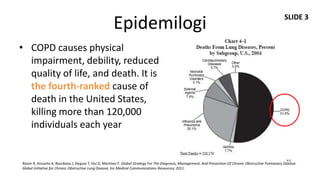
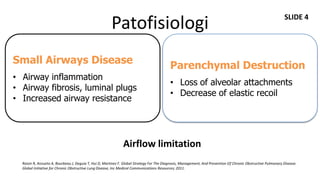
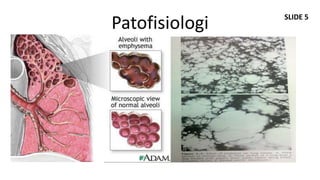
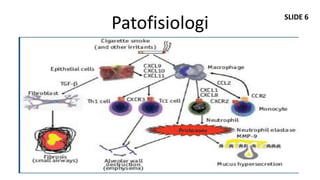
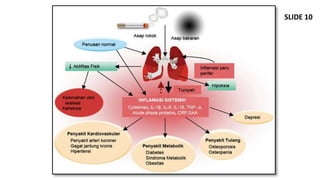
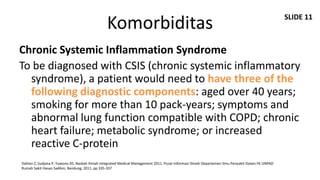
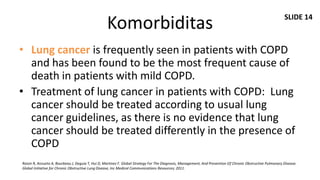
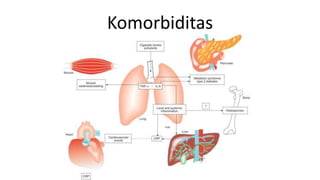
Dokumen ini membahas mengenai komorbiditas pada penderita penyakit paru obstruktif kronis (PPOK) yang mencakup faktor risiko, patofisiologi, dan dampak berbagai kondisi medis lain yang sering terjadi bersamaan dengan PPOK, seperti penyakit kardiovaskular, diabetes, dan osteoporosis. Ditekankan pentingnya pendekatan pengobatan yang komprehensif, mengingat dampak komorbiditas terhadap prognosis dan mortalitas pasien. Penelitian menunjukkan bahwa pengobatan simultan dan pemantauan yang cermat dapat mengurangi morbiditas dan meningkatkan kualitas hidup pasien dengan PPOK.