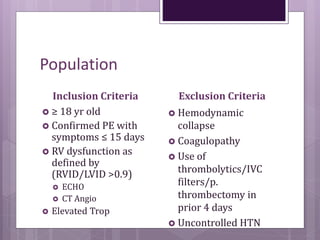
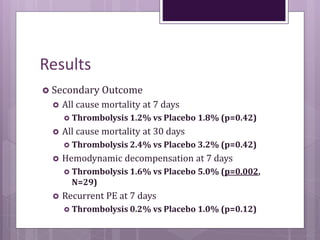
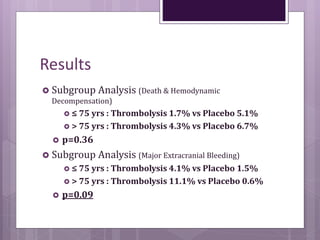
This randomized controlled trial compared tenecteplase to placebo in 1,005 patients with intermediate risk pulmonary embolism. Patients receiving tenecteplase had a lower combined rate of all-cause mortality or hemodynamic decompensation at 7 days compared to placebo (2.6% vs 5.6%), but they also experienced higher rates of major extracranial bleeding (6.3% vs 1.3%) and stroke (2.4% vs 0.2%). The study demonstrates that thrombolysis reduces early adverse outcomes in intermediate risk PE, but is associated with increased bleeding risks.