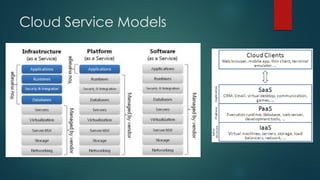
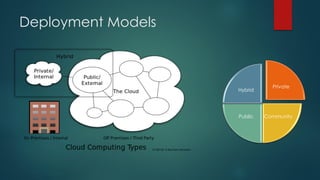
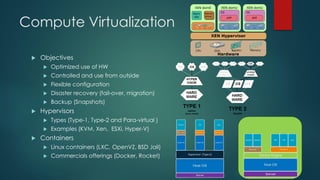
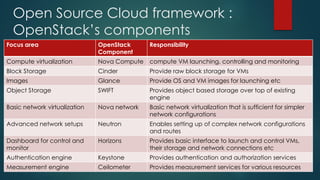
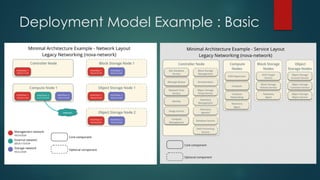
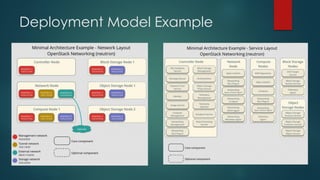
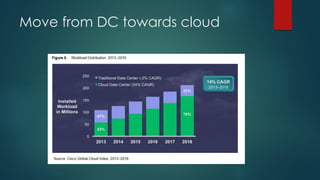
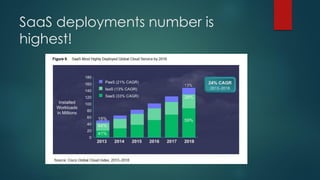
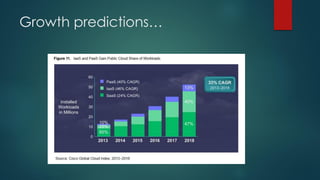
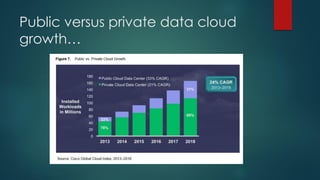
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its definition, essential characteristics, service and deployment models, enabling technologies, applications and use cases, architecture, and market growth. It defines cloud computing as on-demand network access to configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned with minimal management effort. Key technologies enabling clouds include compute and storage virtualization, distributed infrastructure, and frameworks like OpenStack. The cloud market is growing rapidly with public cloud services seeing the highest adoption rates and projections of continued strong growth in both public and private cloud deployments.