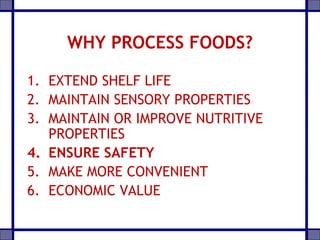
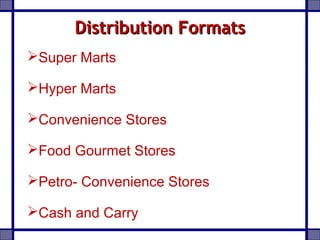
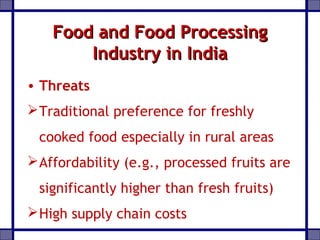
This document provides an overview of the processed food industry and food processing machinery industry in India. It discusses key segments of the food industry including fruits and vegetables, dairy, grains, and packaged foods. It outlines the size and growth of the processed food market in India. It also analyzes the competitive landscape and discusses major players in various industry segments. The document concludes by discussing opportunities and challenges for the food and food processing industry in India.