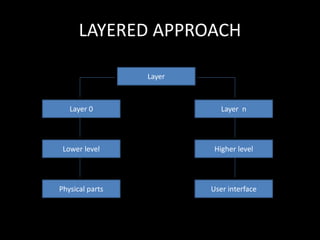
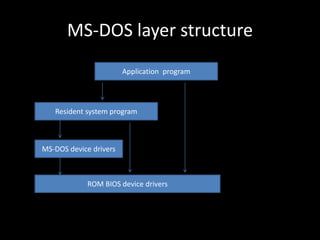
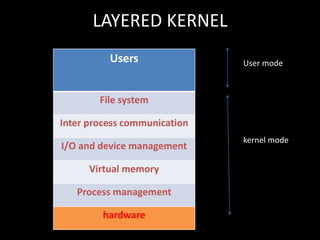
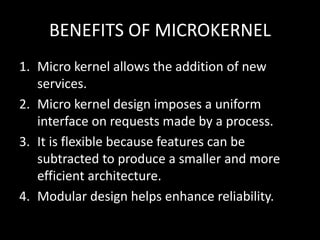
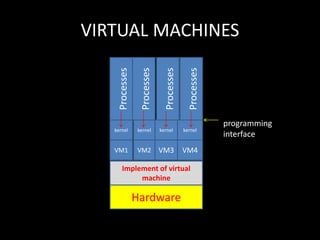
The document discusses system structure using a layered approach. It describes how systems are organized into layers, with each layer built upon the one below it. An interface separates each pair of adjacent layers. Typical layers consist of data structures and routines that higher layers can invoke, while lower layers provide operations to the layer above. This modular approach simplifies debugging and verification. The document also discusses microkernel architecture, which assigns only essential functions like address space and scheduling to the kernel. Virtual machines provide a simulated hardware interface identical to the underlying hardware.