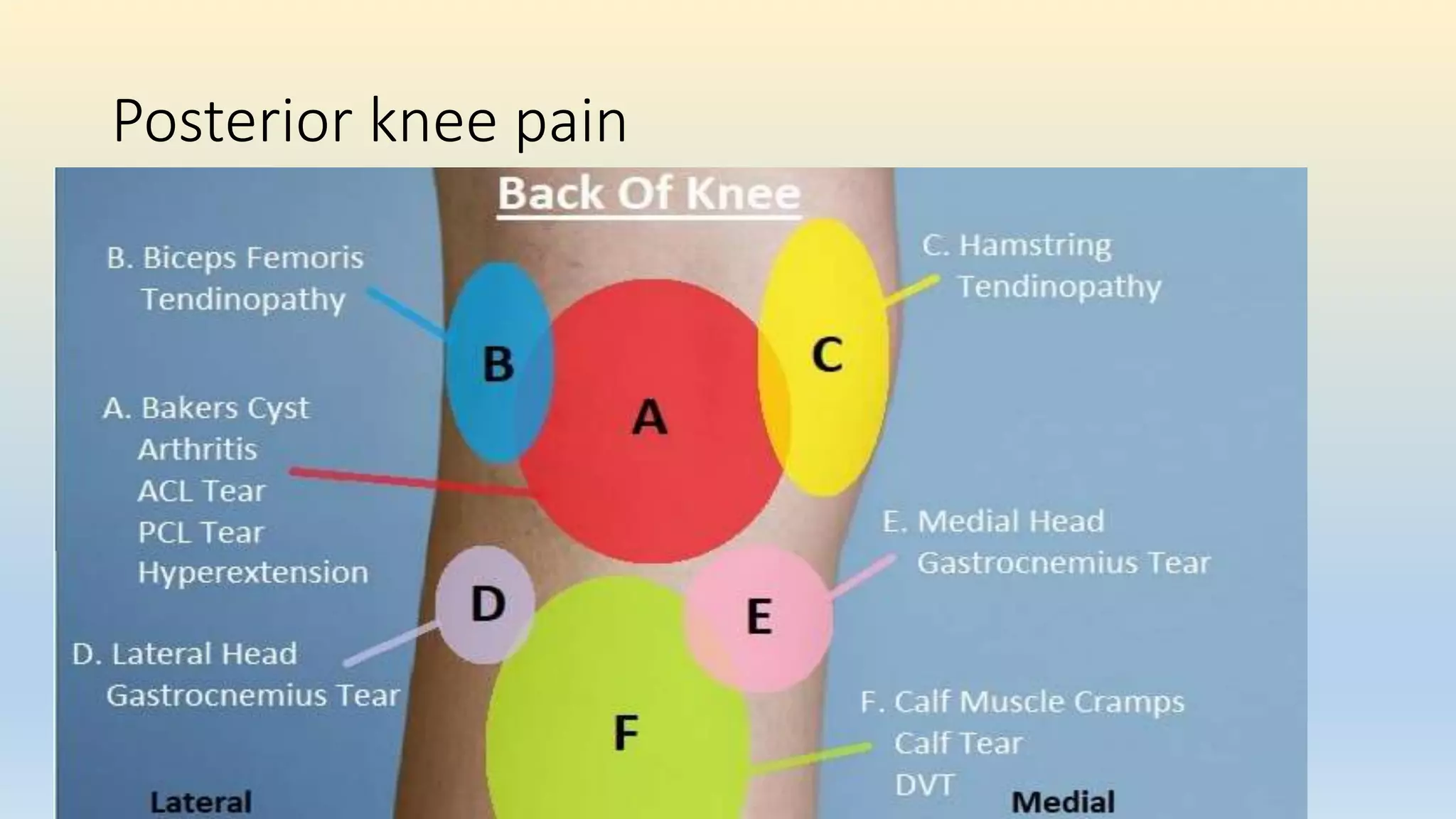
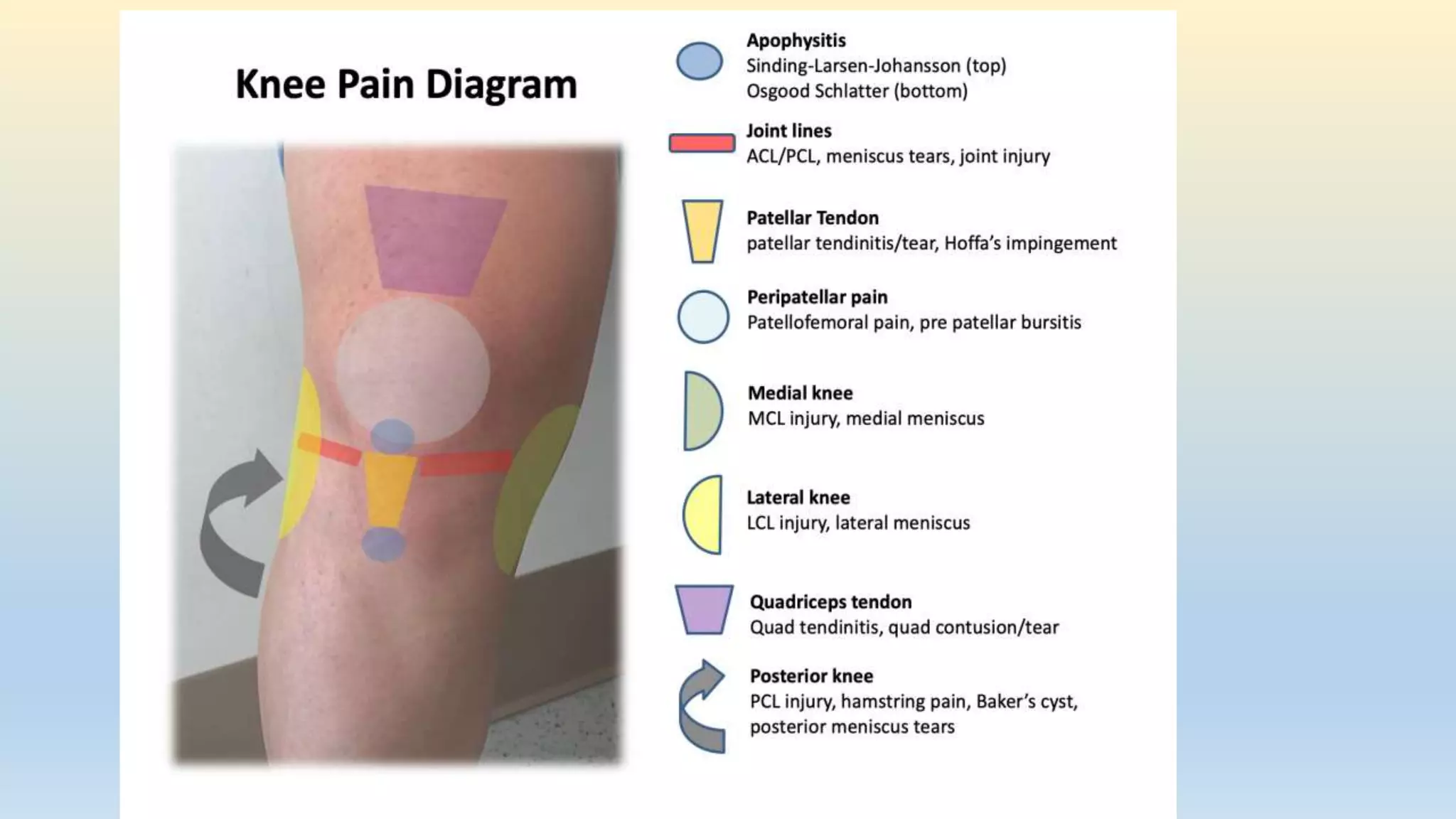
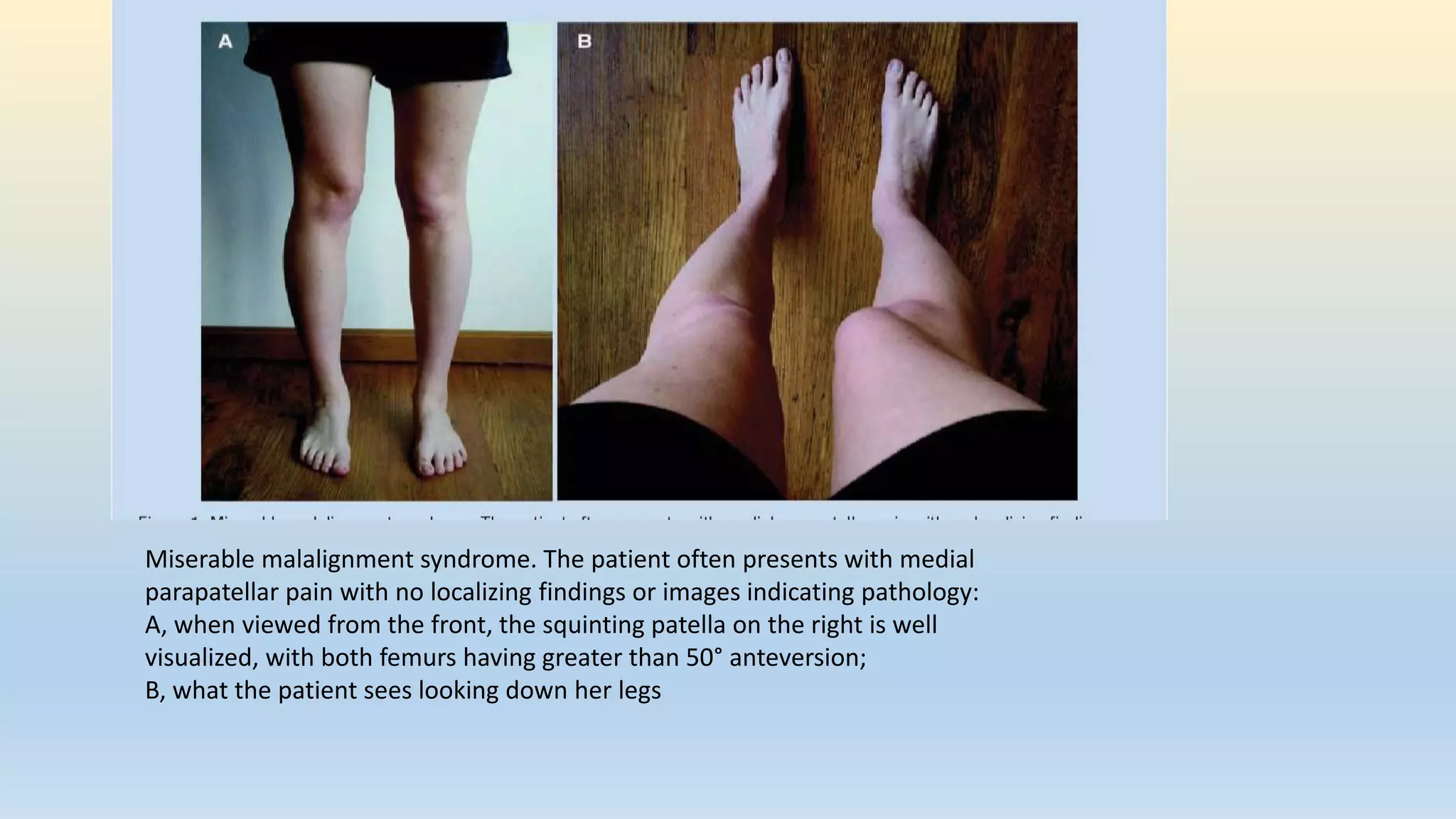
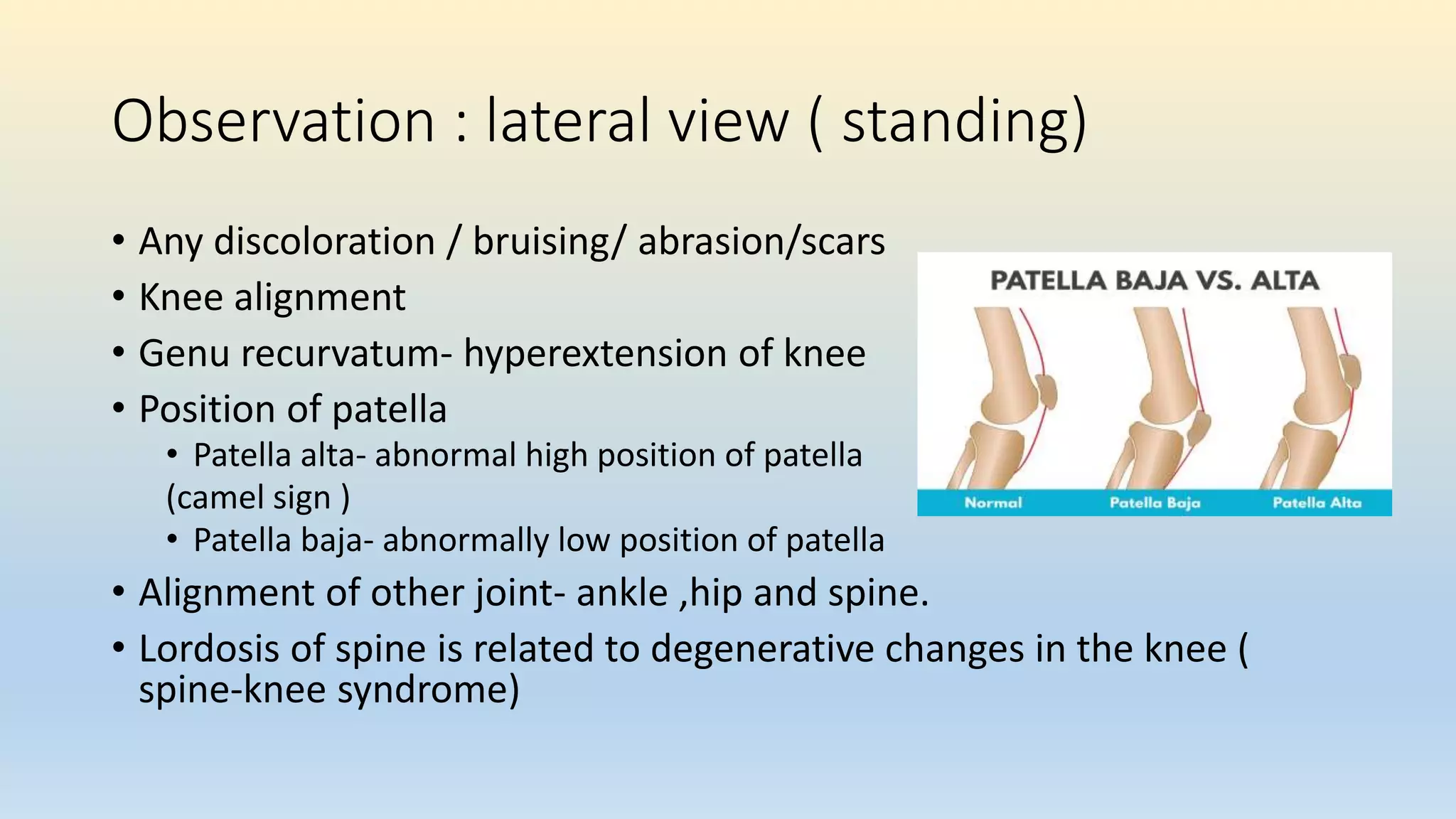
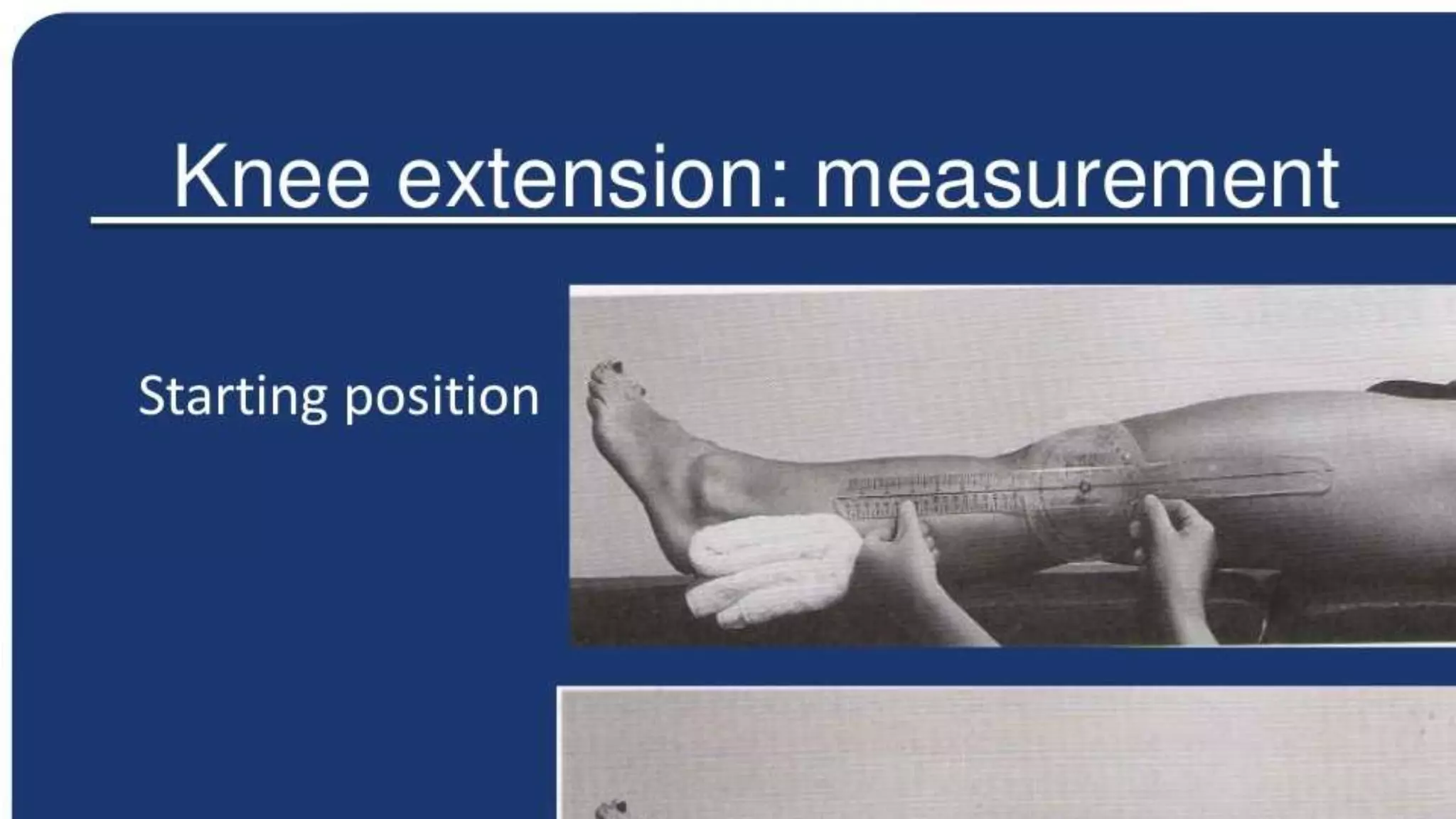
The document is a comprehensive assessment protocol for knee joint evaluation by physical therapists, detailing anatomy, common injuries, patient demographics, and assessments. It outlines various tests for diagnosing knee conditions, including pain location, examination procedures, and differential diagnoses. The document emphasizes the importance of thorough history-taking and physical examination to accurately assess knee disorders.