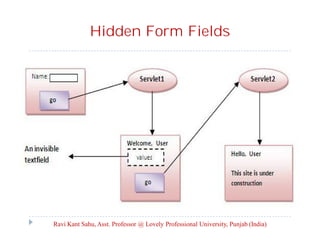
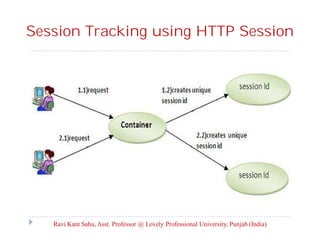
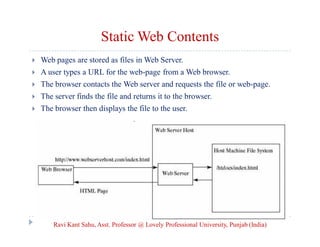
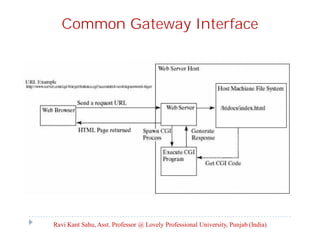
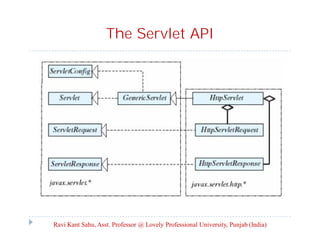
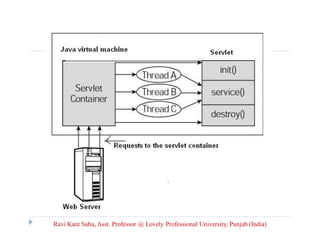
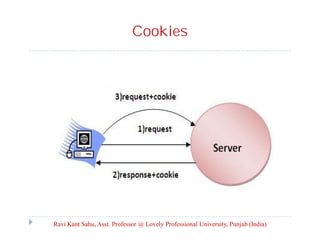
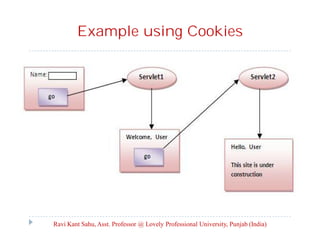
The document provides an overview of servlets and related technologies. It discusses that servlets are Java programs that run on a web or application server, process client requests, and produce dynamic web pages. Servlets act as a middle layer between requests from browsers/clients and databases on the server. The document also covers common gateway interface (CGI), GET and POST methods, query strings, advantages of servlets over CGI, the servlet API, servlet lifecycle, session tracking techniques including cookies, and examples of using cookies to track sessions.

















![ServletRequest Interface
String getParameter(String name)
String[] getParameterValues(String name)
String getRemoteAddr()
String getRemoteHost()
Ravi Kant Sahu, Asst. Professor @ Lovely Professional University, Punjab (India)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serv-131130063900-phpapp01/85/Servlets-22-320.jpg)
![HttpServletRequest Interface
String getHeader(String name)
String getMethod()
String getQueryString()
javax.servlet.http.Cookies[] getCookies()
HttpSession getSession(boolean create)
Ravi Kant Sahu, Asst. Professor @ Lovely Professional University, Punjab (India)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serv-131130063900-phpapp01/85/Servlets-23-320.jpg)













![Retrieving Parameter Values
Each GUI component in the form has a name attribute.
The servlet uses the name attribute in the following method to
obtain the parameter value as a string.
String getParameter(attributeName)
In case of a list with multiple values, use the following method to
return the parameter values in an array of strings:
String[] getParameterValues(attributeName)
NOTE: If an attribute doesn’t exist, the getParameter method returns null.
If an empty value of the parameter is passed to the servlet, the
getParameter method returns a string with an empty value.
Ravi Kant Sahu, Asst. Professor @ Lovely Professional University, Punjab (India)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serv-131130063900-phpapp01/85/Servlets-37-320.jpg)








![Session Tracking using Cookies (Servlet 2)
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletRespon
se response)
{ try{
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Cookie ck[]=request.getCookies();
out.print("Hello "+ck[0].getValue());
out.close();
}
catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
Ravi Kant Sahu, Asst. Professor @ Lovely Professional University, Punjab (India)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serv-131130063900-phpapp01/85/Servlets-48-320.jpg)