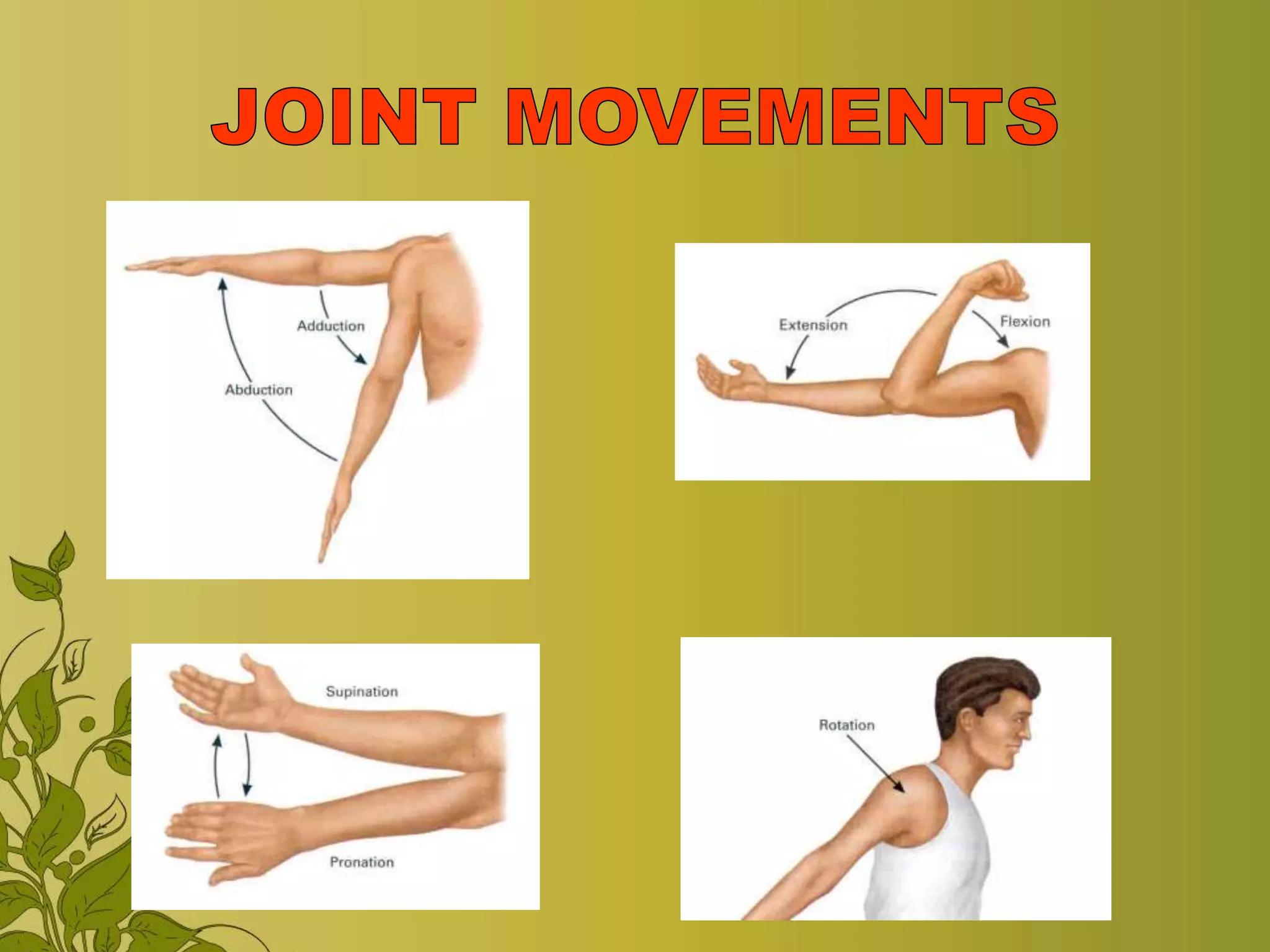
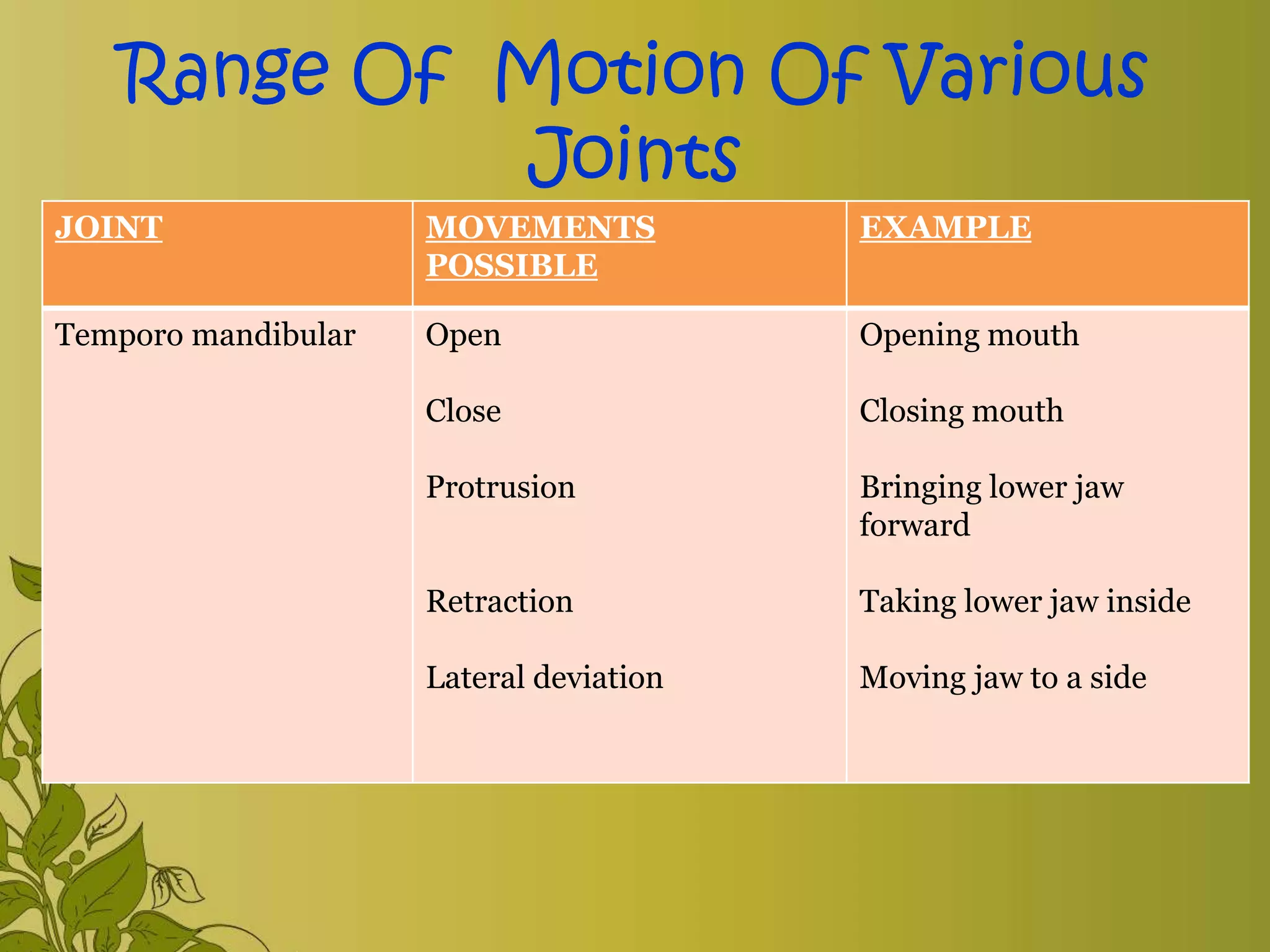
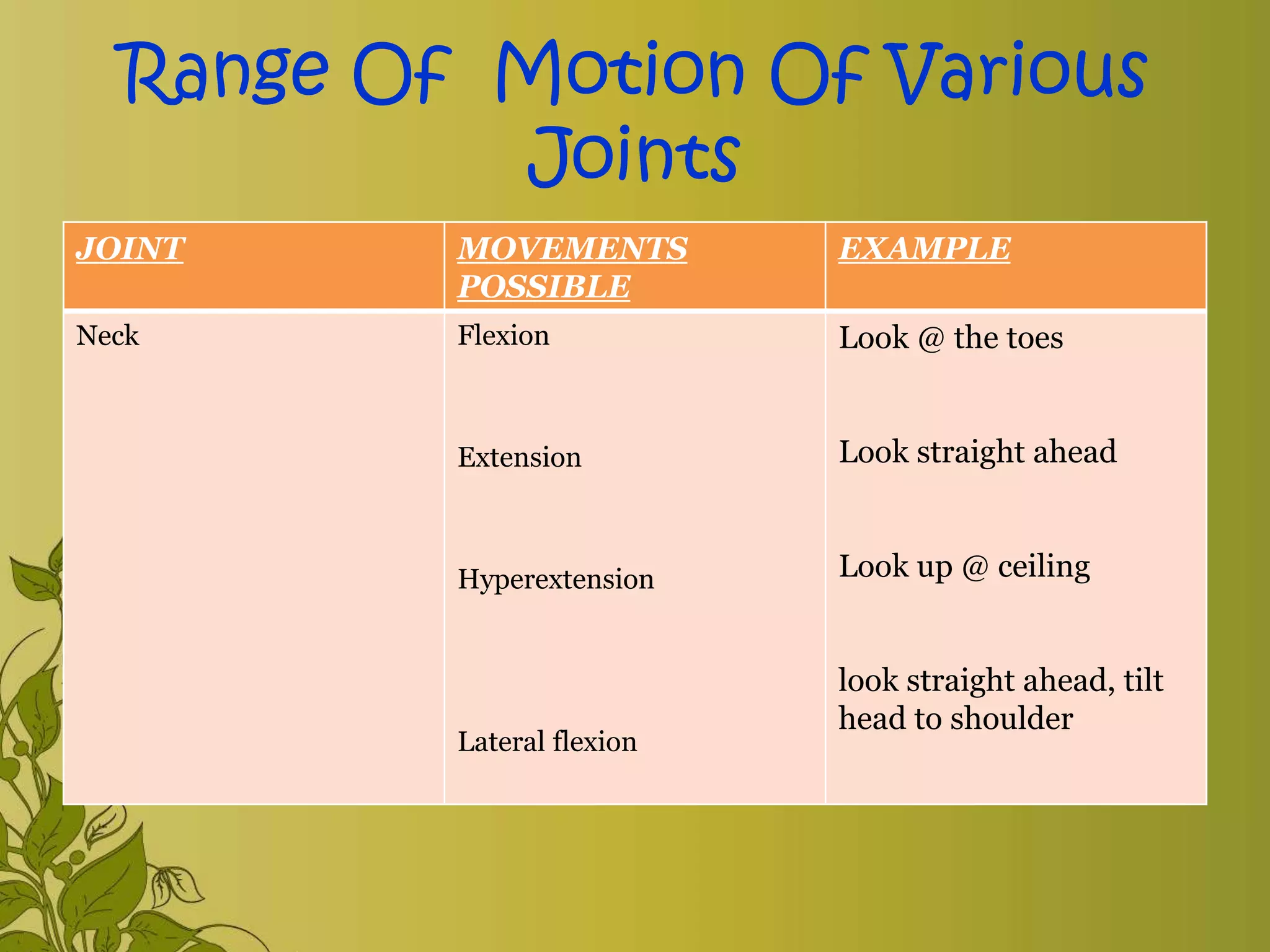
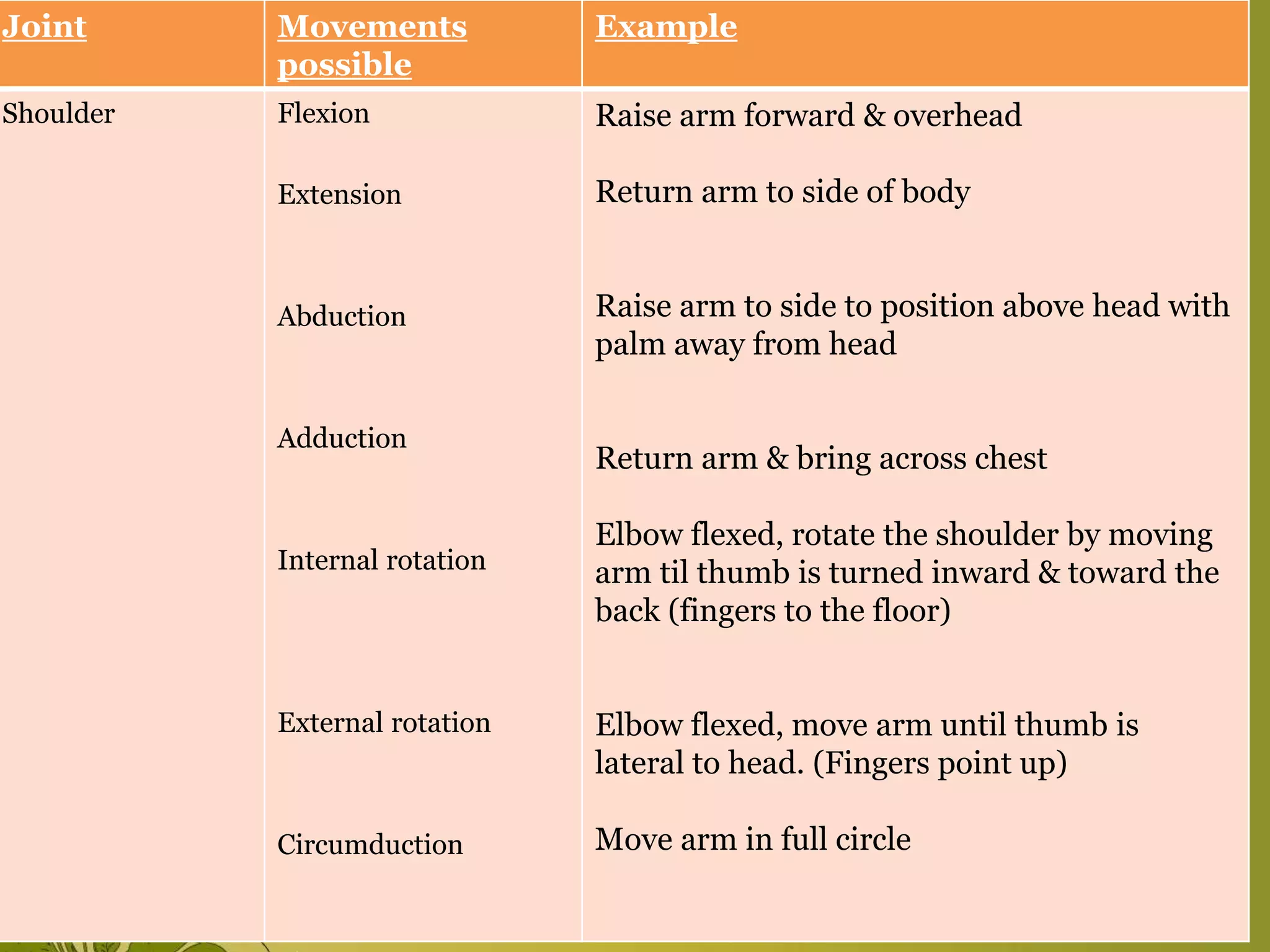
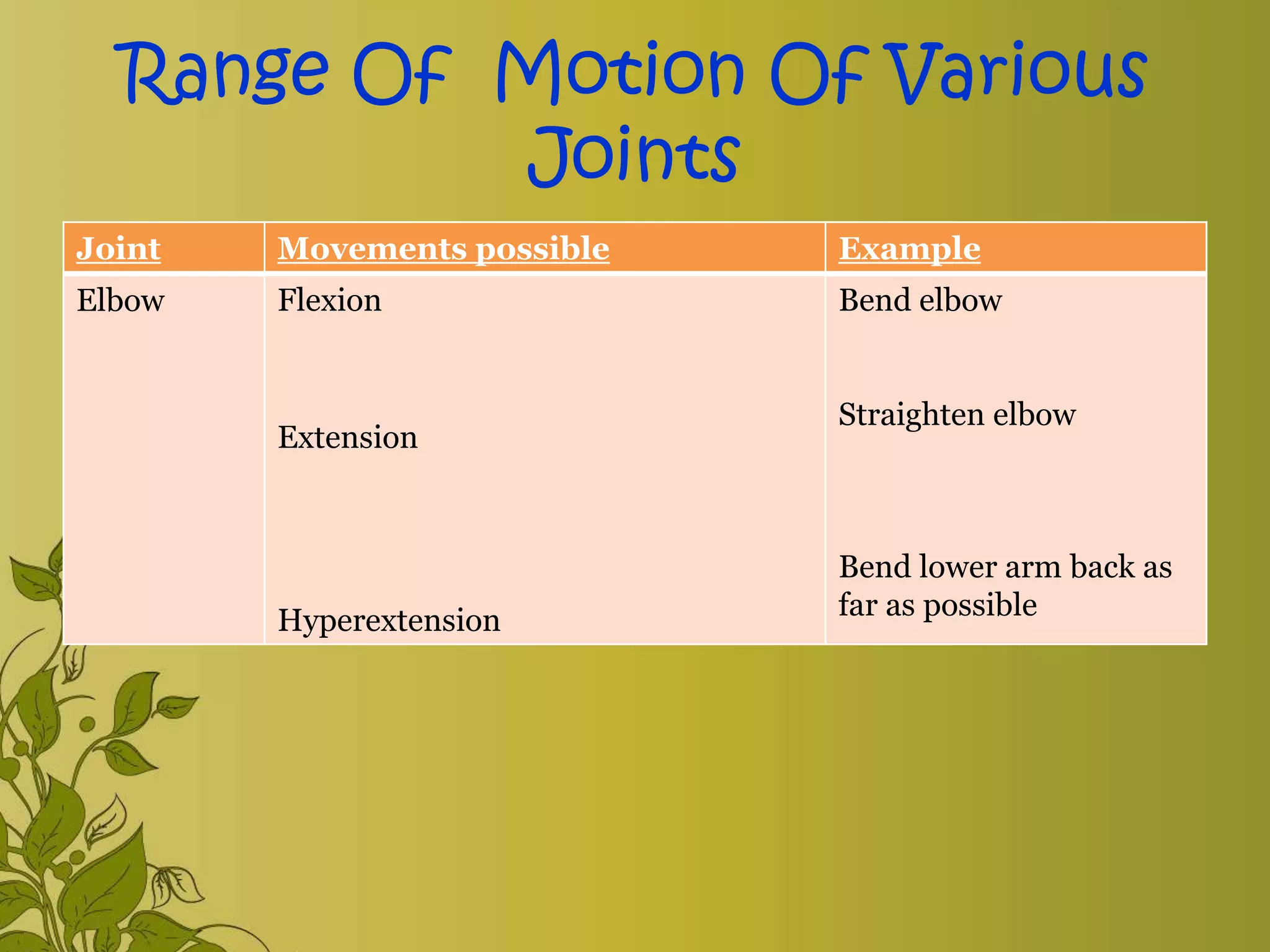
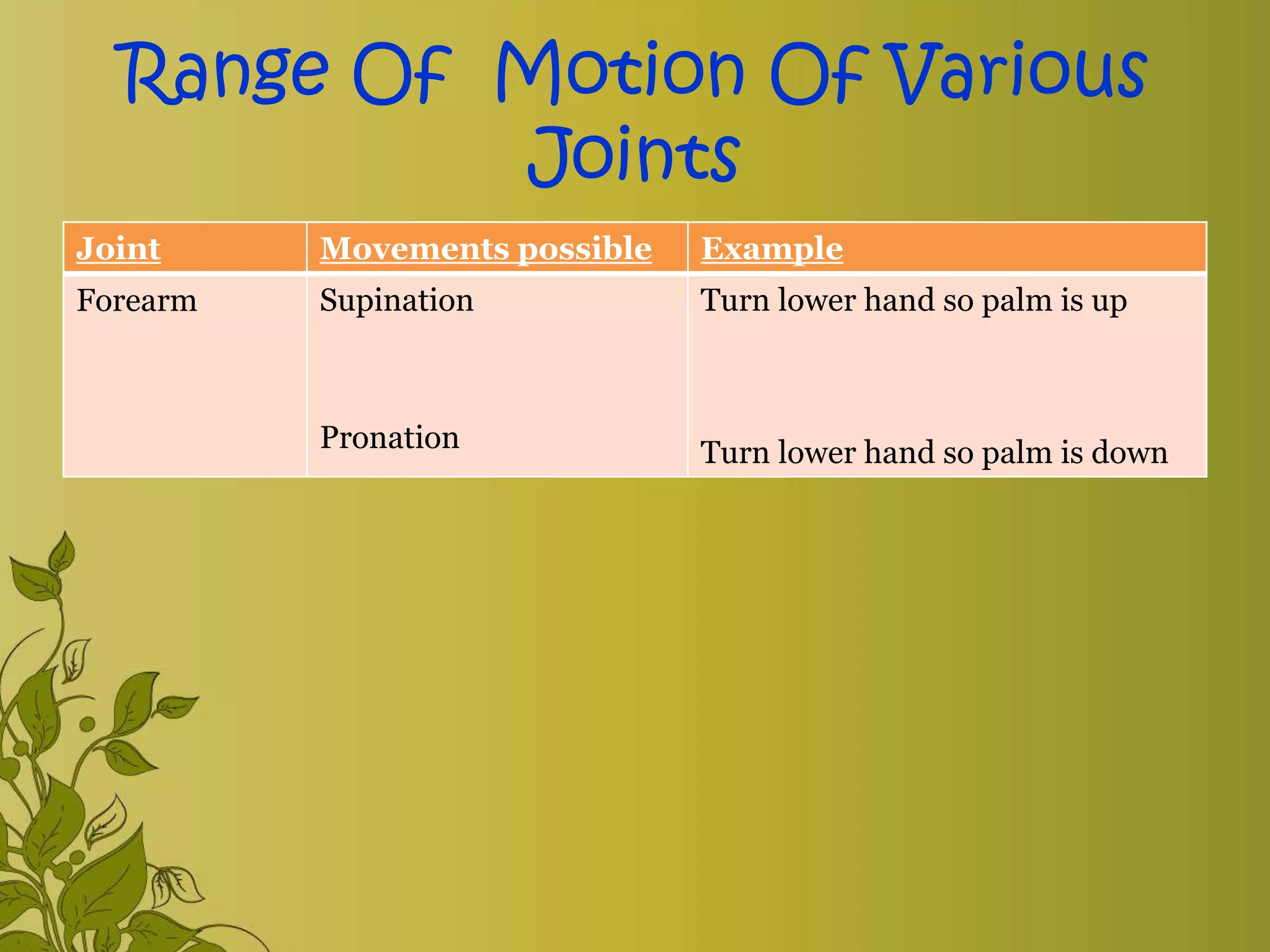
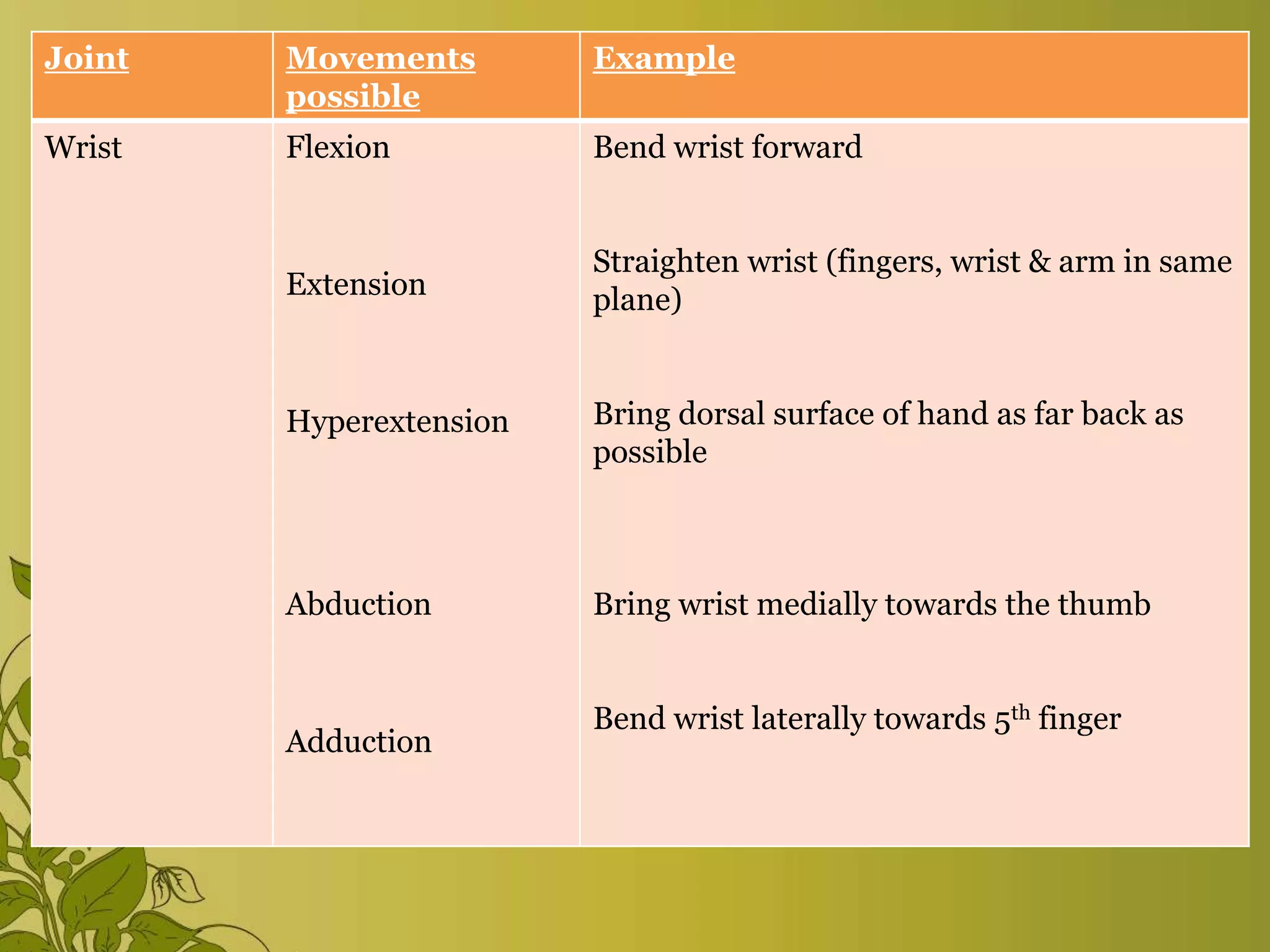
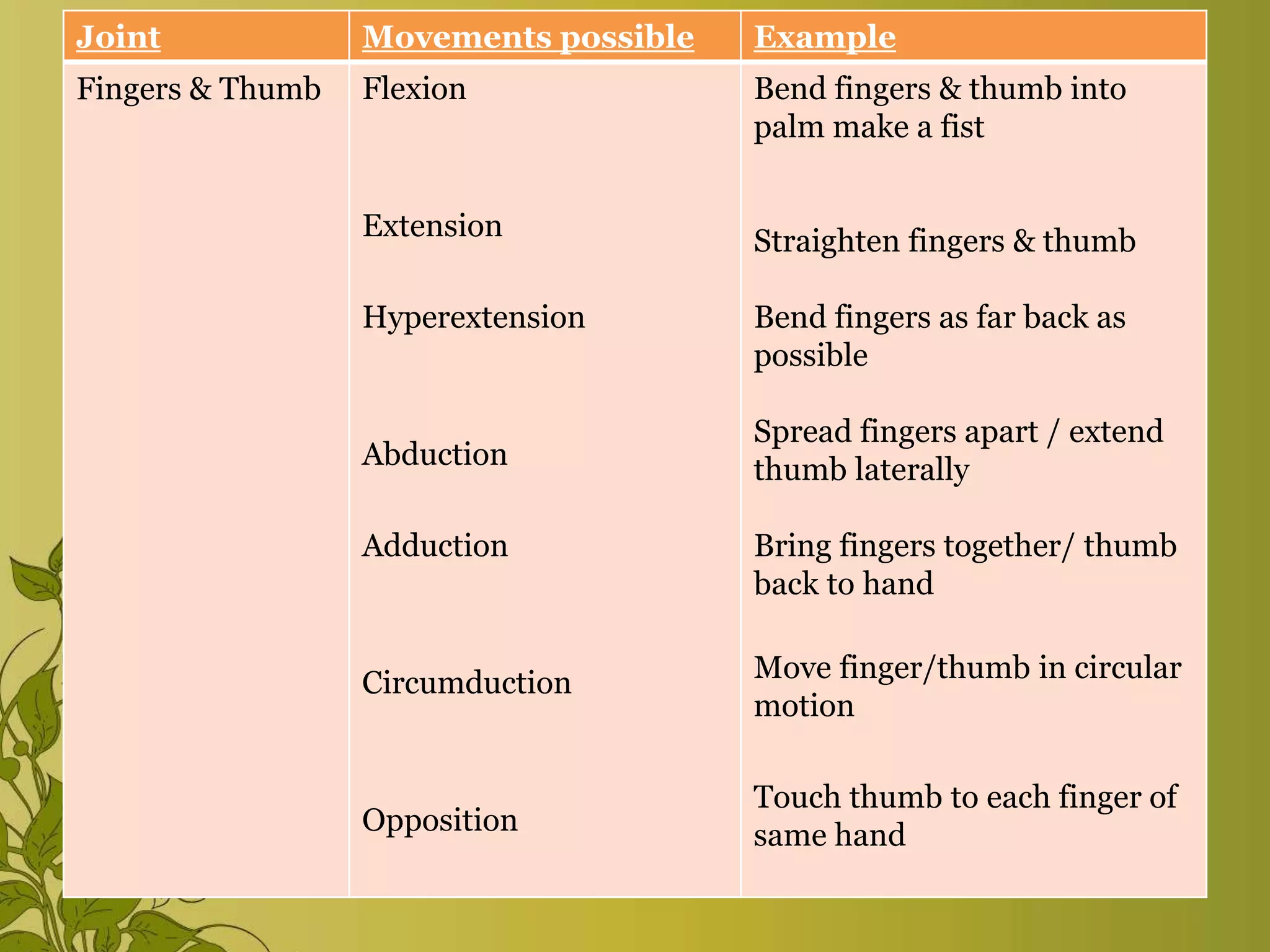
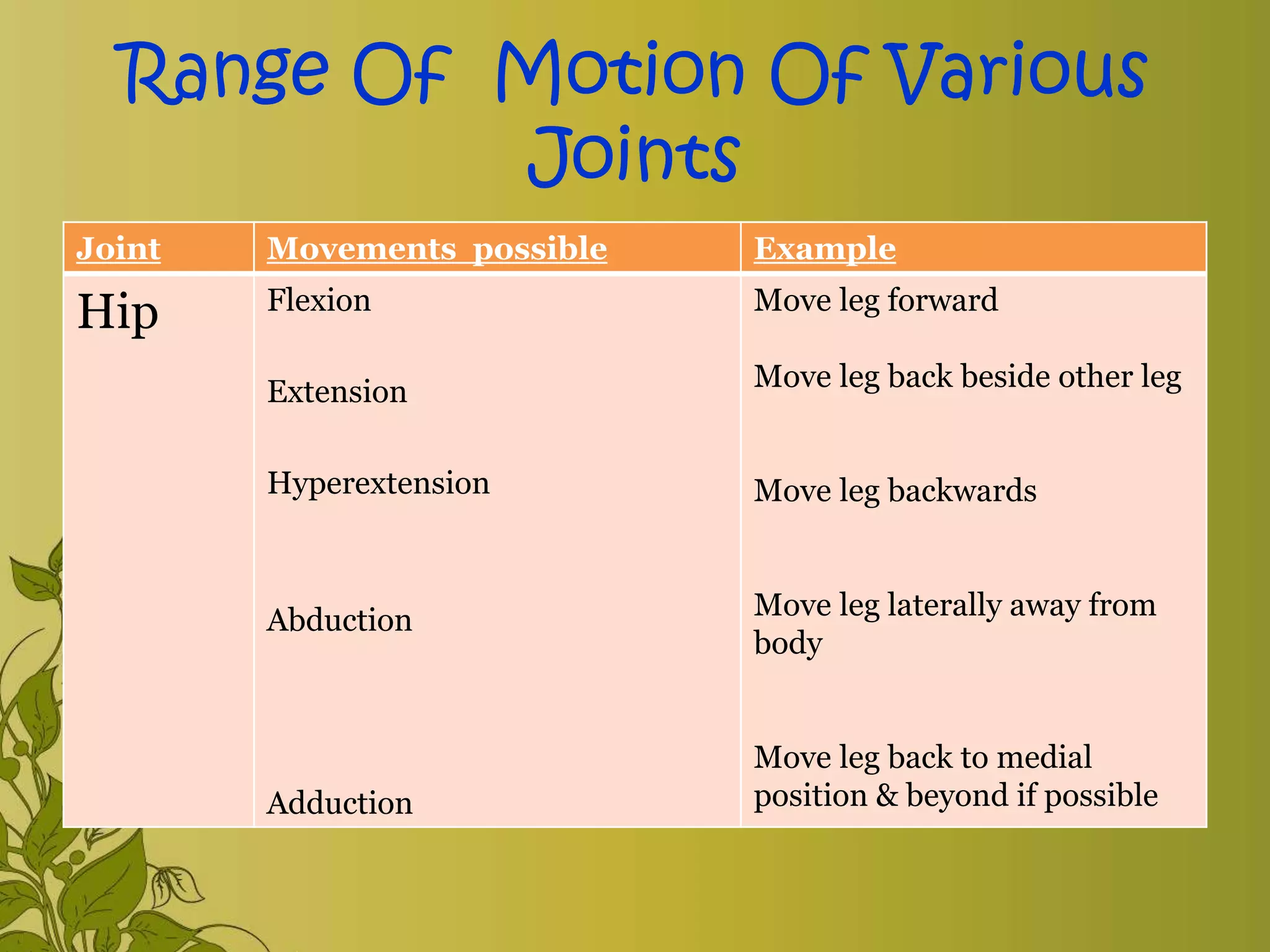
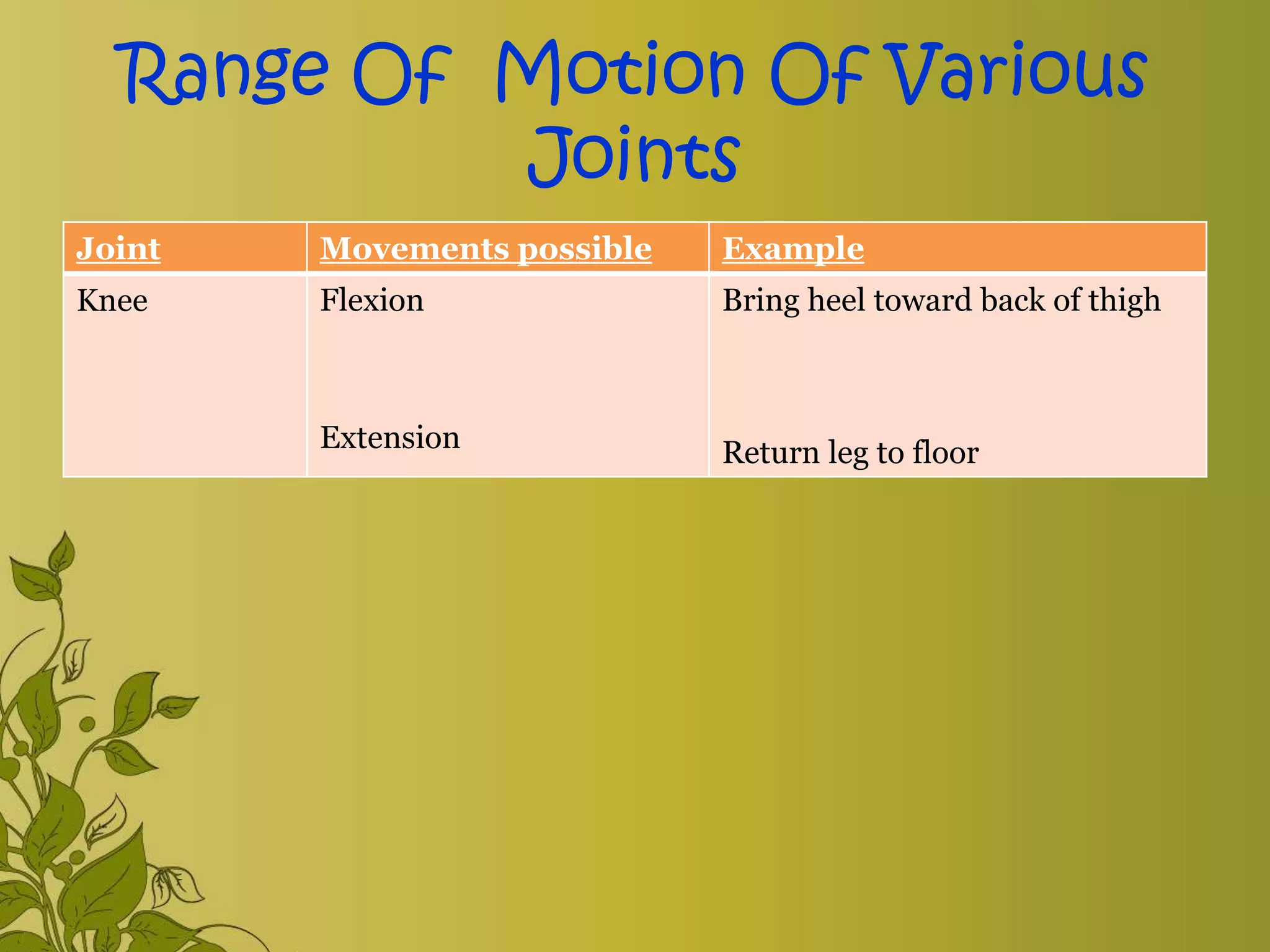
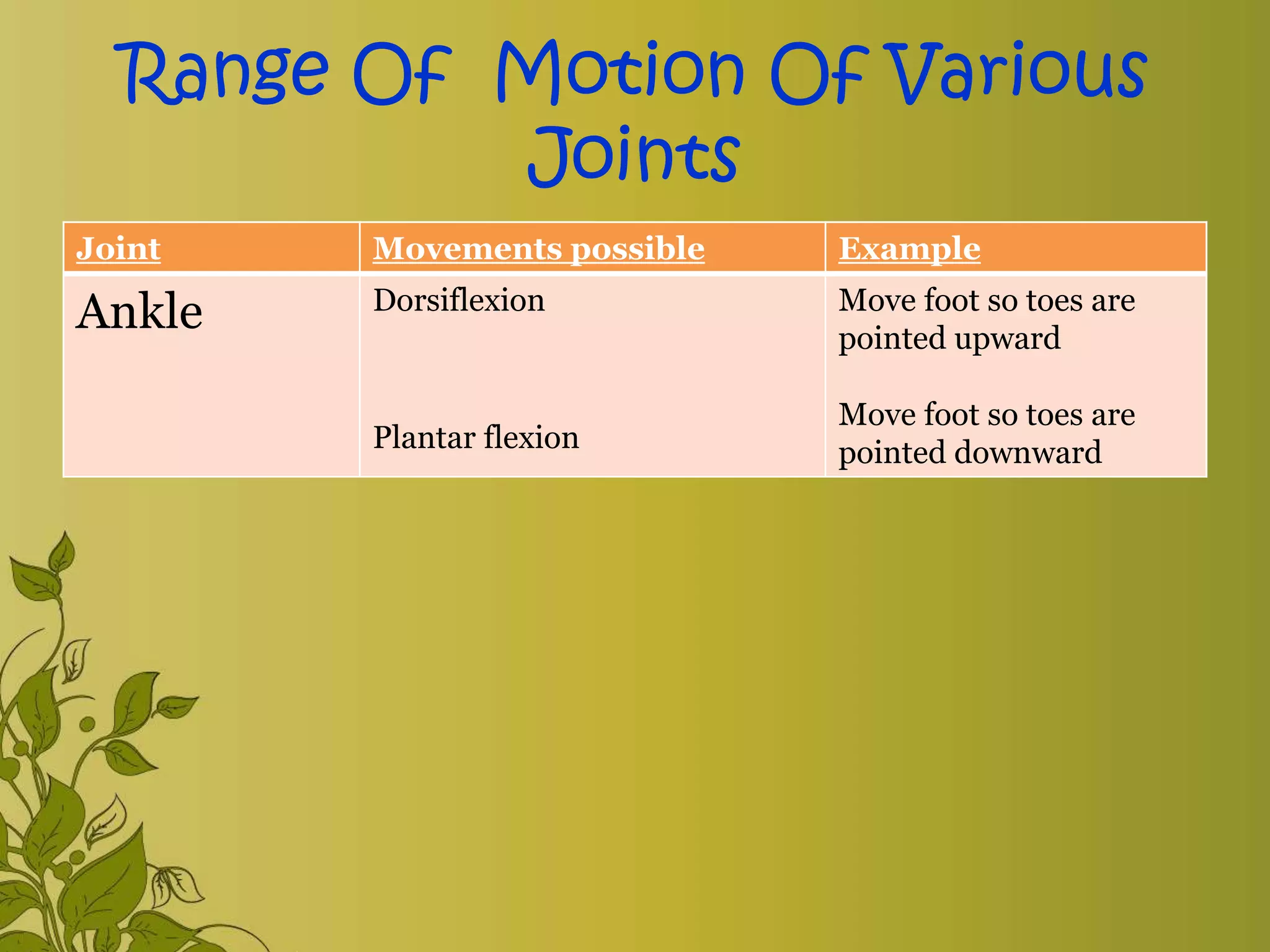
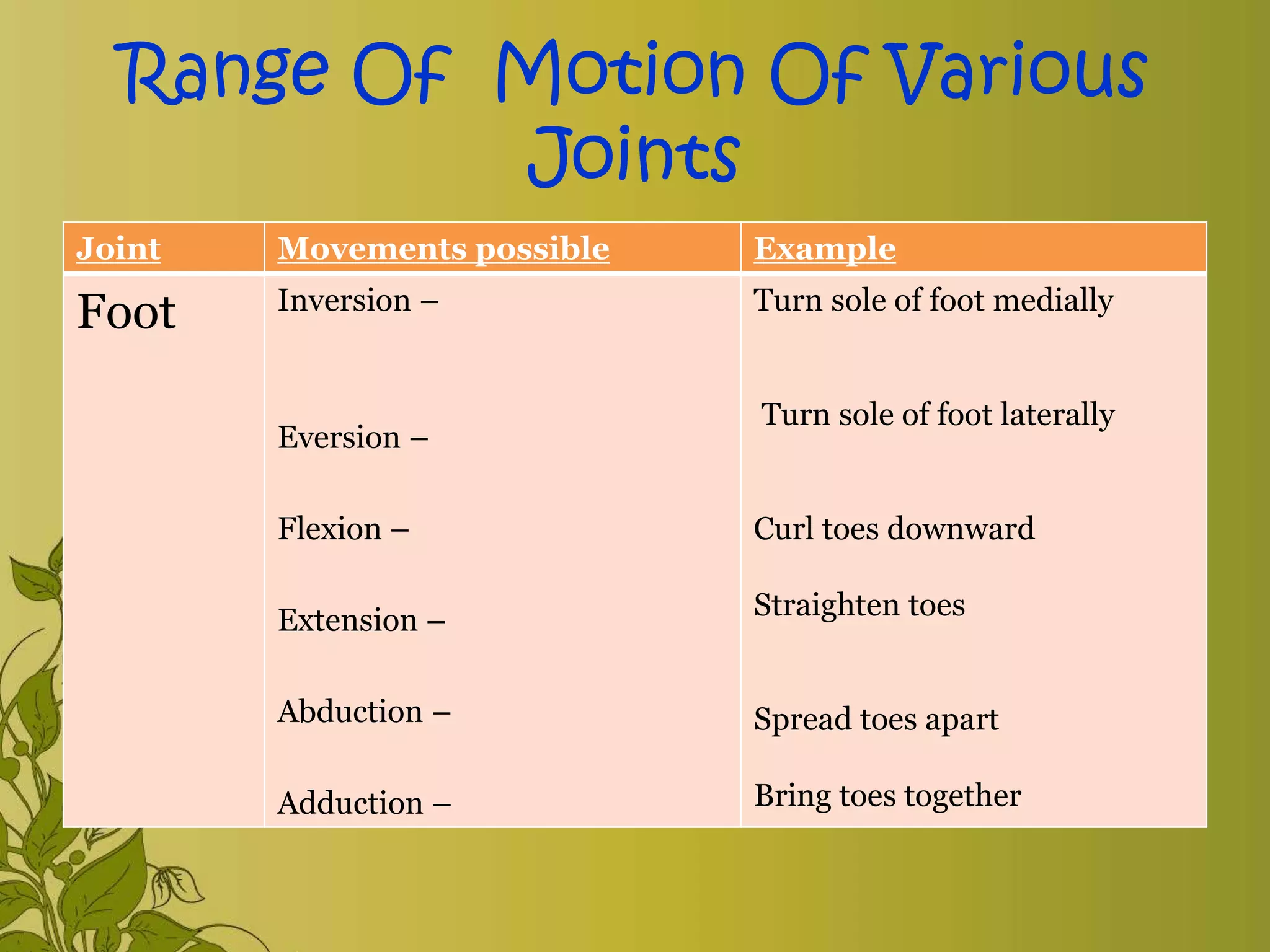
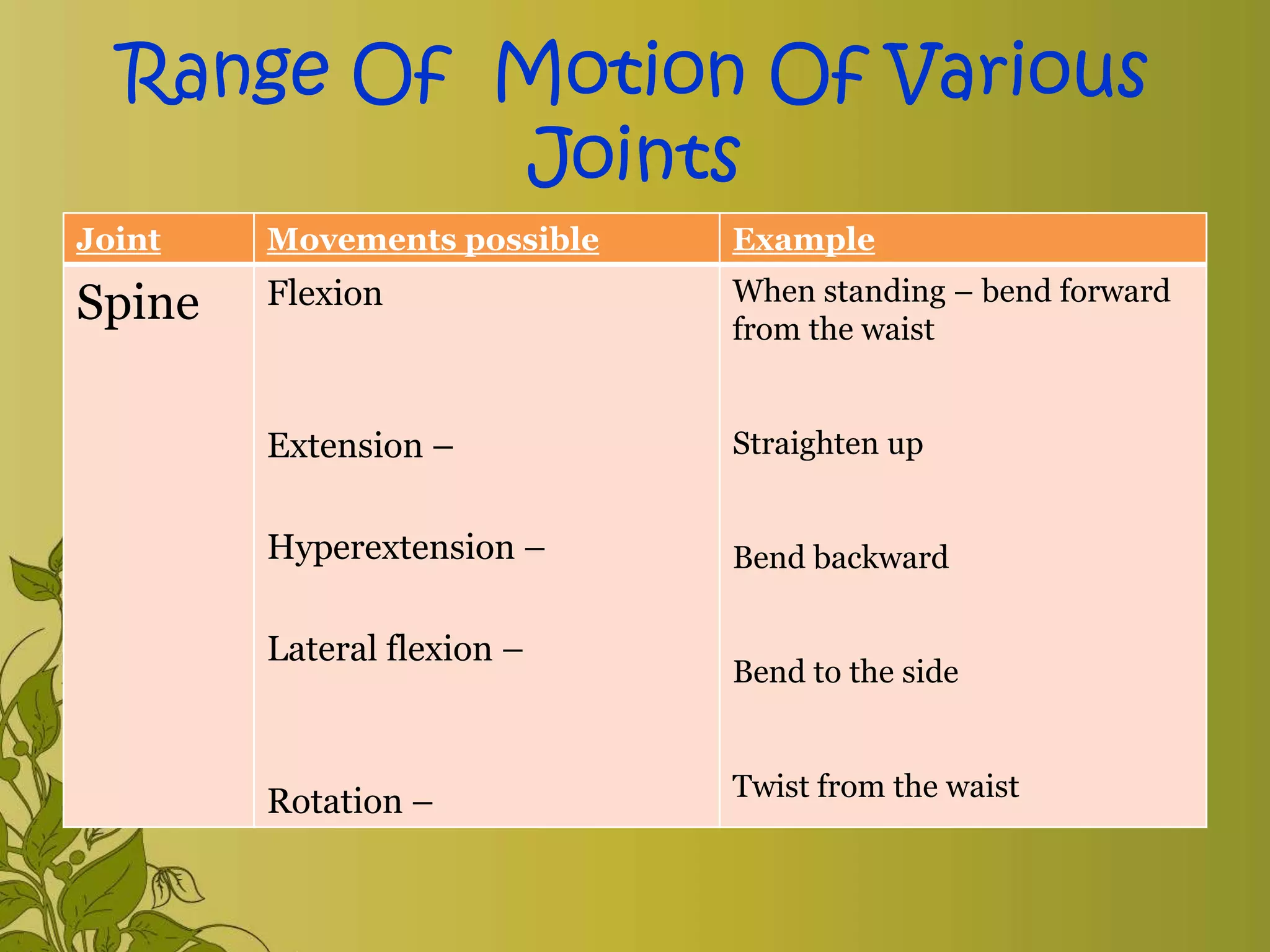
The document provides an overview of exercise, including its definition, benefits, classifications, and guidelines for range of motion (ROM) exercises. It details types of exercises such as isotonic, isometric, and isokinetic, and outlines the importance of ROM exercises for joint mobility and overall health. Additionally, it includes joint movements and recommended practices for performing exercises safely and effectively.