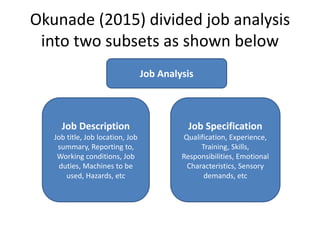
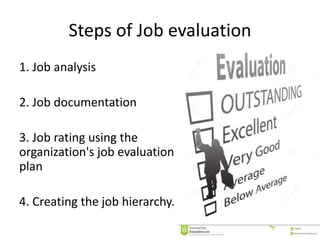
The document discusses job analysis, which involves systematically studying and documenting the tasks, responsibilities, skills, and working conditions of a specific job. It outlines the key components of job analysis including job description, job specification, and job evaluation. Methods for conducting job analysis such as observation, interviews, and questionnaires are also reviewed. The results of job analysis are used for various human resource functions like recruitment, performance management, and compensation.