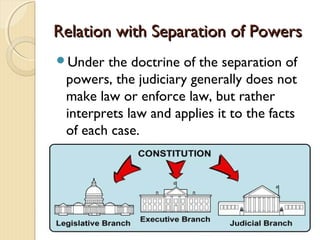
The judiciary in India is based on the common law system established by the British and consists of a hierarchy of courts with the Supreme Court at the top. Below the Supreme Court are High Courts at the state level and district courts at the local level. While the judiciary interprets laws and ensures equal justice, it faces issues like delays, understaffing, and corruption. Various e-governance projects aim to address these issues by computerizing court operations.










![E-Courts Mission Mode ProjectE-Courts Mission Mode Project
The E-courts project was established in
the year 2005.[23] According to the
project, all the courts including taluk
courts will get computerised. As per the
project in 2008, all the District courts
were initialised under the project. In
2010, all the District court were
computerised.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/commonmanandjudiciary-160126112901/85/Common-man-and-judiciary-13-320.jpg)

