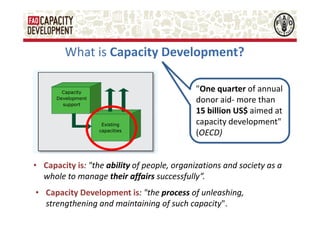
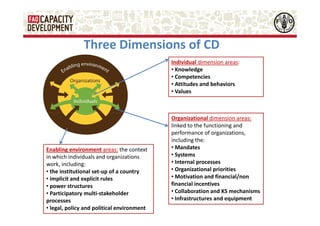
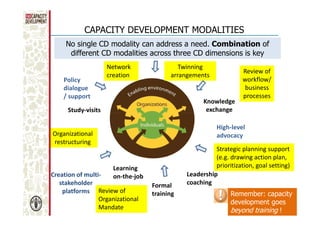
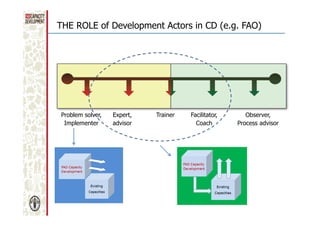
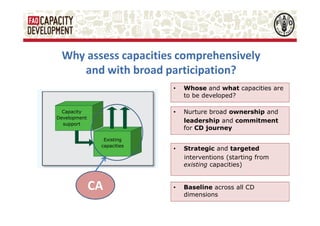
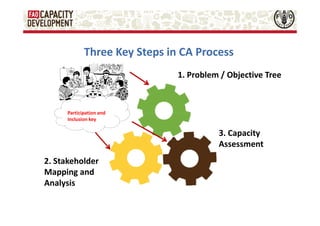
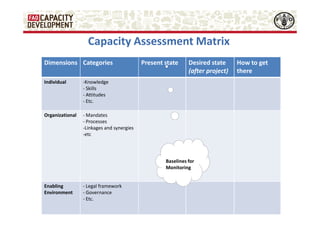
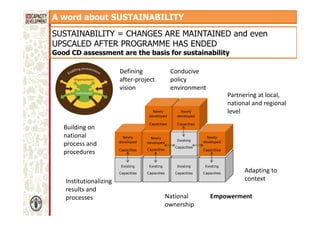
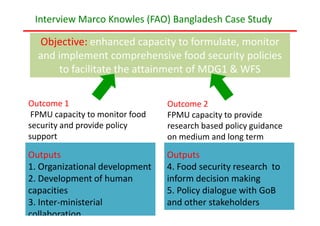
The document discusses capacity development as a process to enhance the ability of individuals, organizations, and societies to manage their affairs effectively, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach that goes beyond mere training. It identifies three dimensions of capacity development—individual, organizational, and enabling environment—and highlights the importance of nurturing existing capacities through targeted interventions and local ownership. The FAO's analysis reveals that although many capacity development interventions are relevant, sustainability remains a challenge, necessitating strategic assessments and a focus on collaboration across sectors.