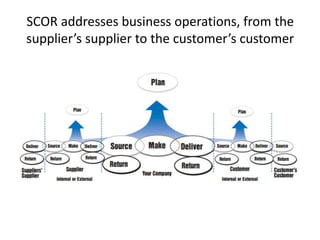
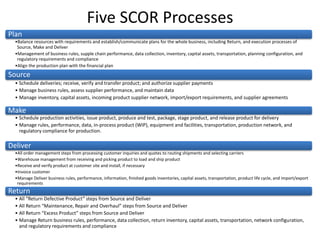
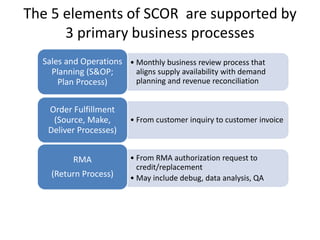
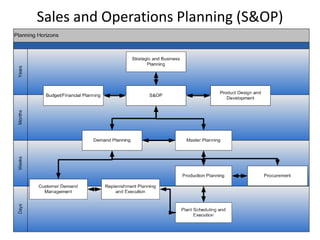
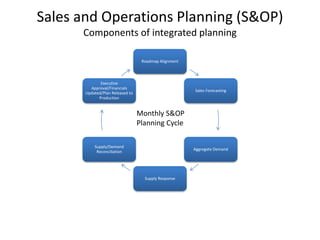
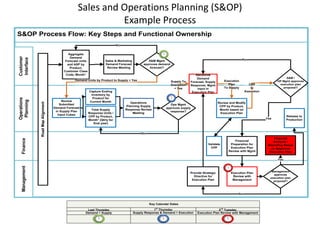
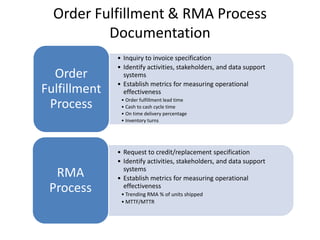
The document provides an introduction to the Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) model. It describes the five core SCOR processes - Plan, Source, Make, Deliver, and Return. Plan involves balancing resources with requirements. Source includes procurement activities. Make covers production. Deliver encompasses order fulfillment and distribution. Return manages product returns. The document also outlines three primary business processes supported by SCOR: sales and operations planning (S&OP), order fulfillment, and returns management (RMA). It provides high-level descriptions of each as well as their advantages and implementation requirements.