The document discusses the structure and functions of state governments in India. It describes the key elements as follows:
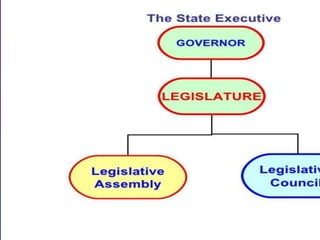
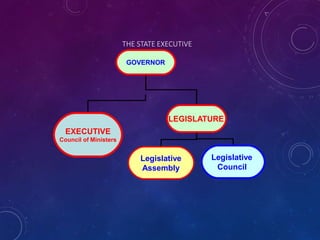
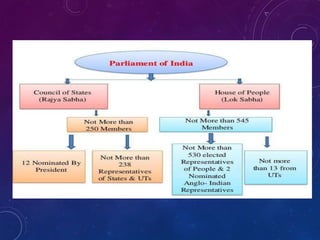
1) The state legislative assembly is the lawmaking body, consisting of between 60-500 members elected for 5-year terms. It exercises legislative powers over state subjects.
2) Some states have an upper house called the legislative council as well. Members are elected or nominated by the governor.
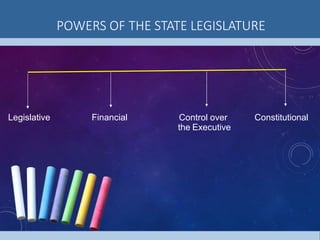
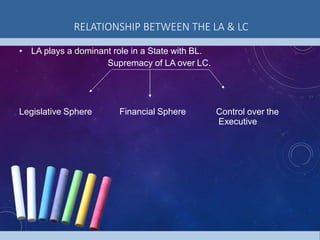
3) The state legislature has powers to make laws, approve the budget, and exercise oversight of the executive. It also has a role in constitutional amendments affecting states.




















![FAMILY LAW
• Indian civil law is complex, with each religion having its own specific laws
which they adhere to.
• After independence Indian laws have adapted to the changing world.
• The most recent being the Domestic Violence Act[2005].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consolidatedppticmodule21-220923164410-f0b6aa81/85/IC-Module-2-1-pptx-22-320.jpg)