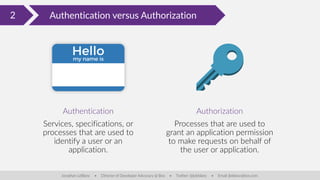
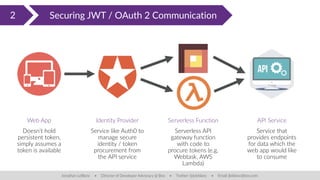
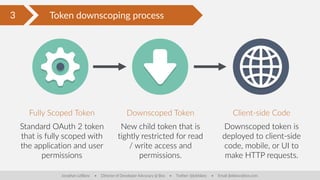
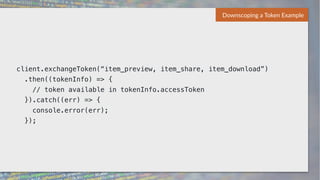
The document discusses client-side security issues in JavaScript applications, focusing on authentication, authorization, and token management. It covers the importance of treating front-end code as insecure, methods for handling cross-origin requests, and technologies like OAuth 2 and JWT for secure identity verification. The final part emphasizes improving token security through downscoping tokens to minimize exposure and adhere to the least privilege principle.