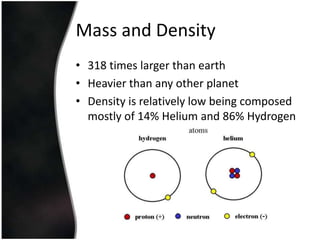
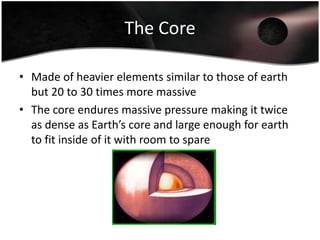
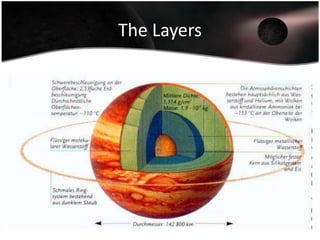
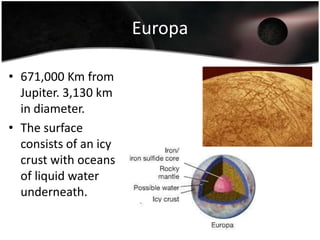
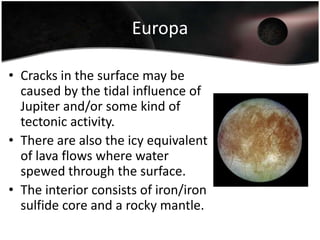
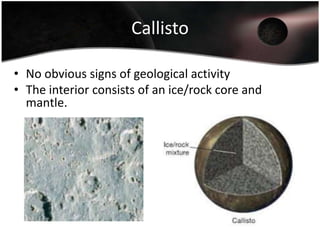
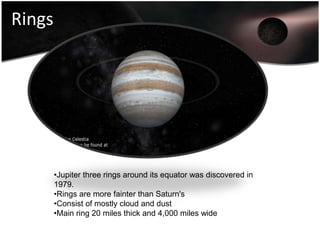
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, with a mass more than twice that of all other planets combined. It is composed primarily of gas and liquid and rotates faster than any other planet. Jupiter has the strongest magnetic field of any planet and has over 60 moons, four of which are large moons called the Galilean satellites that were discovered by Galileo. Europa may have subsurface oceans that could potentially support life. Many missions have been sent to Jupiter to study its atmosphere, magnetosphere, rings and moons.