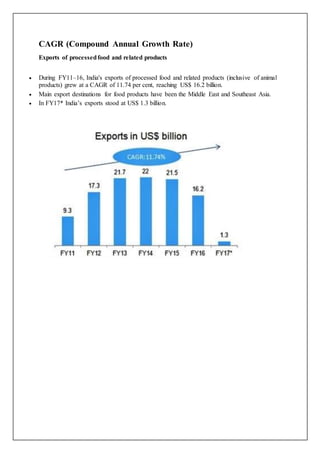
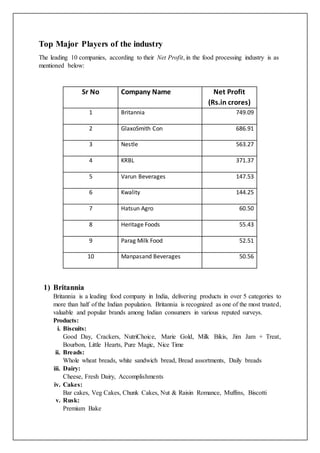
The food processing industry in India has experienced significant growth and is expected to continue growing at a CAGR of 11%. Some of the largest companies in the industry include Britannia, Nestle, and KRBL. The industry faces challenges such as infrastructure issues but has a promising future given the large market size and growing demand for processed foods. The government is also supporting industry growth through favorable policies.