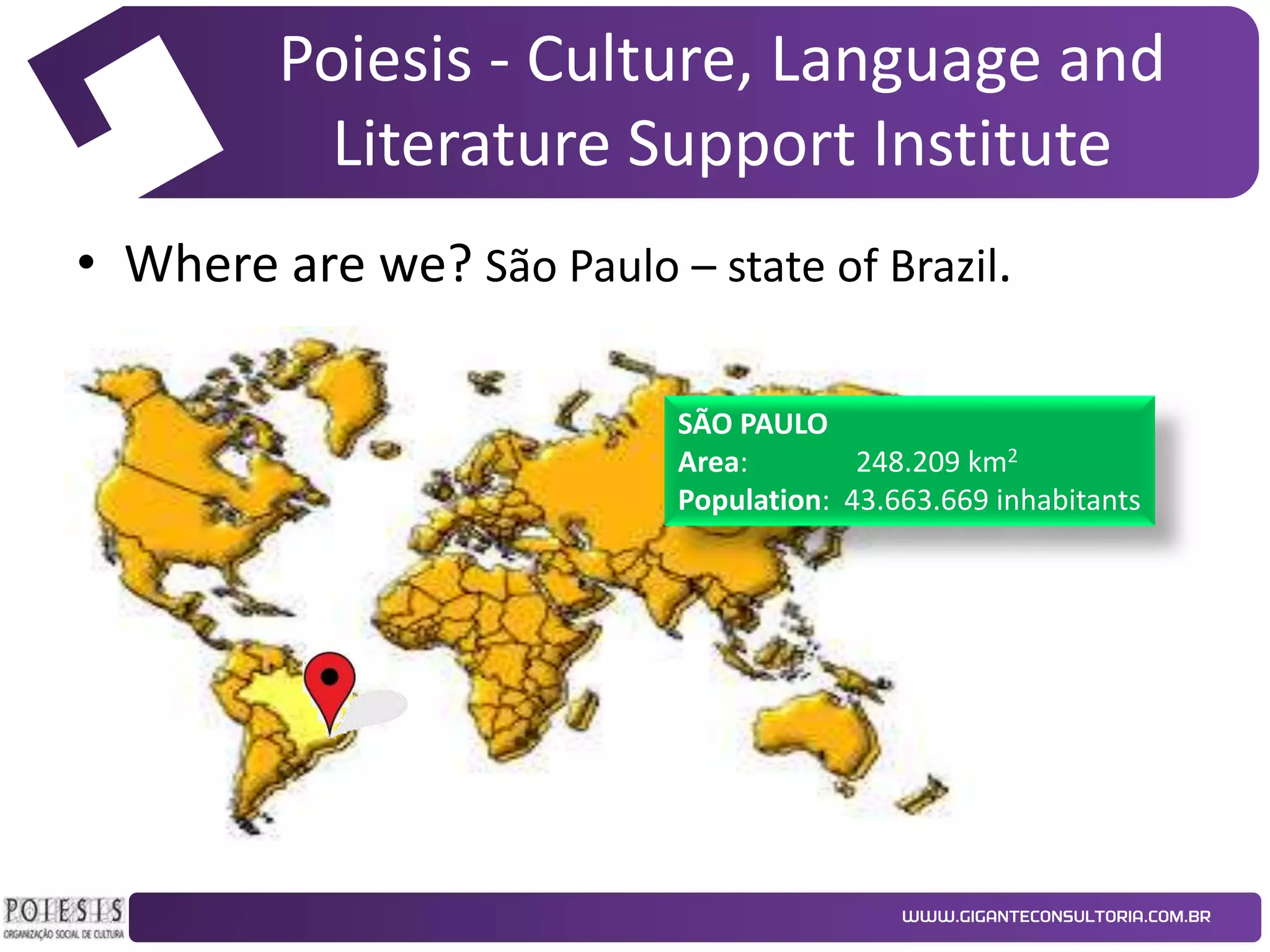
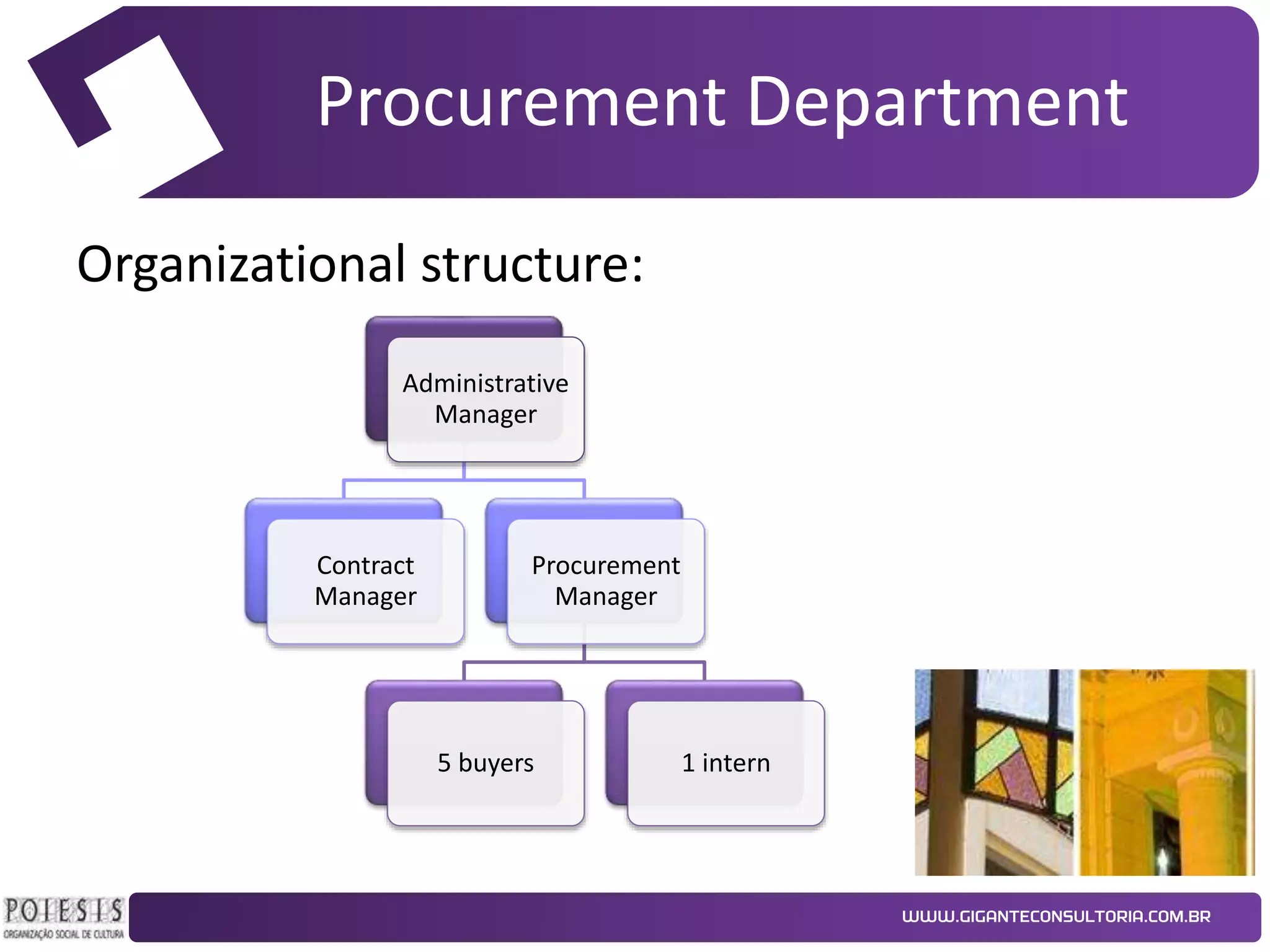
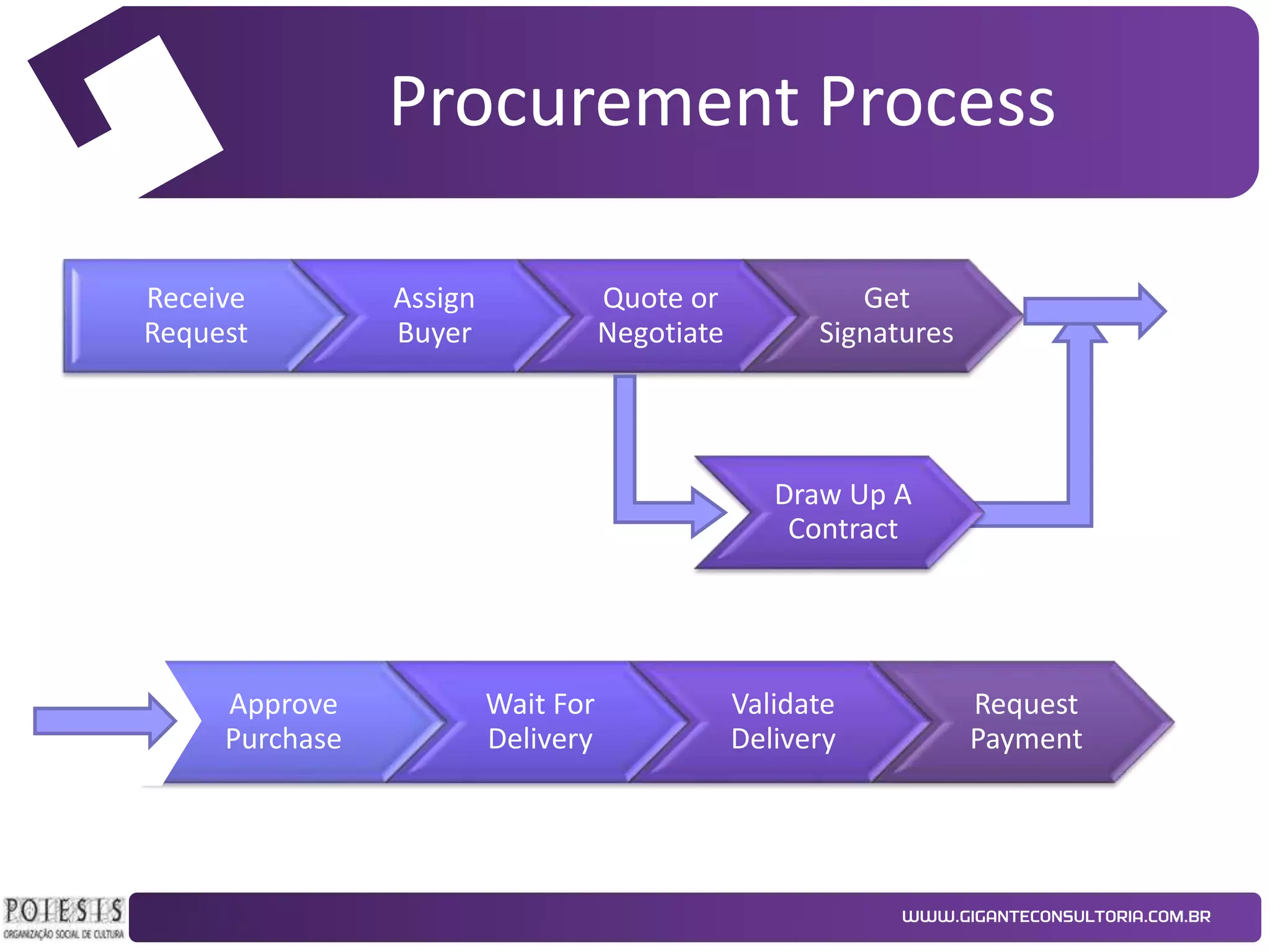
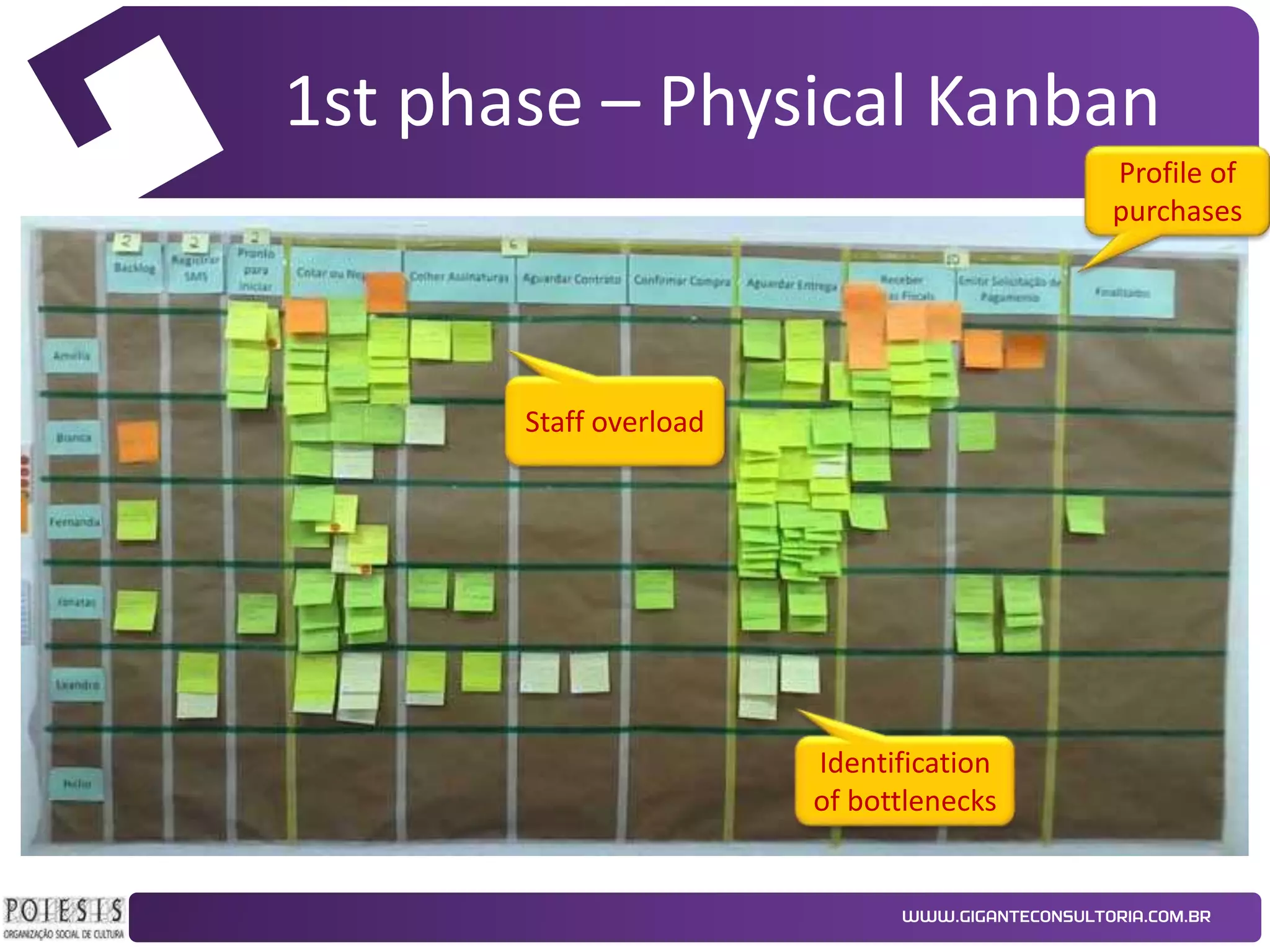
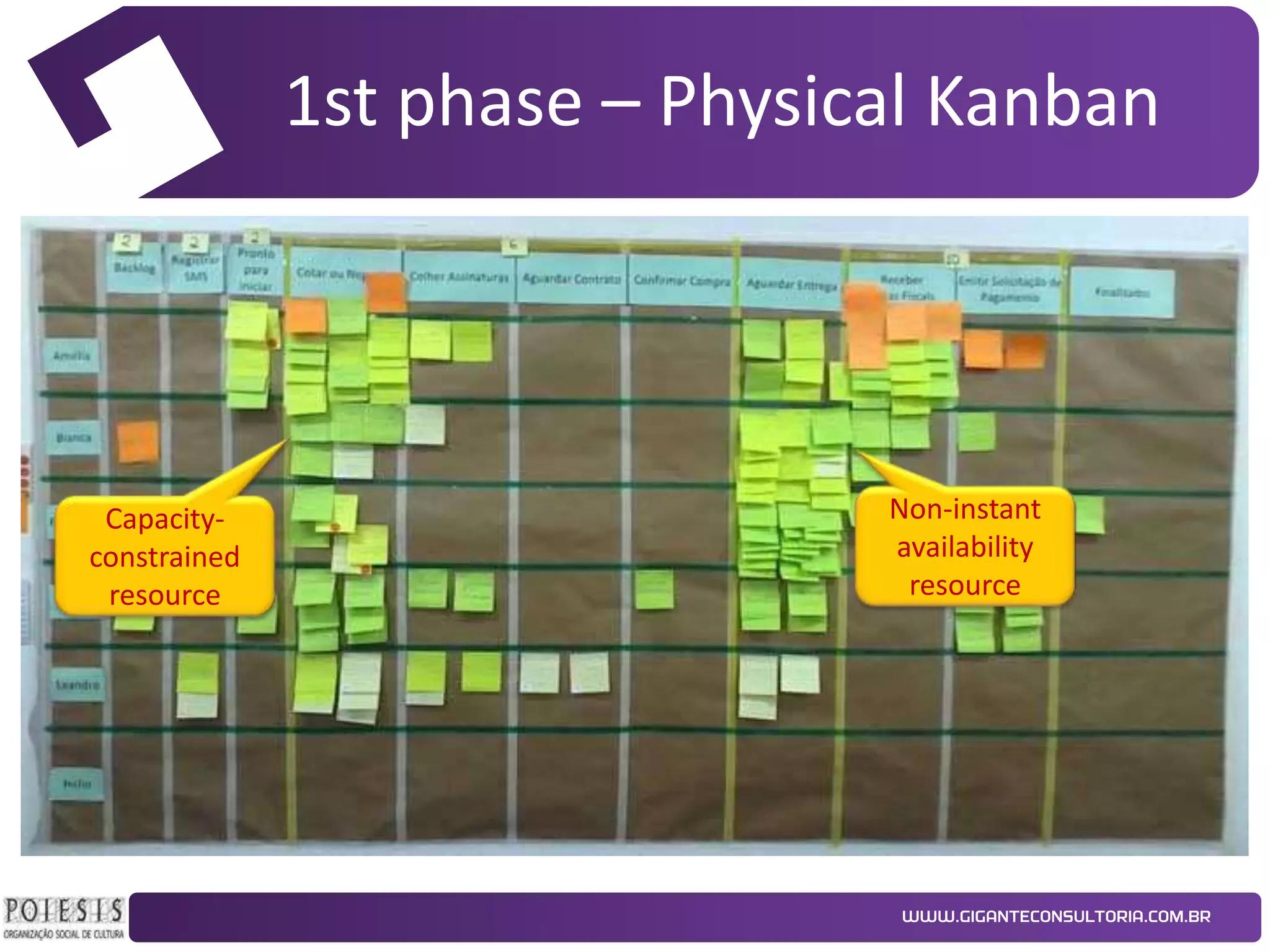
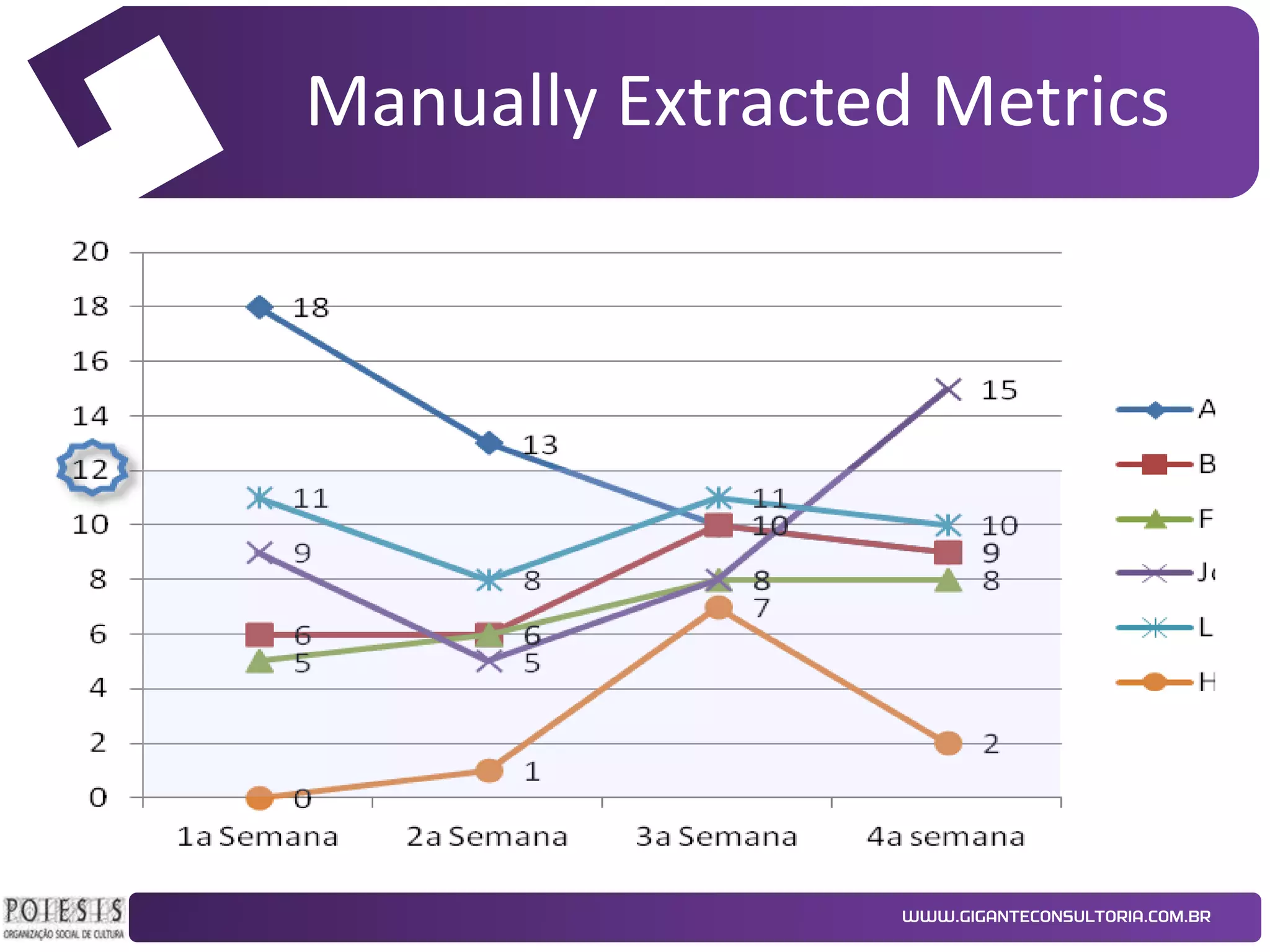
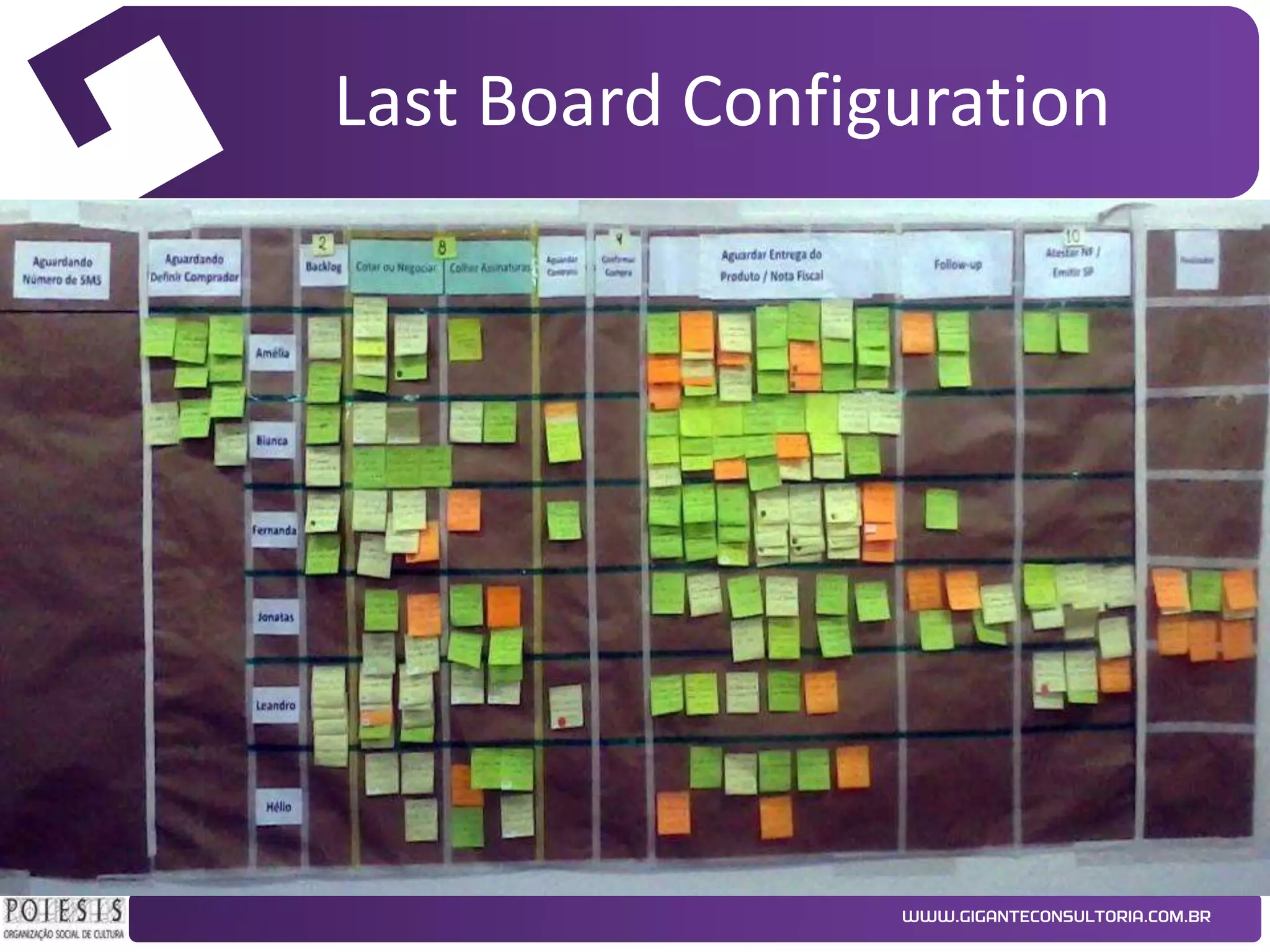
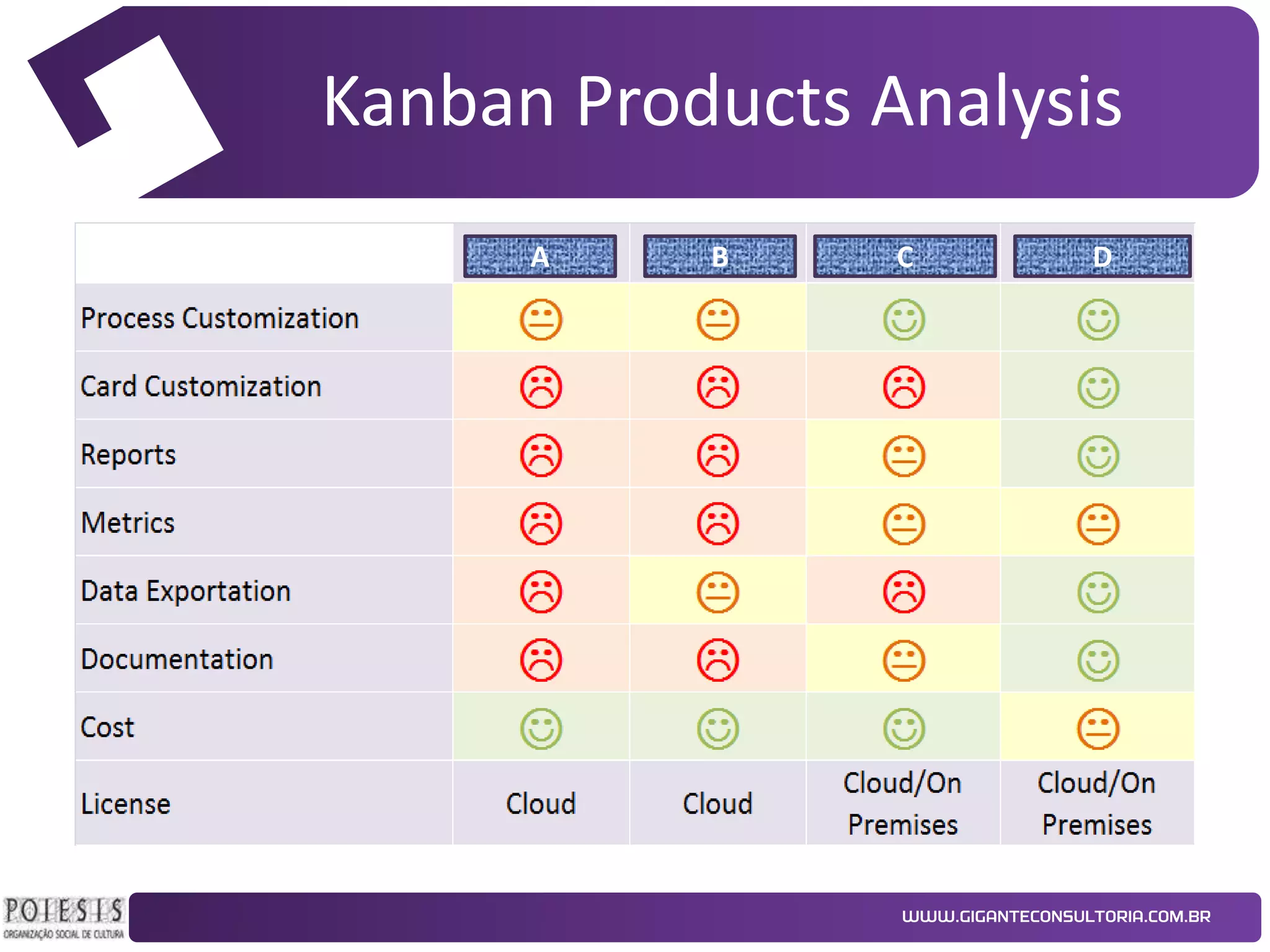
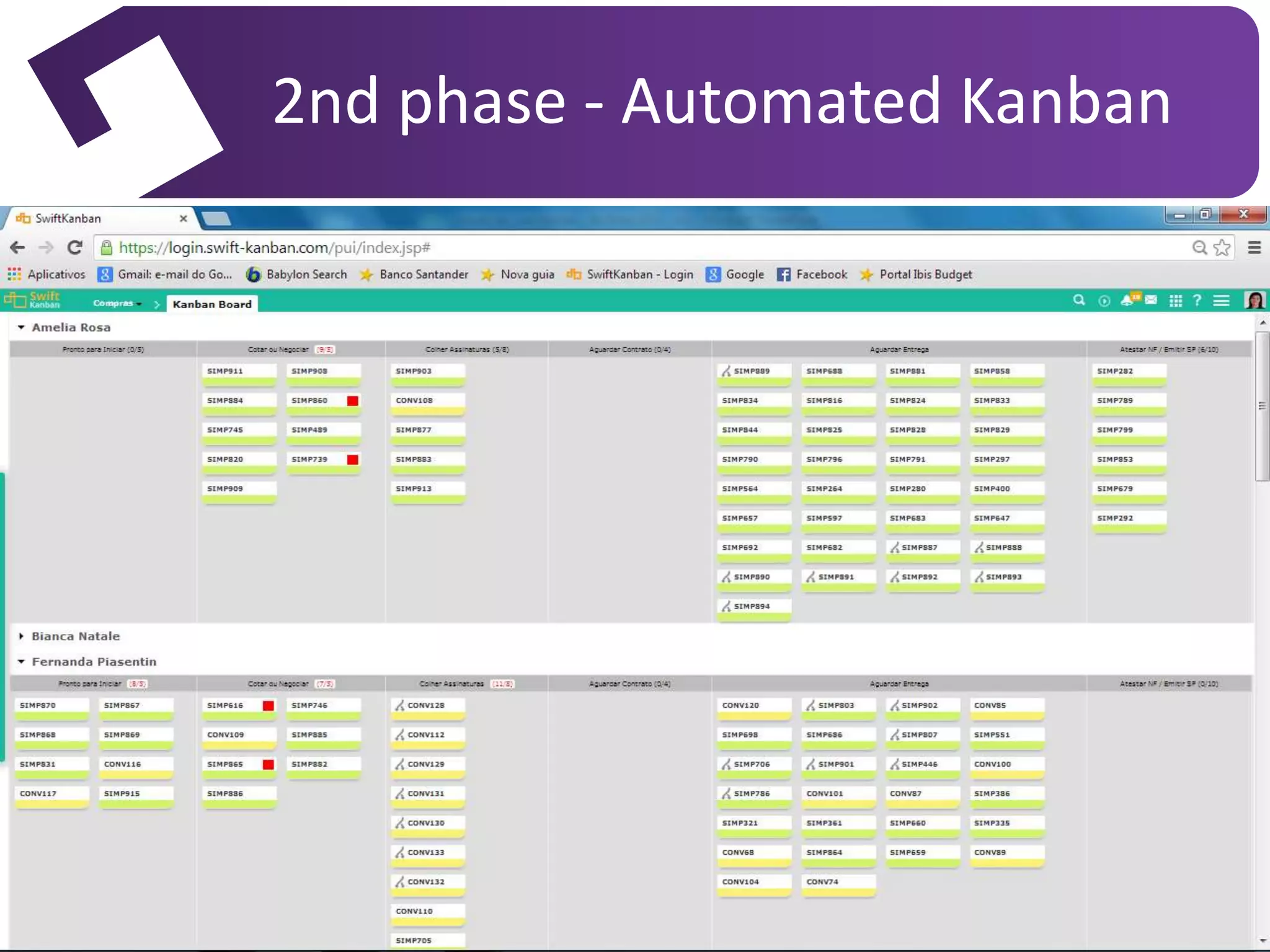
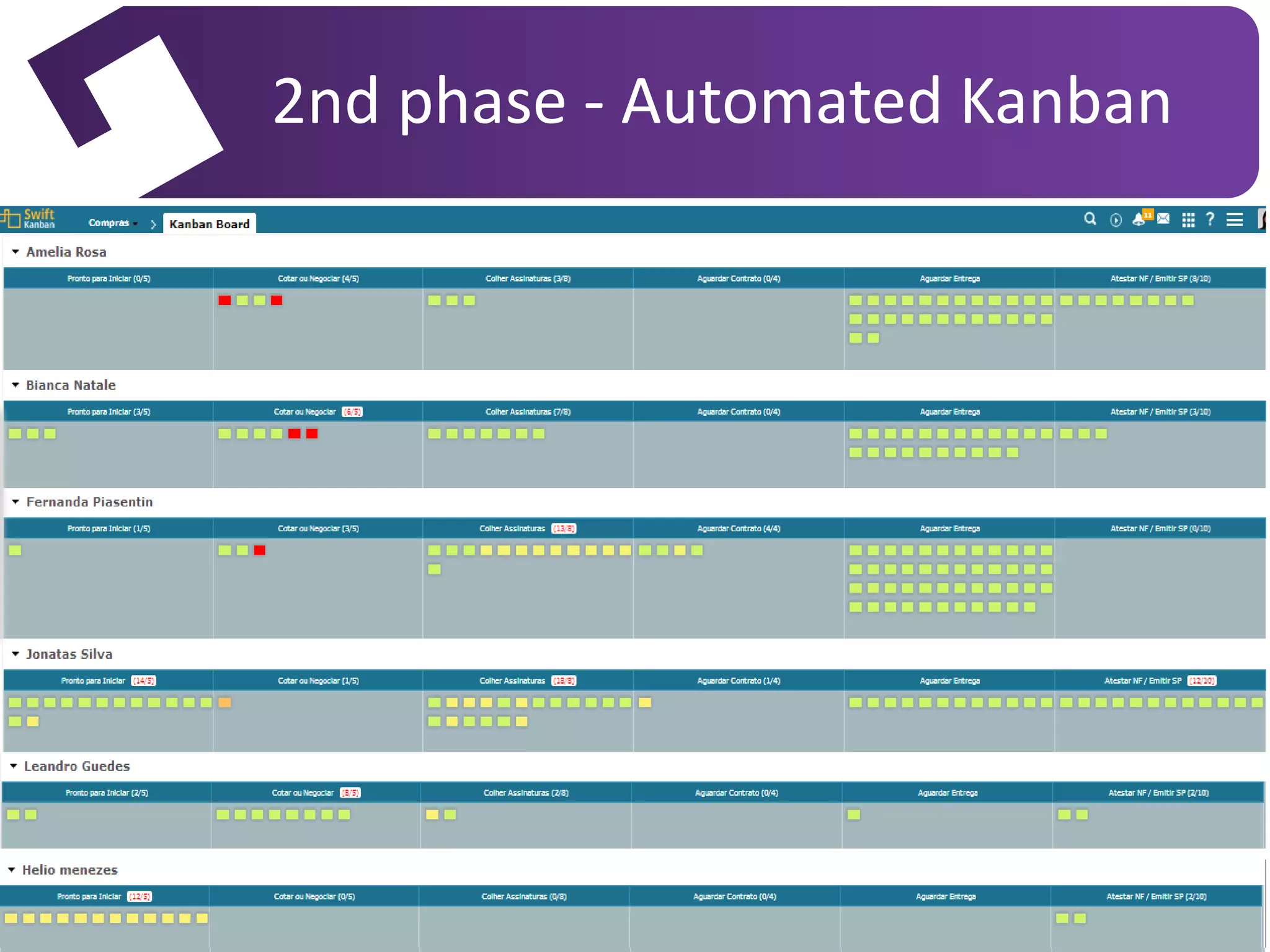
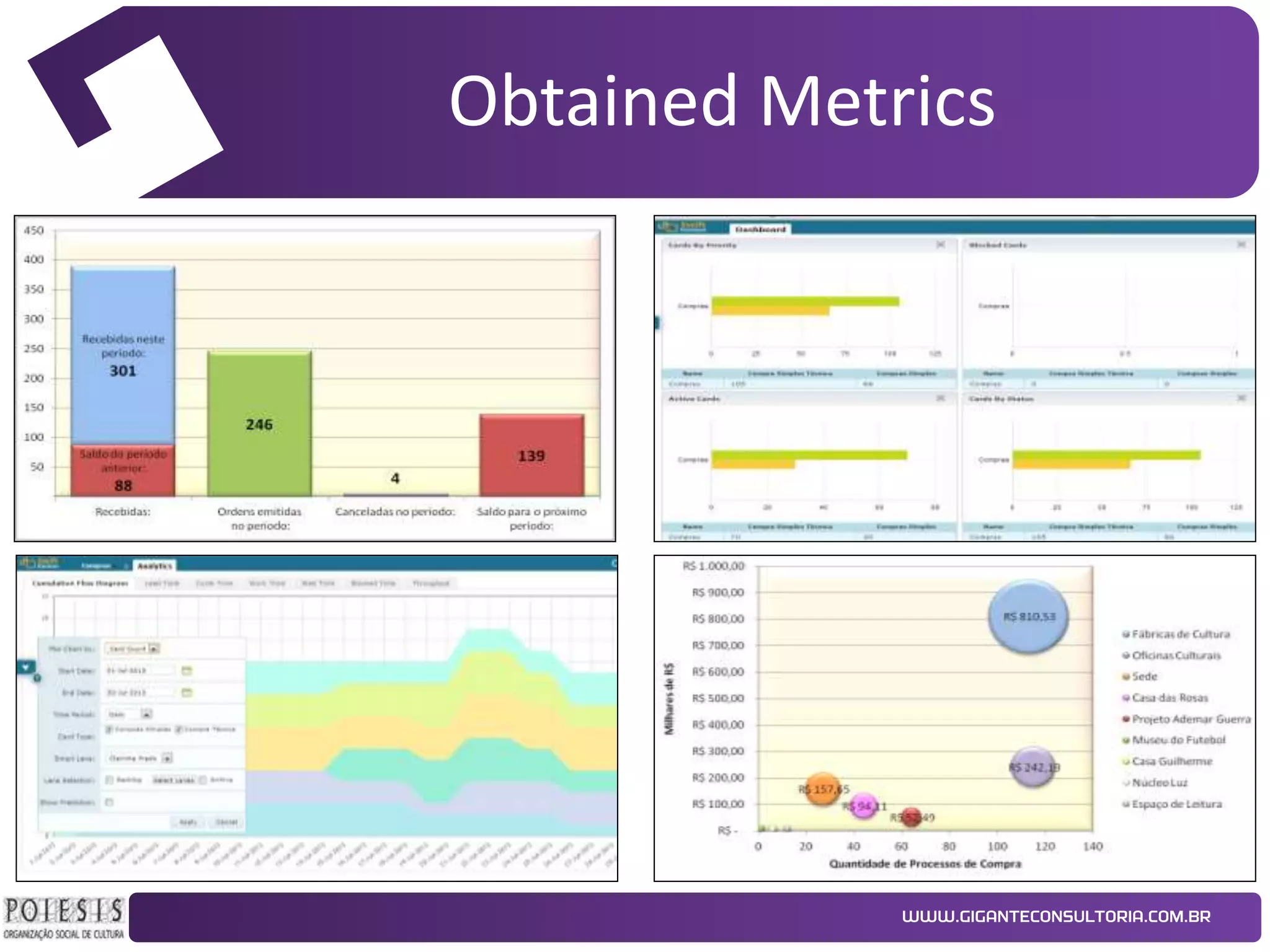
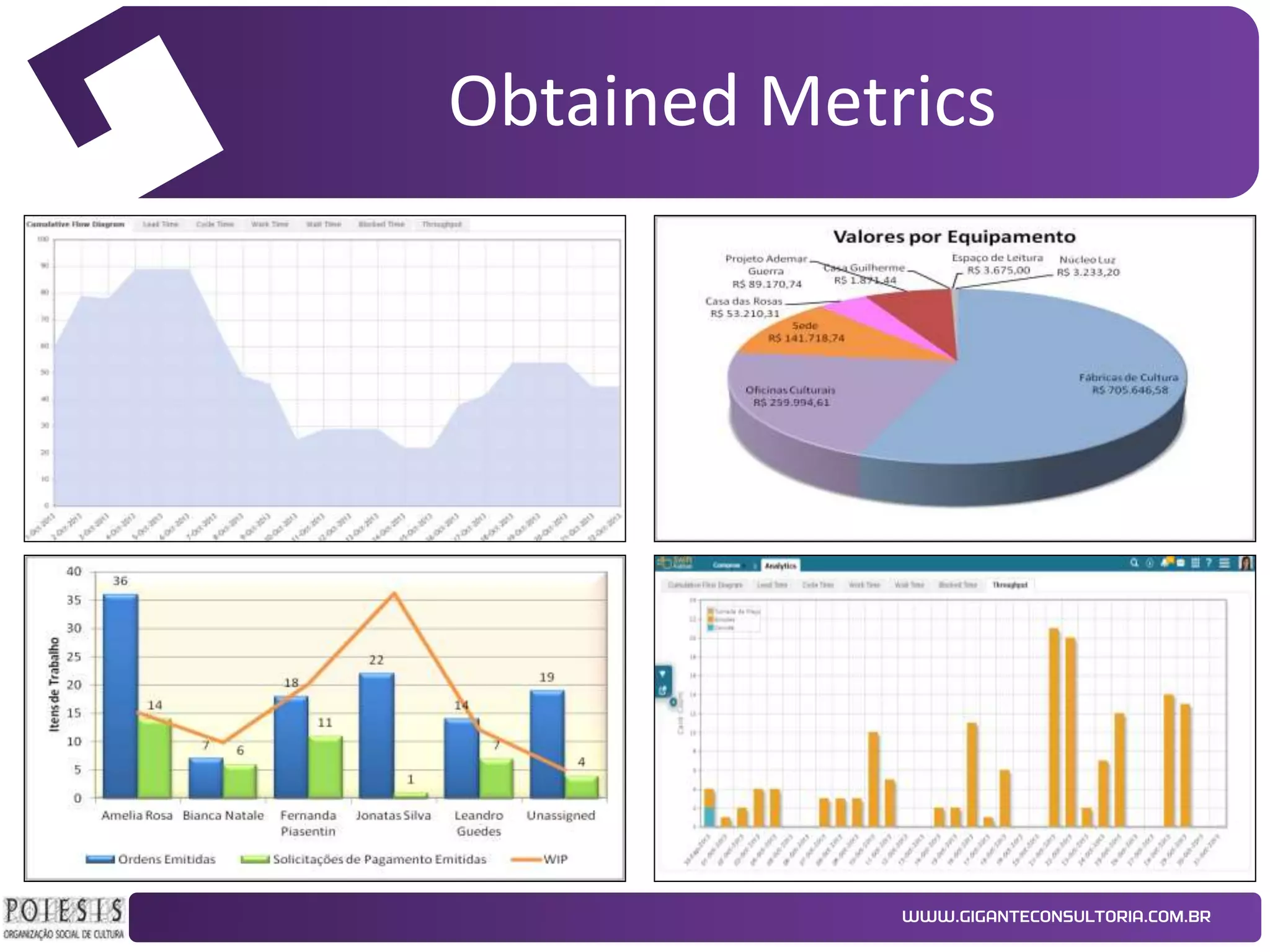
The document discusses the implementation of Kanban as a business analysis tool to improve the procurement process at Poiesis, a cultural support institute in São Paulo, Brazil. It details the challenges faced by the procurement department, the proposed Kanban solution, and the phases of deployment, including both physical and automated Kanban systems. The conclusion highlights Kanban's effectiveness in enhancing transparency, productivity, and managerial support while addressing the identified issues.