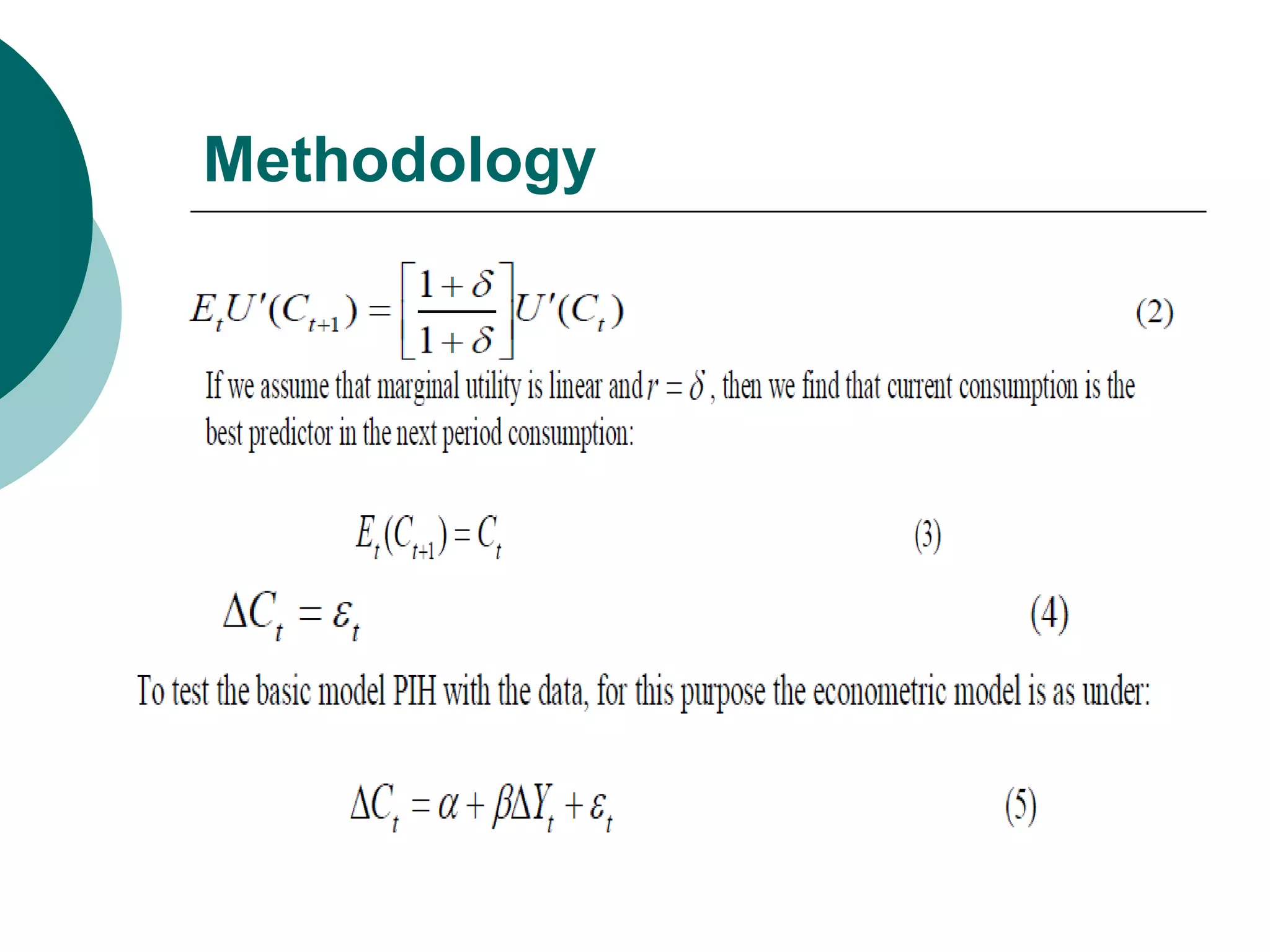
This document outlines the methodology for testing different consumption hypotheses in Pakistan, including the Absolute Income Hypothesis, Relative Income Hypothesis, Permanent Income Hypothesis, and Life Cycle Income Hypothesis. It discusses previous literature on consumption functions and different approaches for estimating consumption, such as Hall's random walk model and the Campbell and Mankiw consumption model. The methodology section describes using an Euler equation approach and consumption data from national accounts and household surveys to test the hypotheses at the macro level, micro level, and for urban vs. rural households.