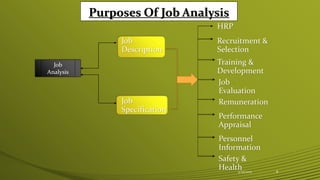
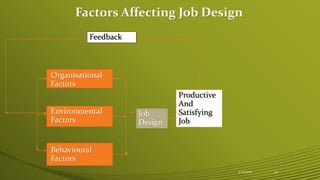
This document discusses job analysis and design. It defines job analysis as collecting information about the tasks, responsibilities and requirements of a specific job to create job descriptions and specifications. The key steps in job analysis are gathering job data through methods like observation and interviews, processing the information, and developing the job description and specification. Job design builds upon job analysis by organizing job tasks and requirements. Important factors that influence job design are organizational, environmental and behavioral elements. Common job design approaches include job rotation, enlargement and enrichment.