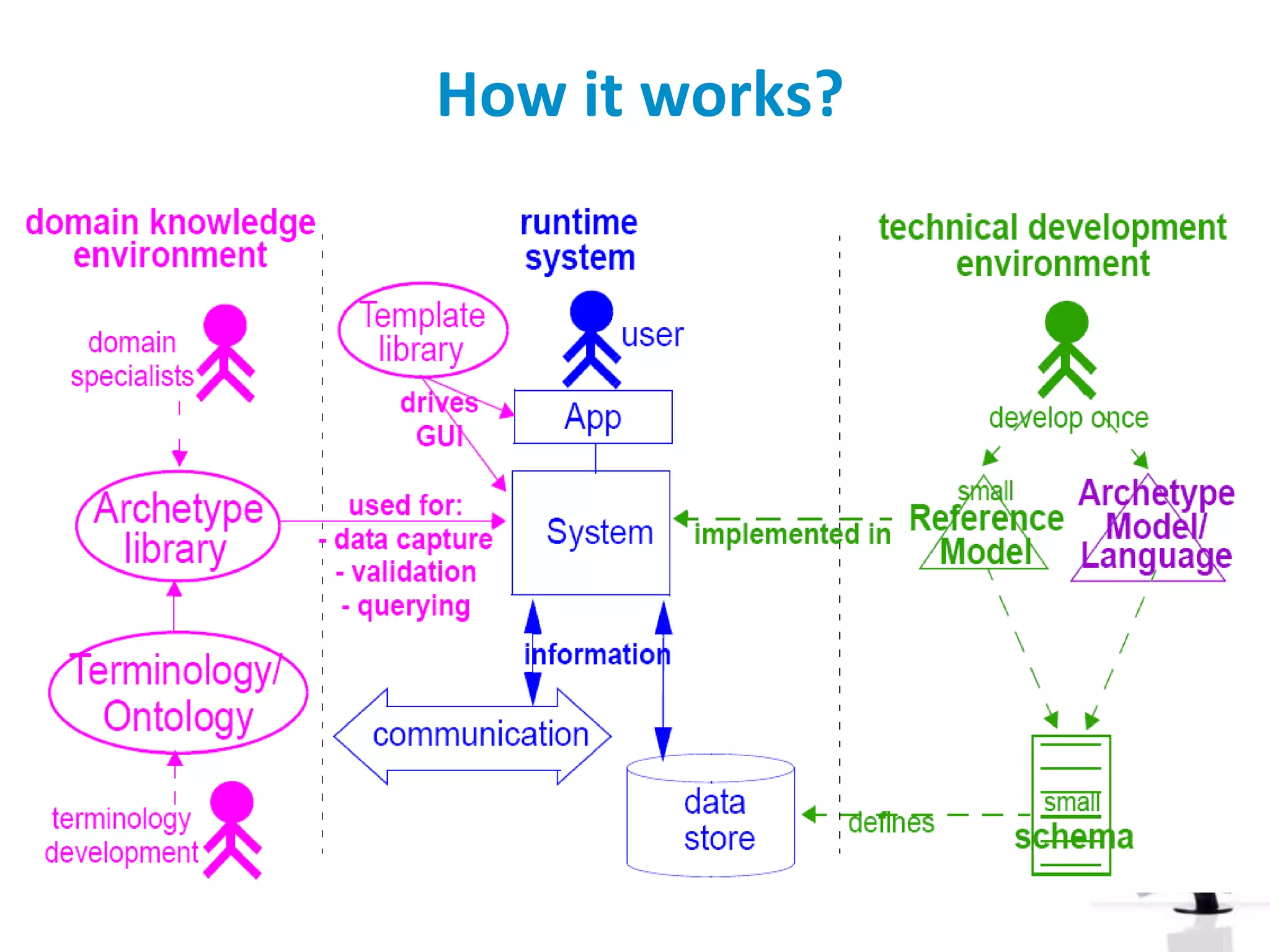
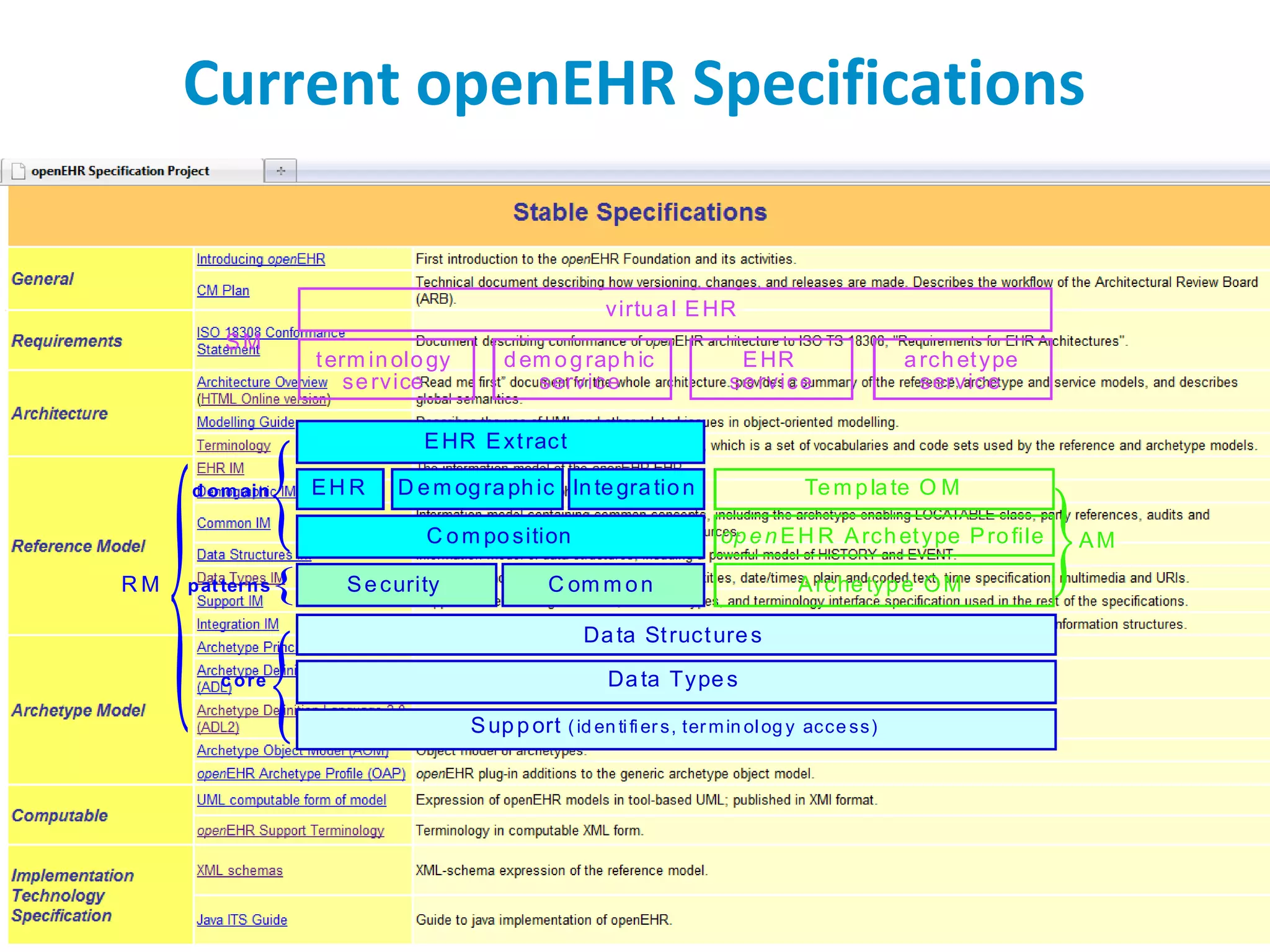
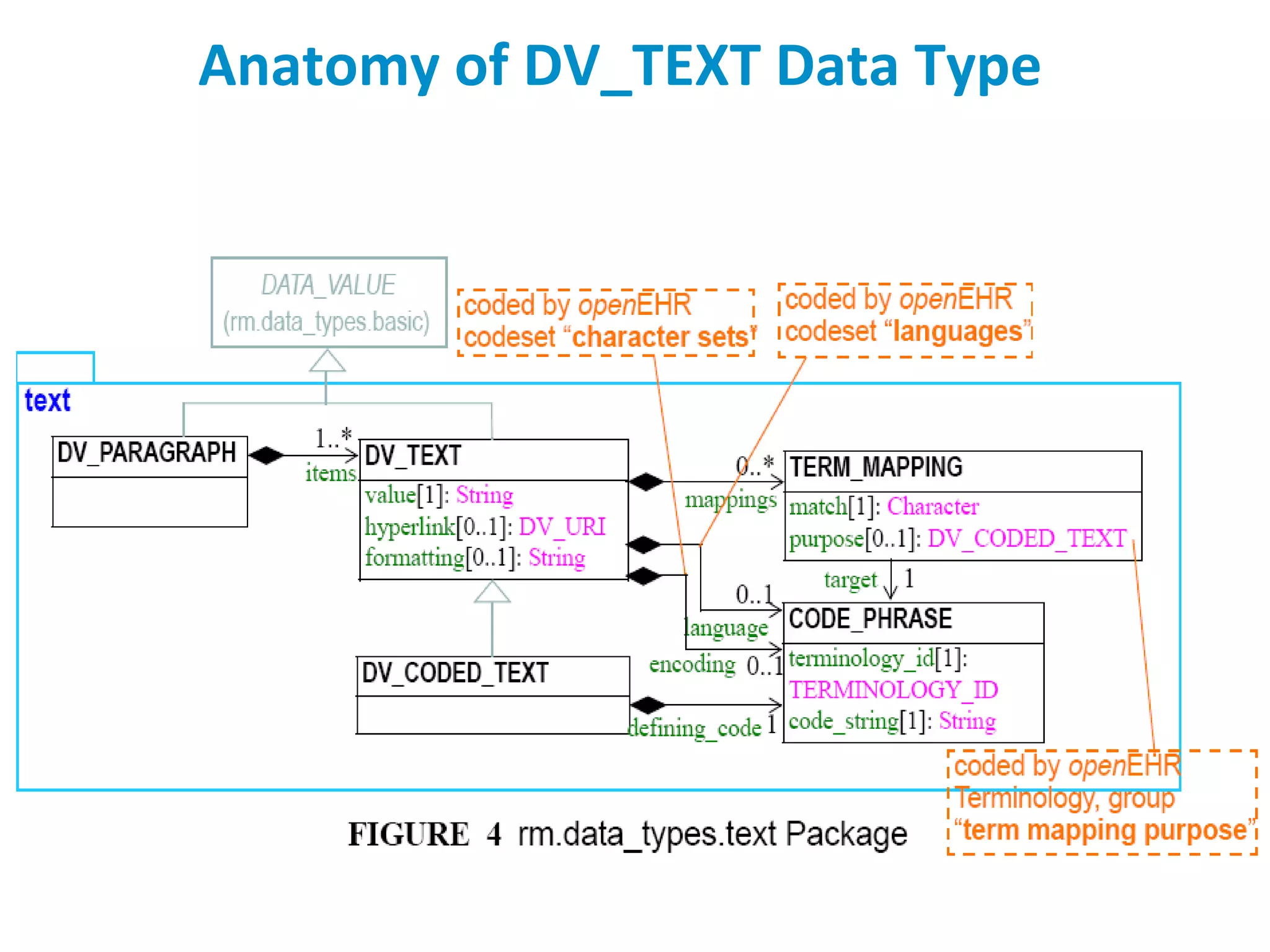
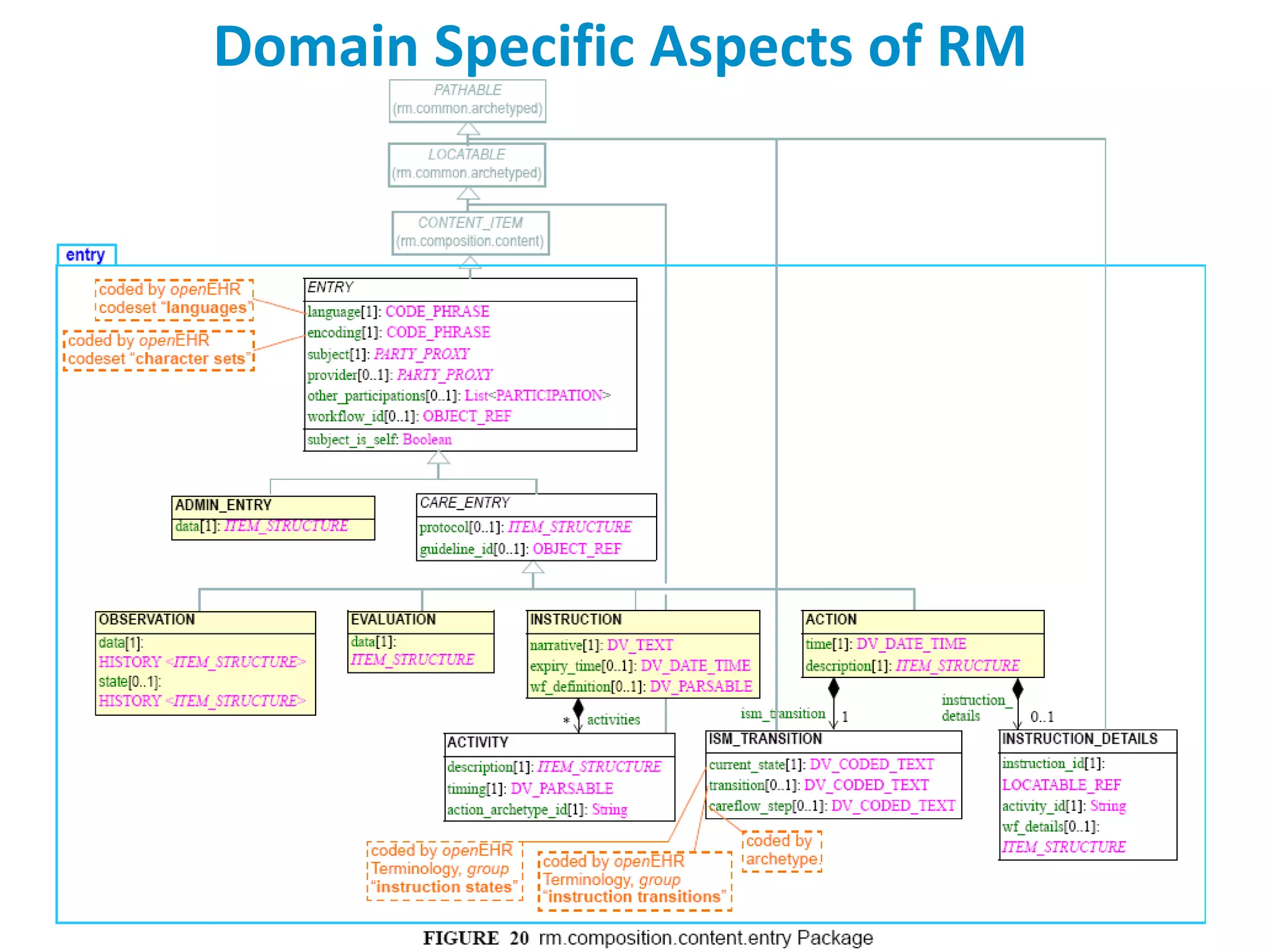
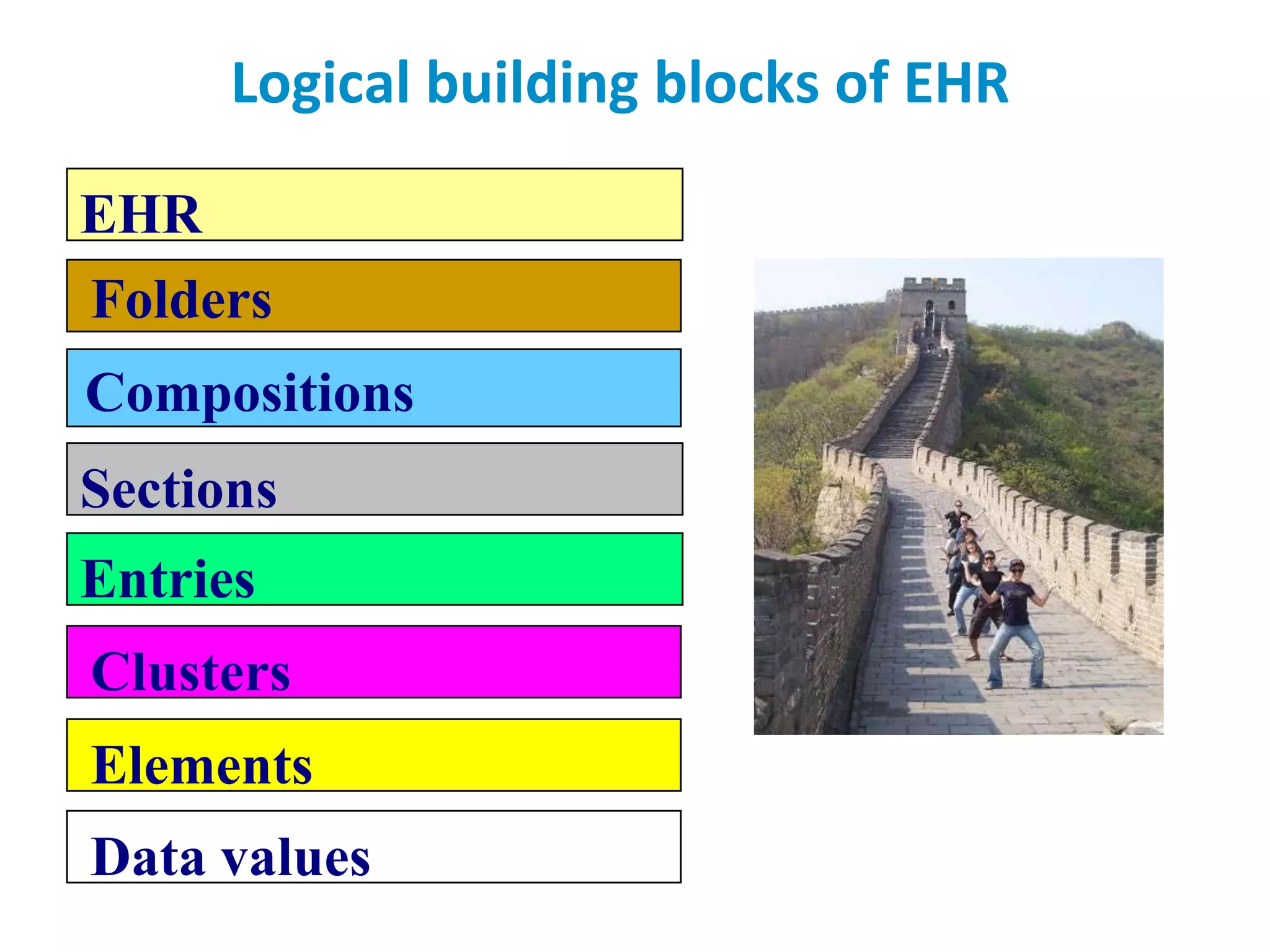
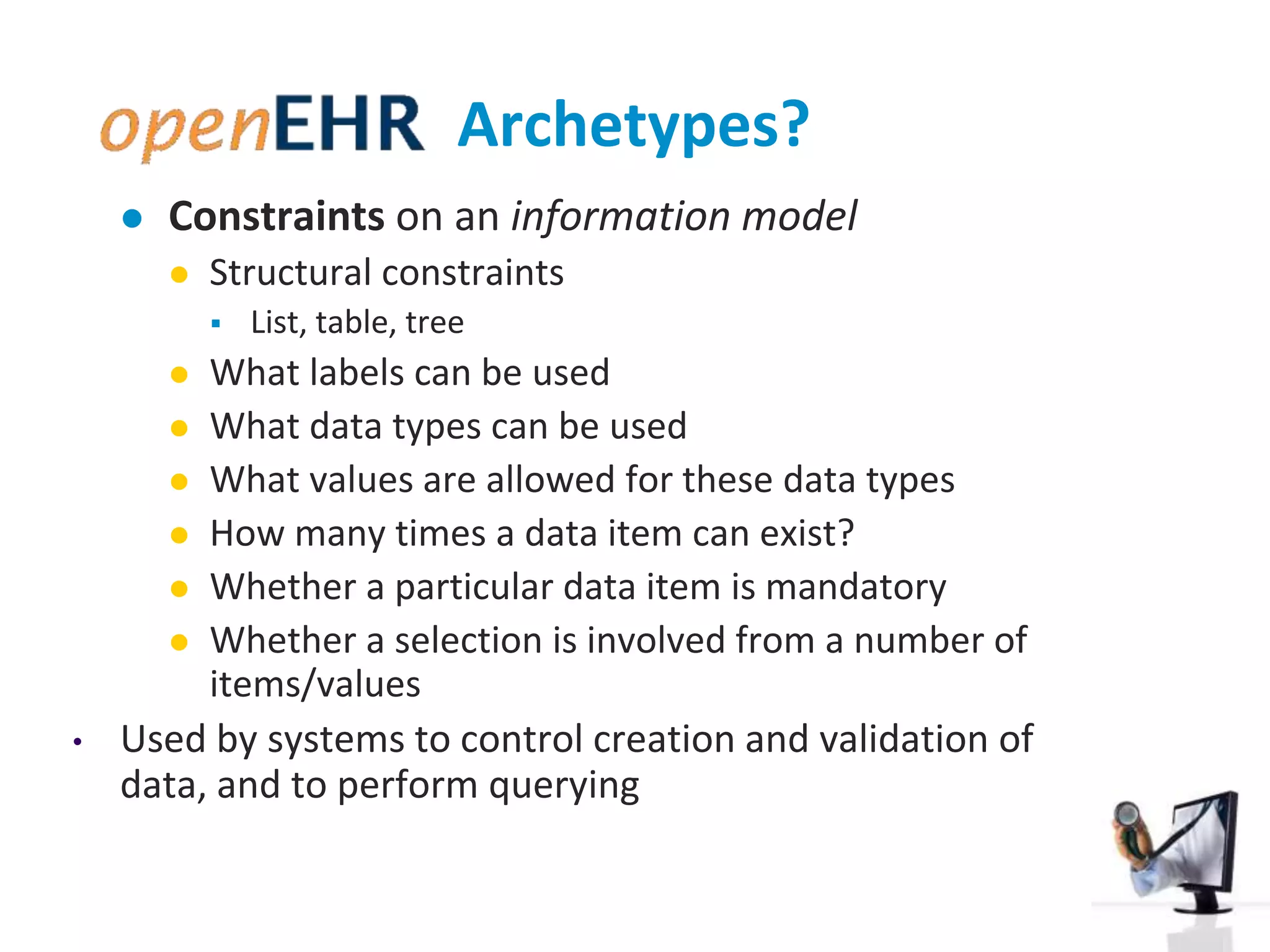
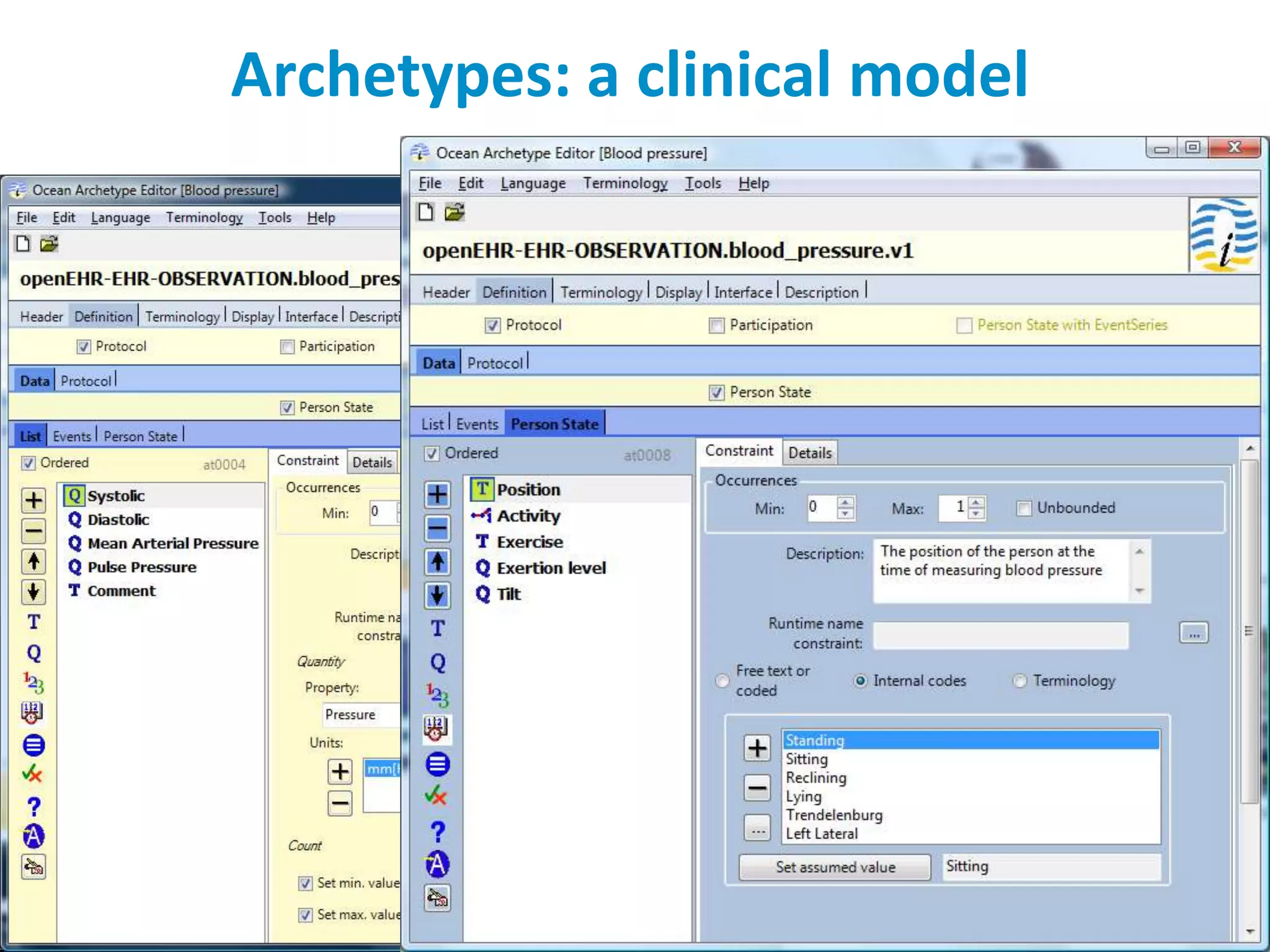
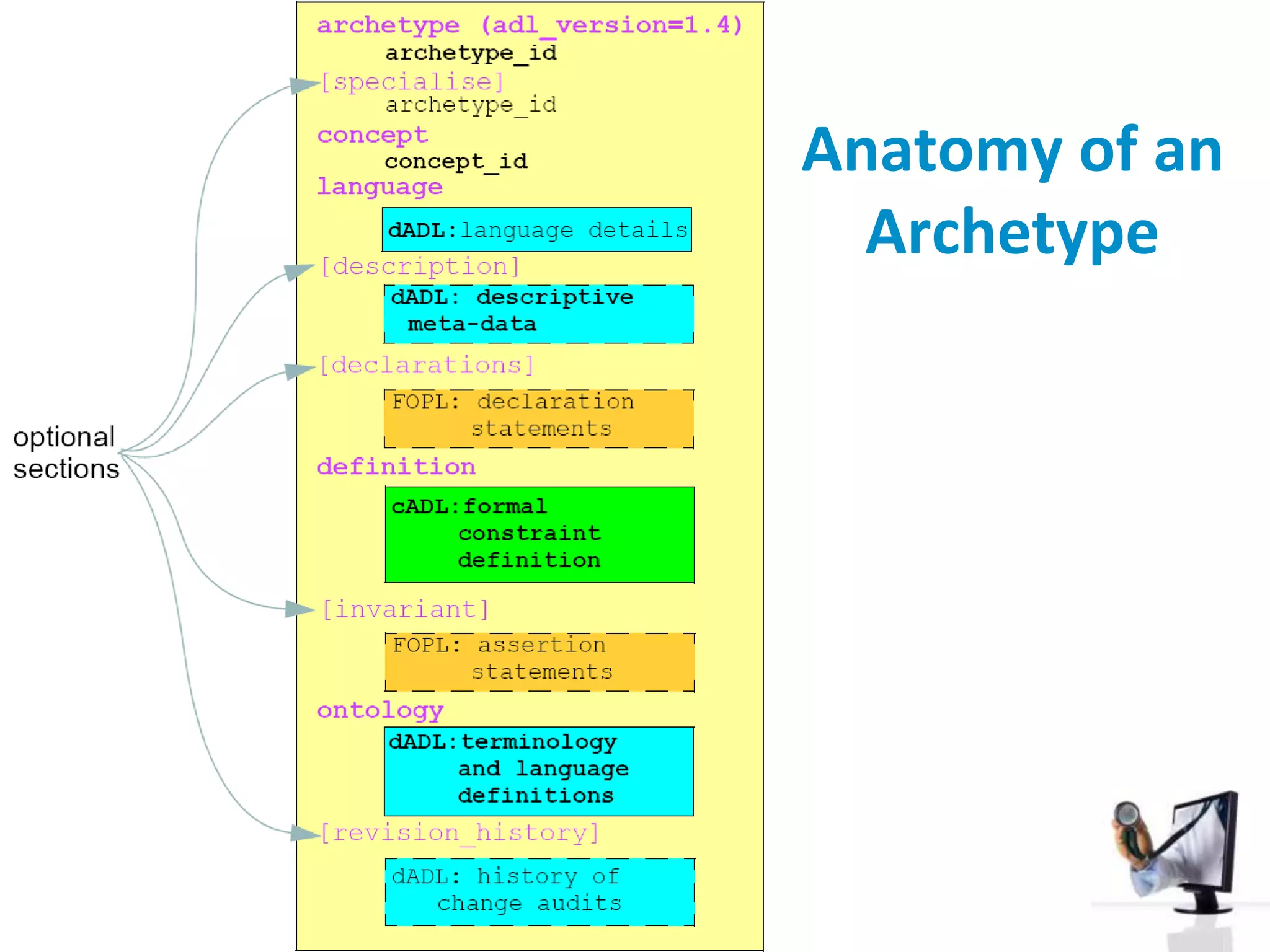
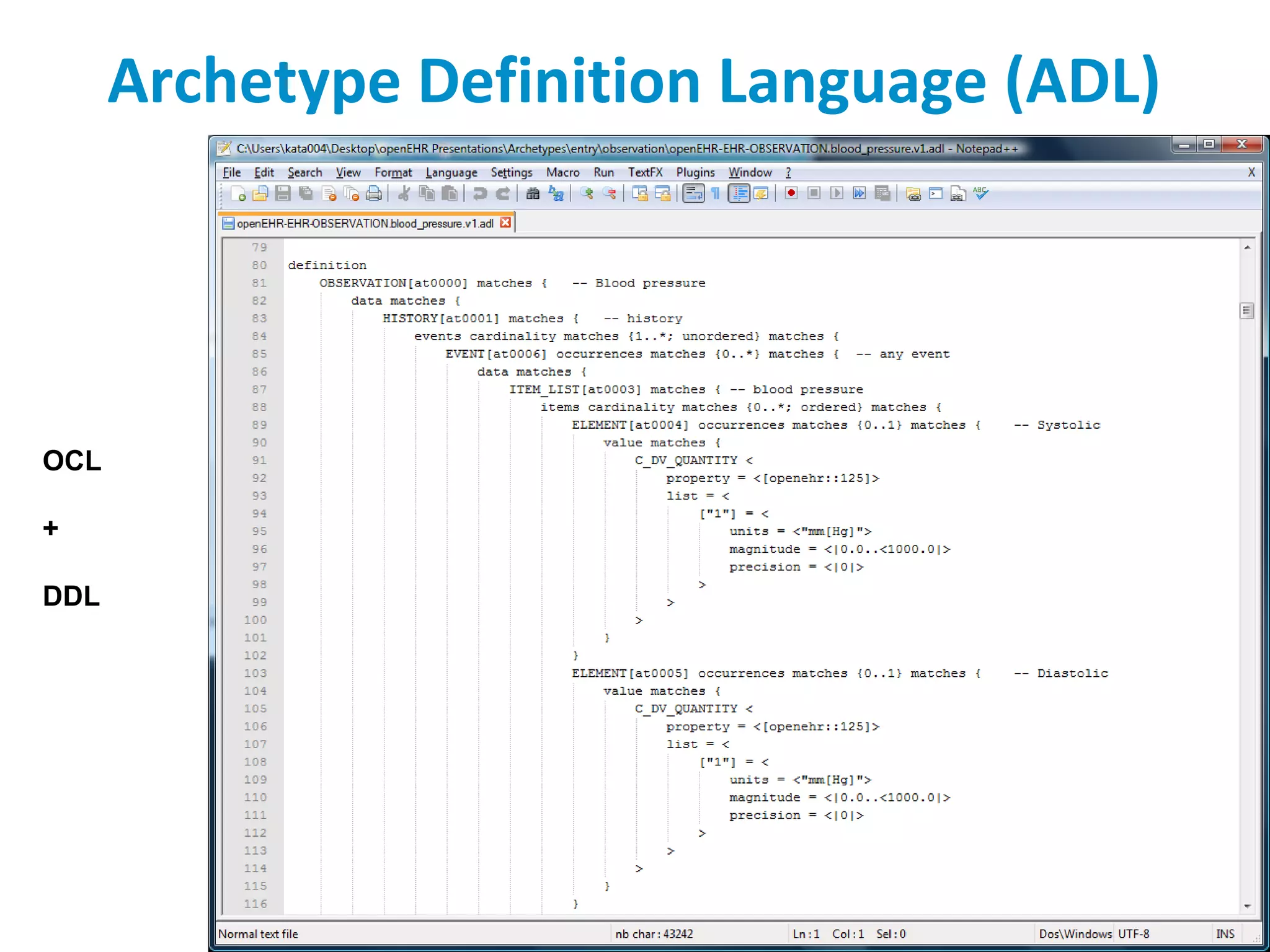
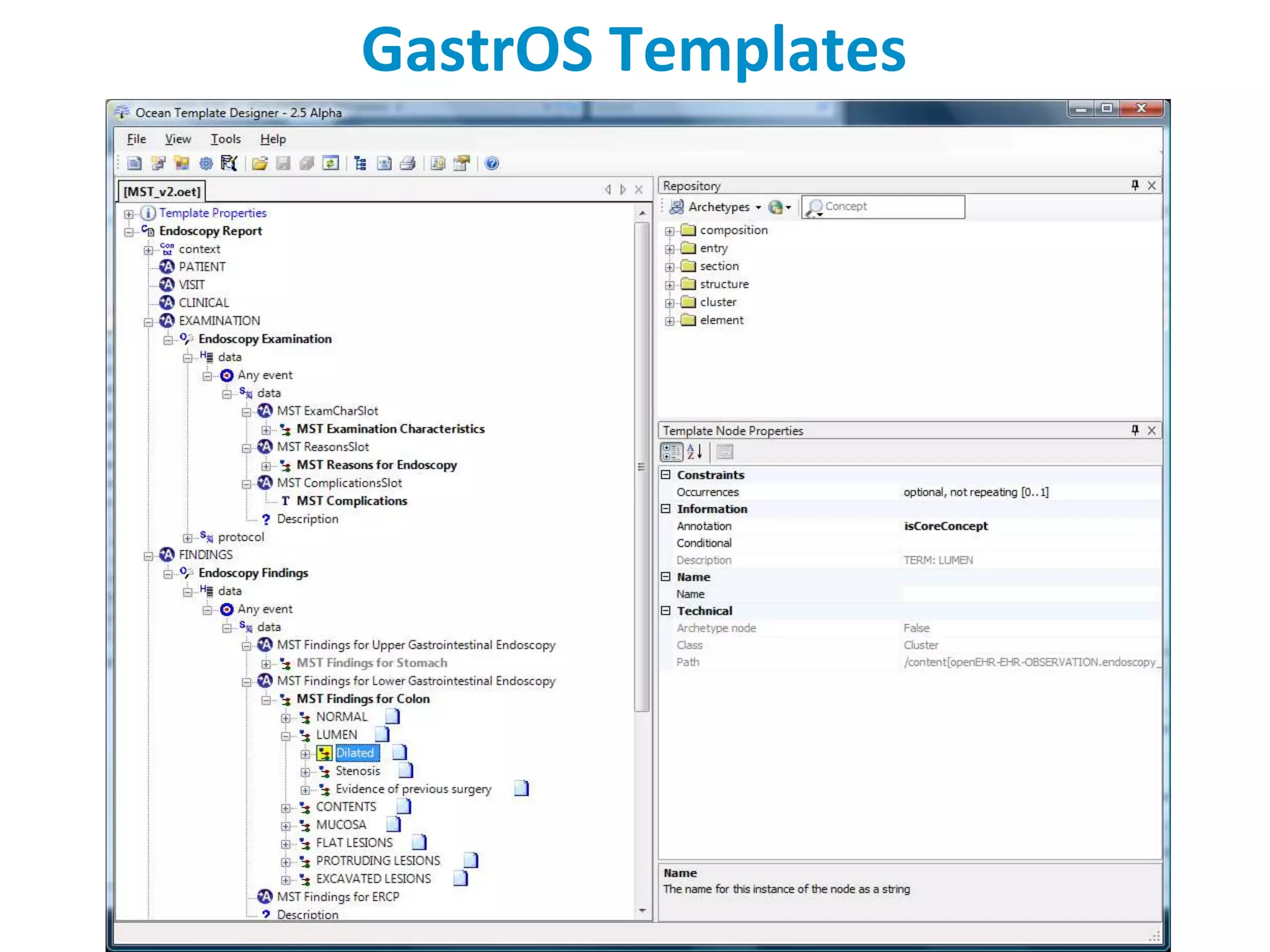
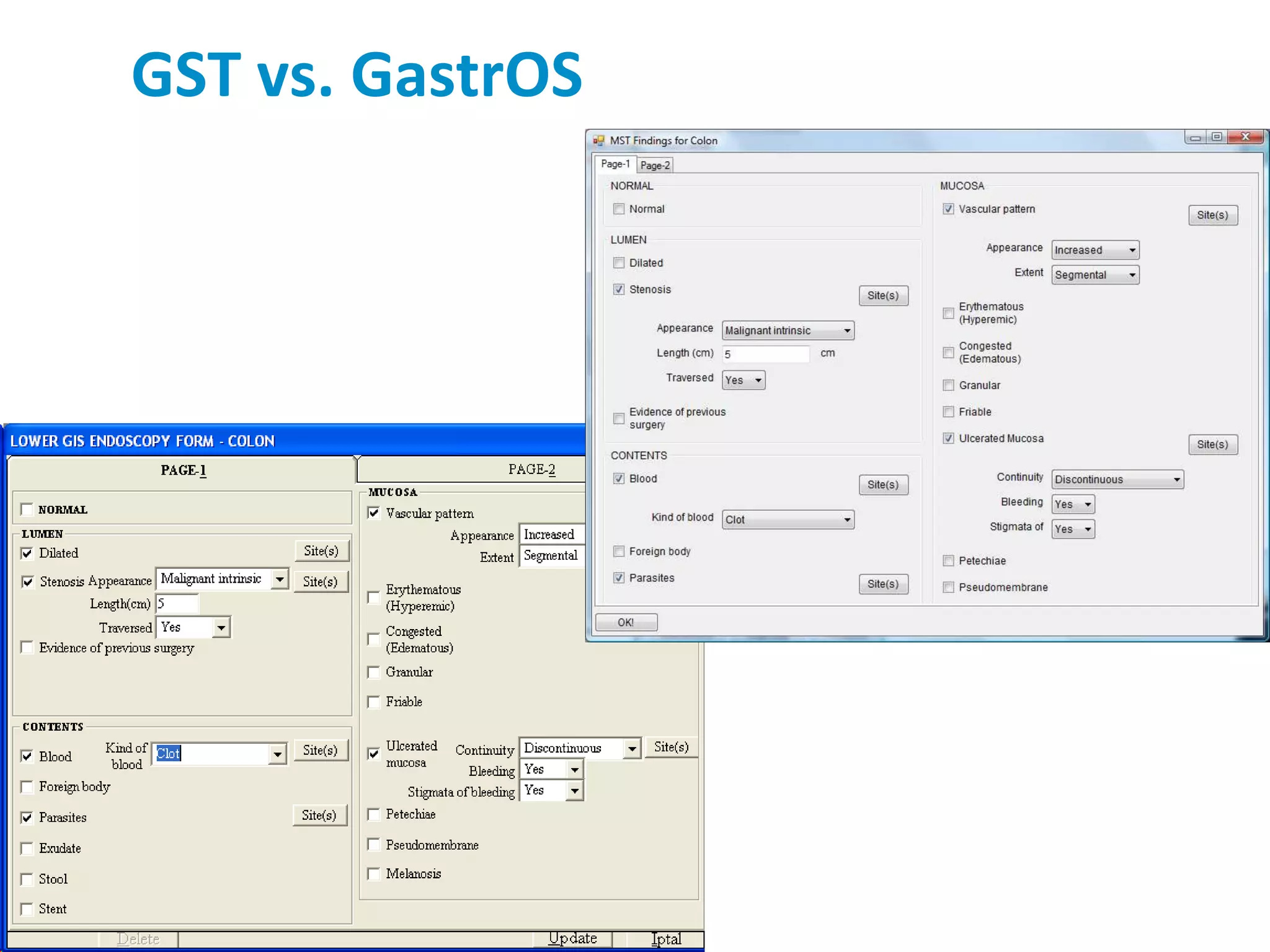
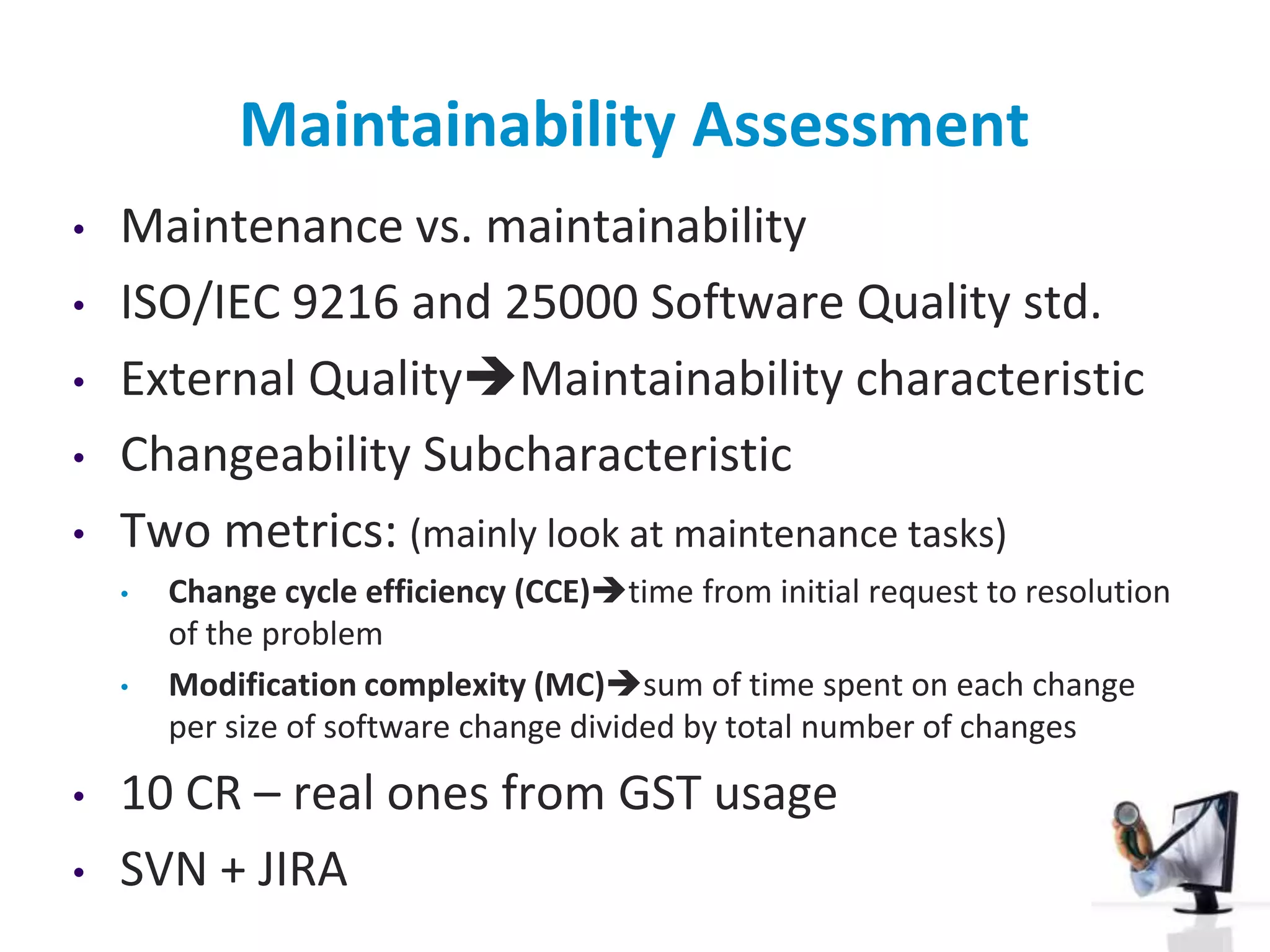
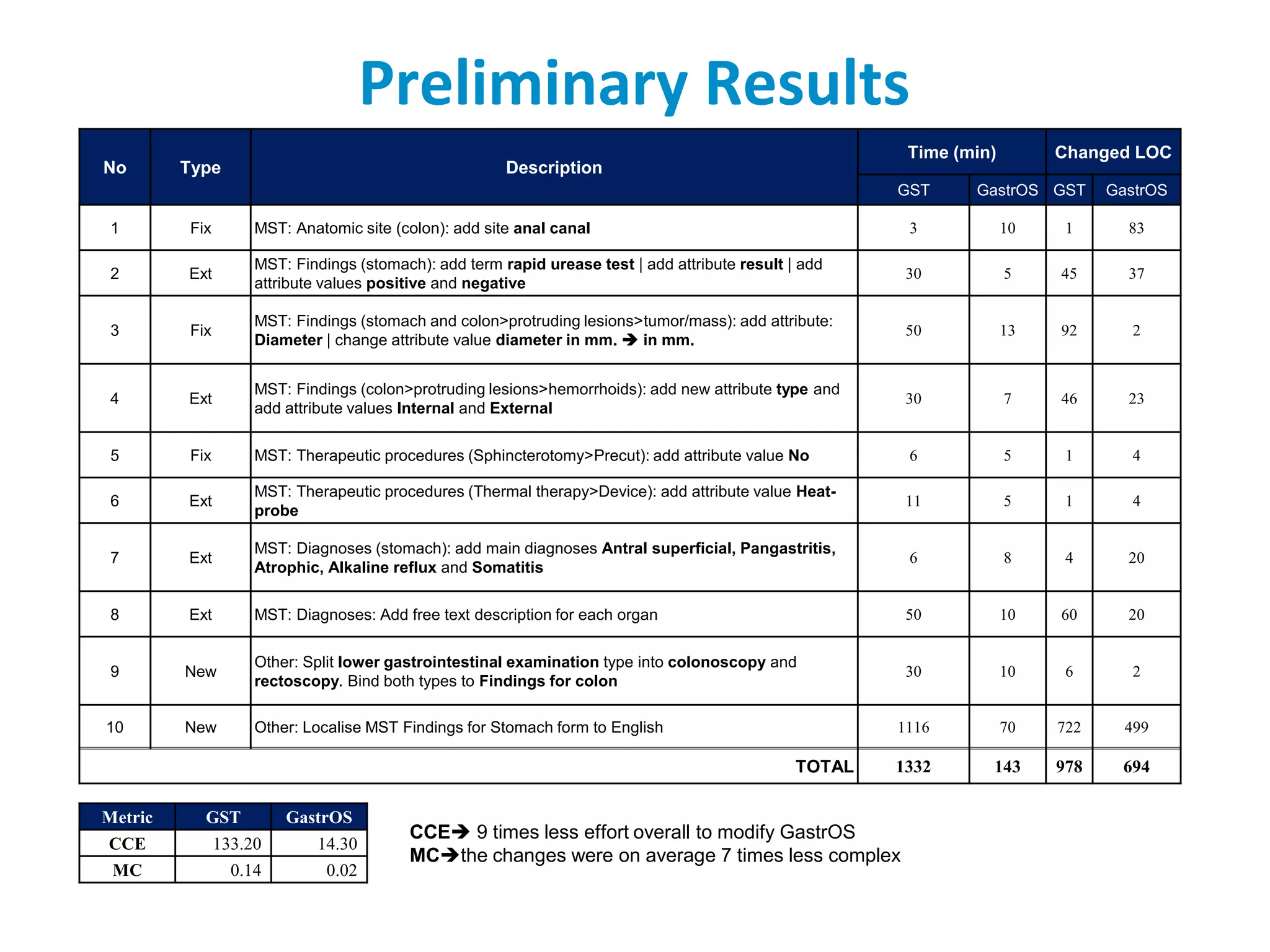
The document discusses the challenges and complexities of software maintenance and maintainability in healthcare, particularly focusing on health information systems and the associated difficulties in meeting changing requirements. It highlights the significant costs and risks involved in healthcare IT projects, as well as the implications of using the openEHR architecture in developing more sustainable software solutions. The author presents a case study comparing two applications to assess maintenance metrics, suggesting that the new architecture can lead to reduced effort and complexity in modifications.