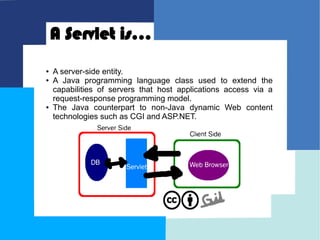
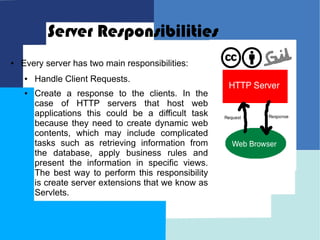
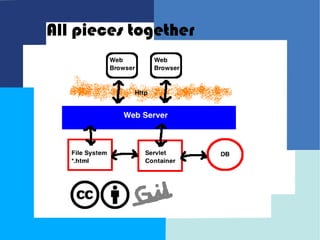
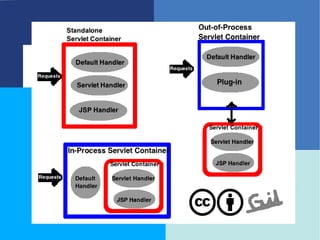
This document provides an introduction to Java Enterprise Edition and servlet technology. It discusses what servlets are, how they are used by servlet containers and application servers to handle client requests and generate dynamic web content, and the relationships between servlets, the servlet API, and servlet containers. The servlet API defines standard interfaces and classes for communication between servlets and containers in a platform-independent way.