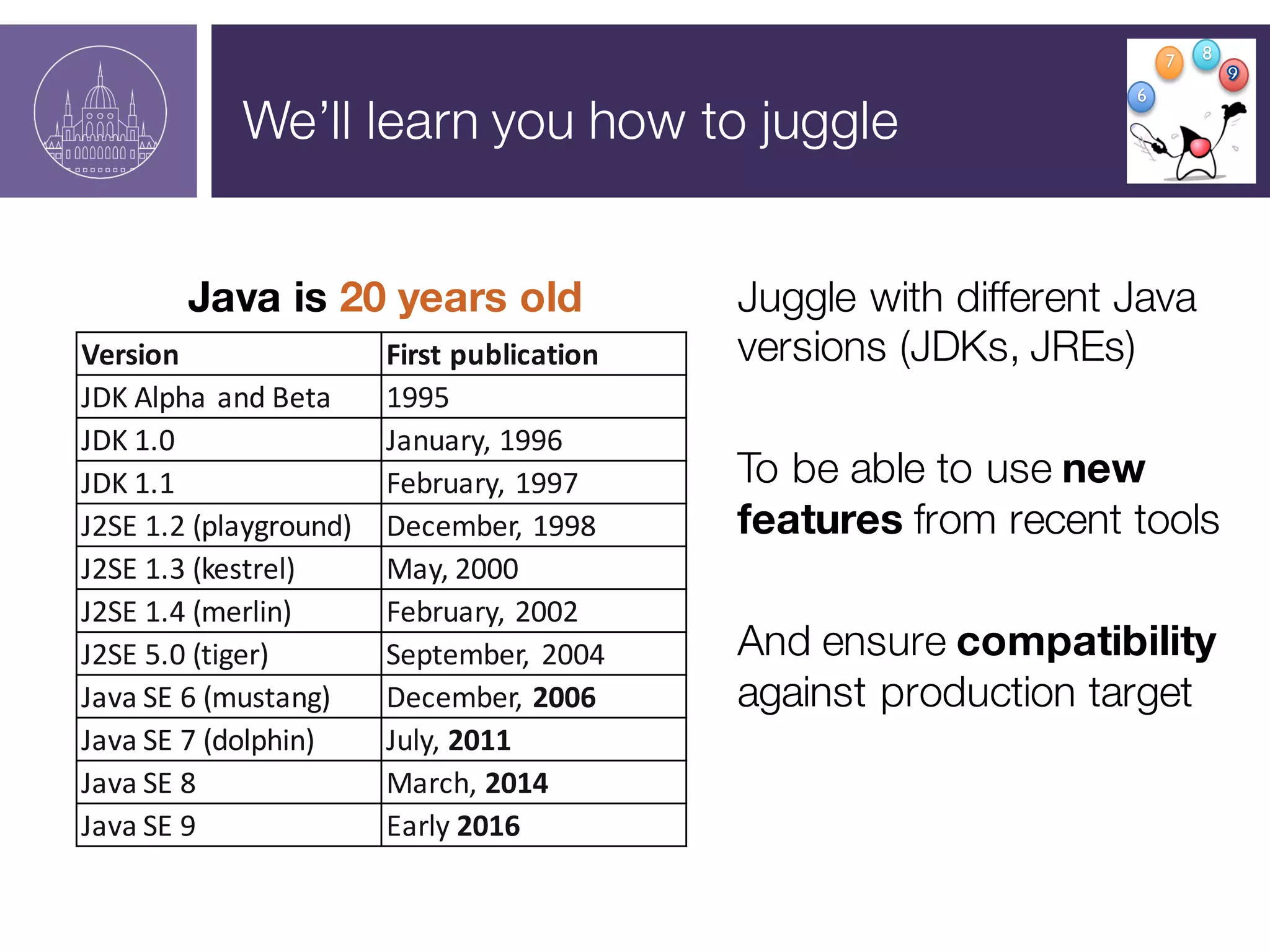
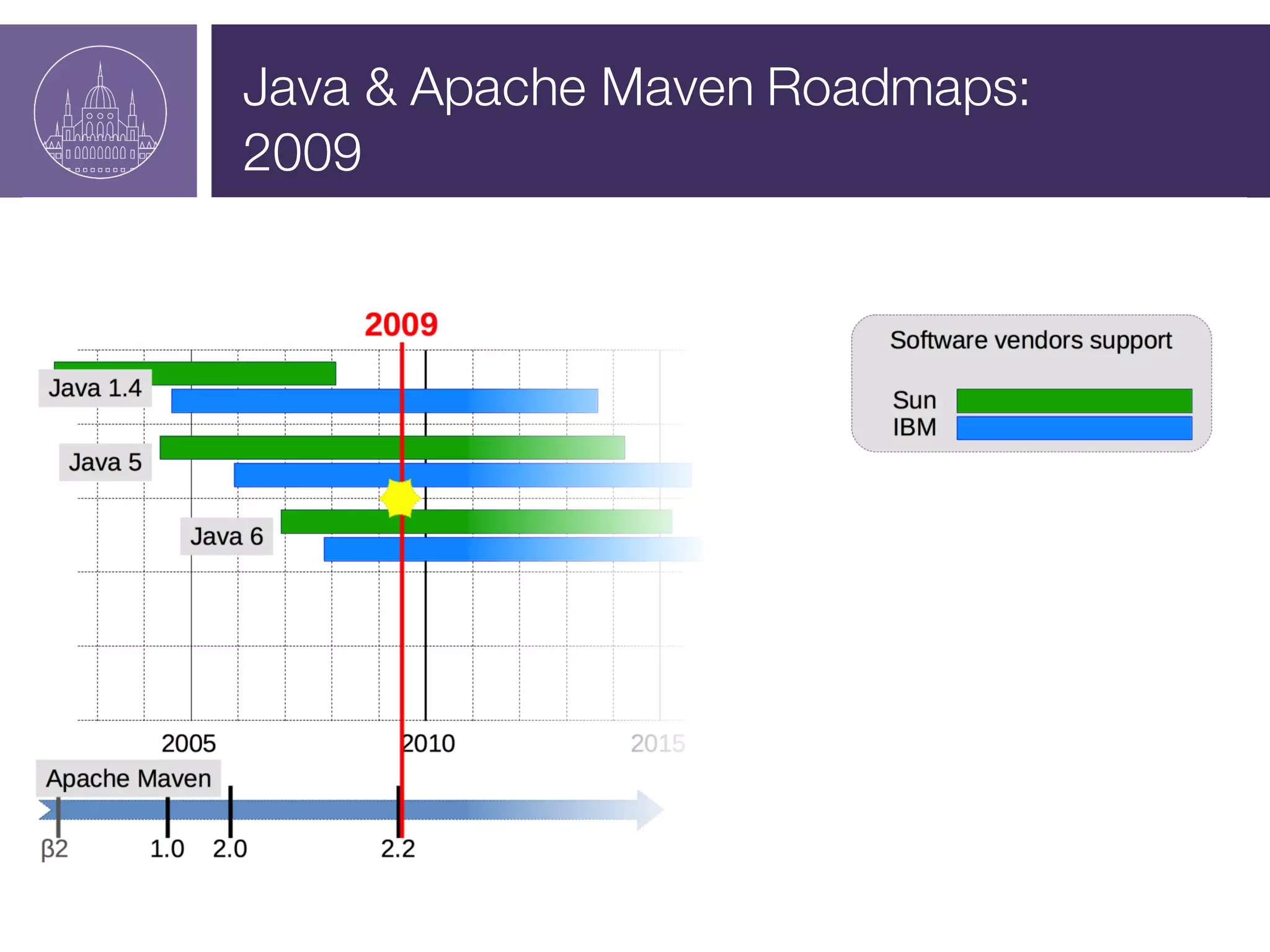
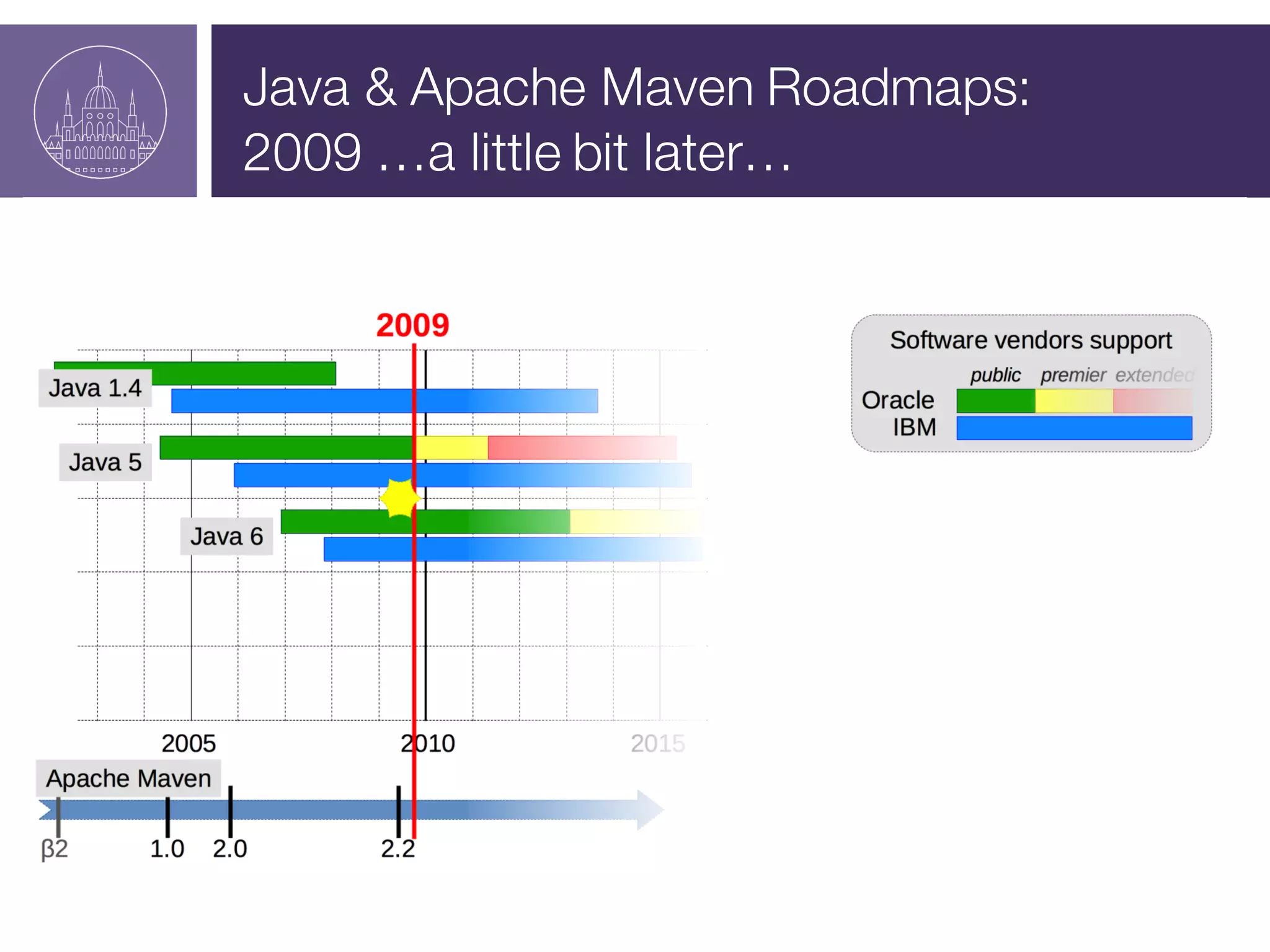
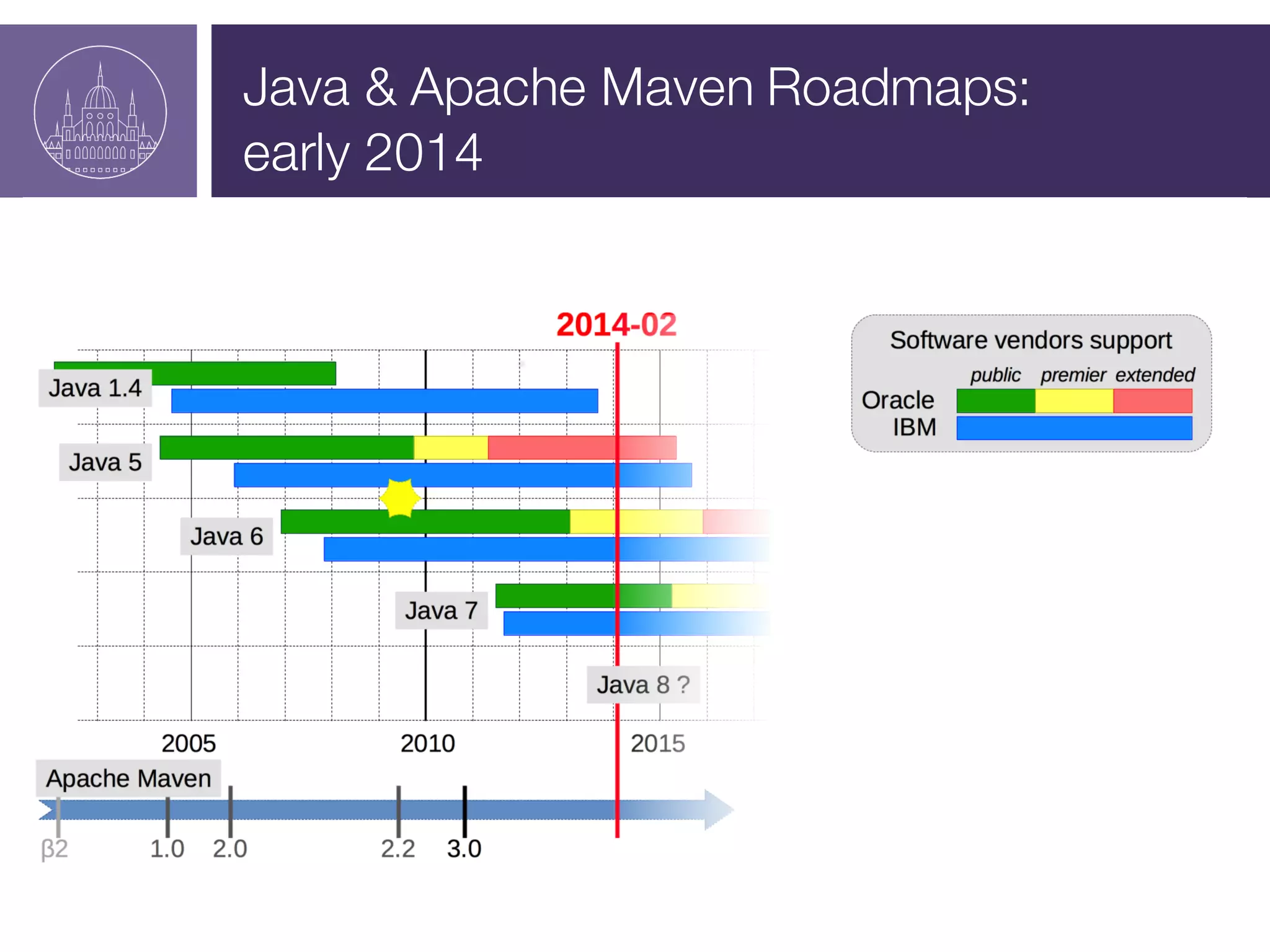
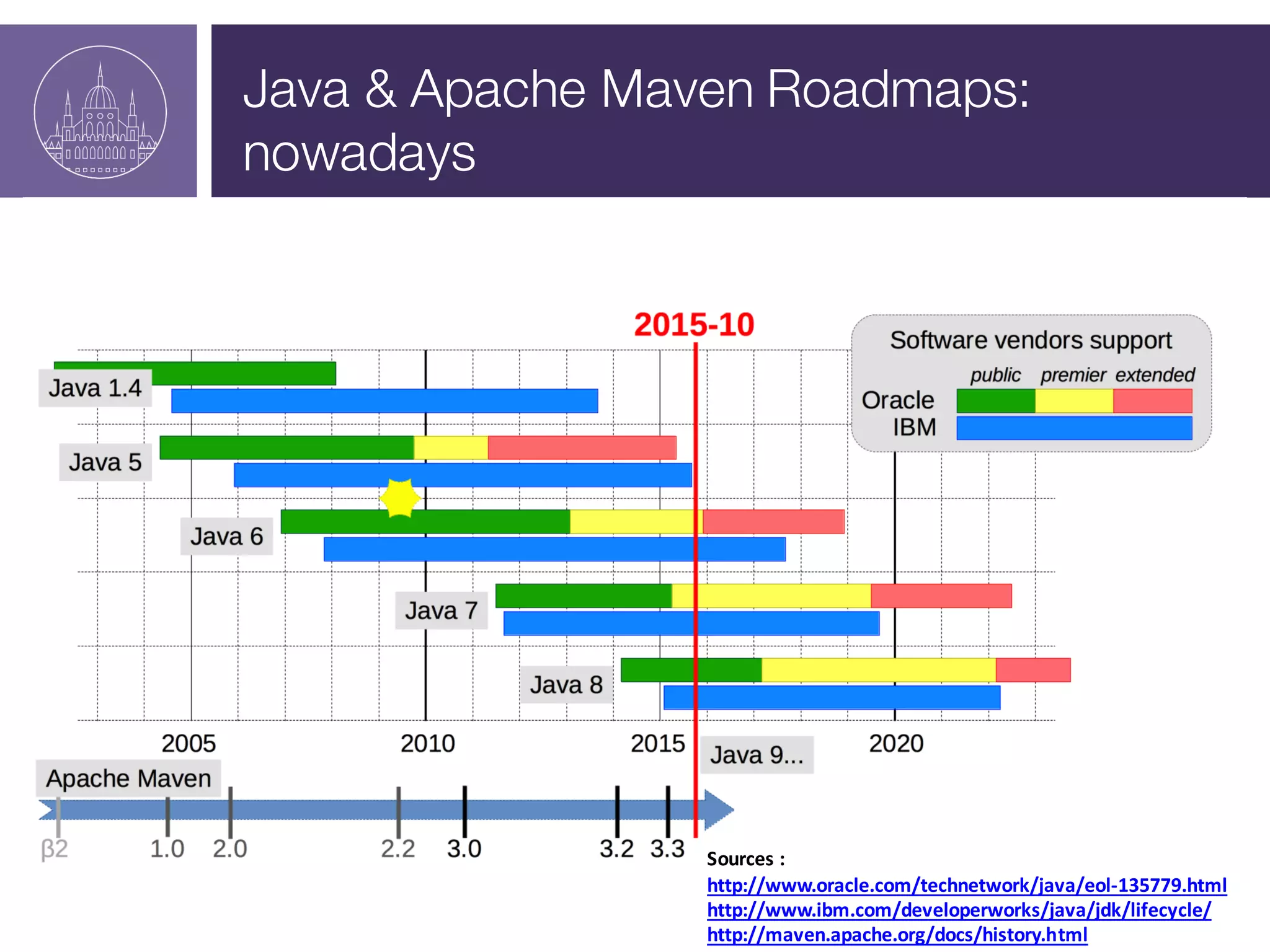
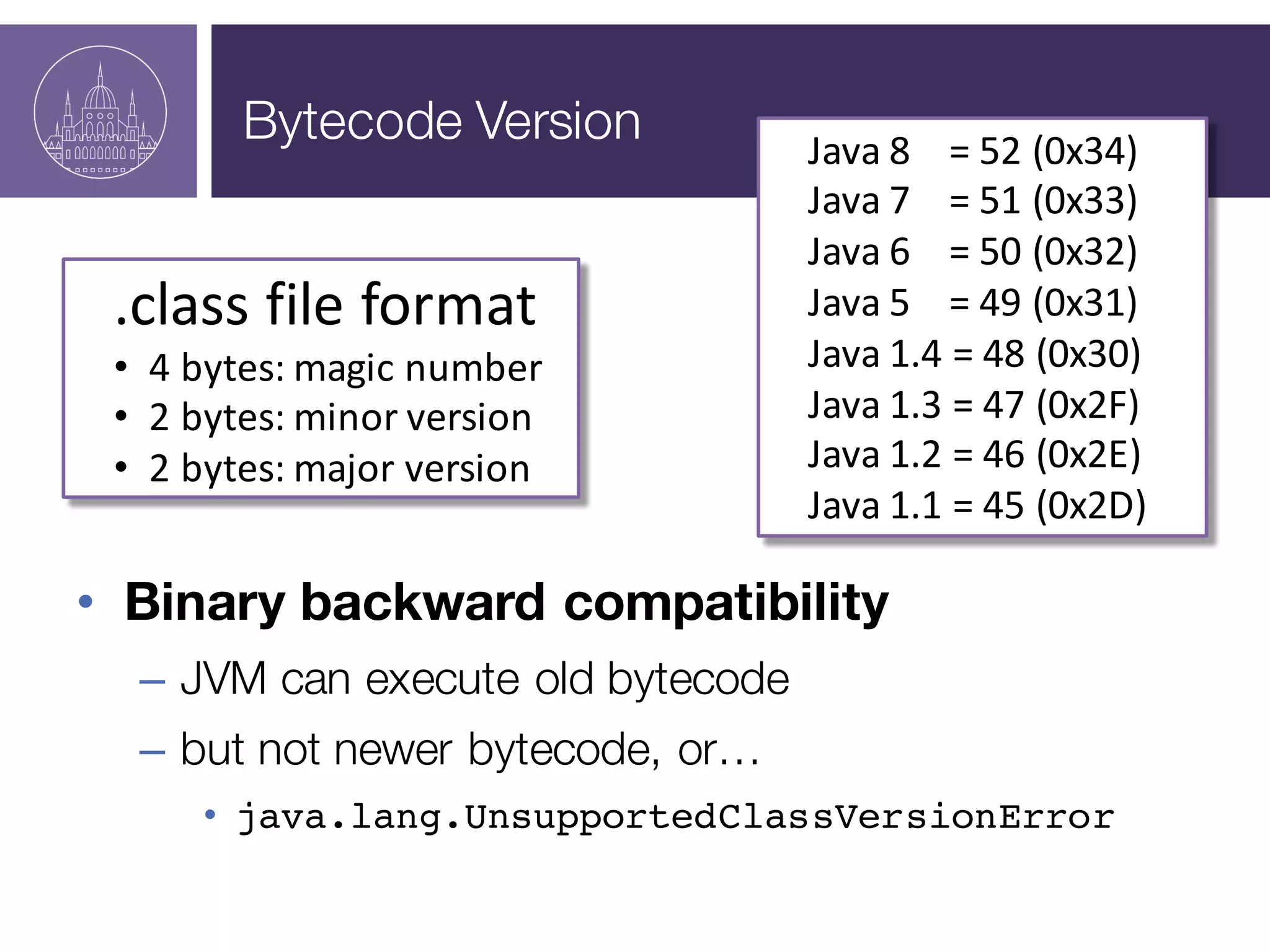
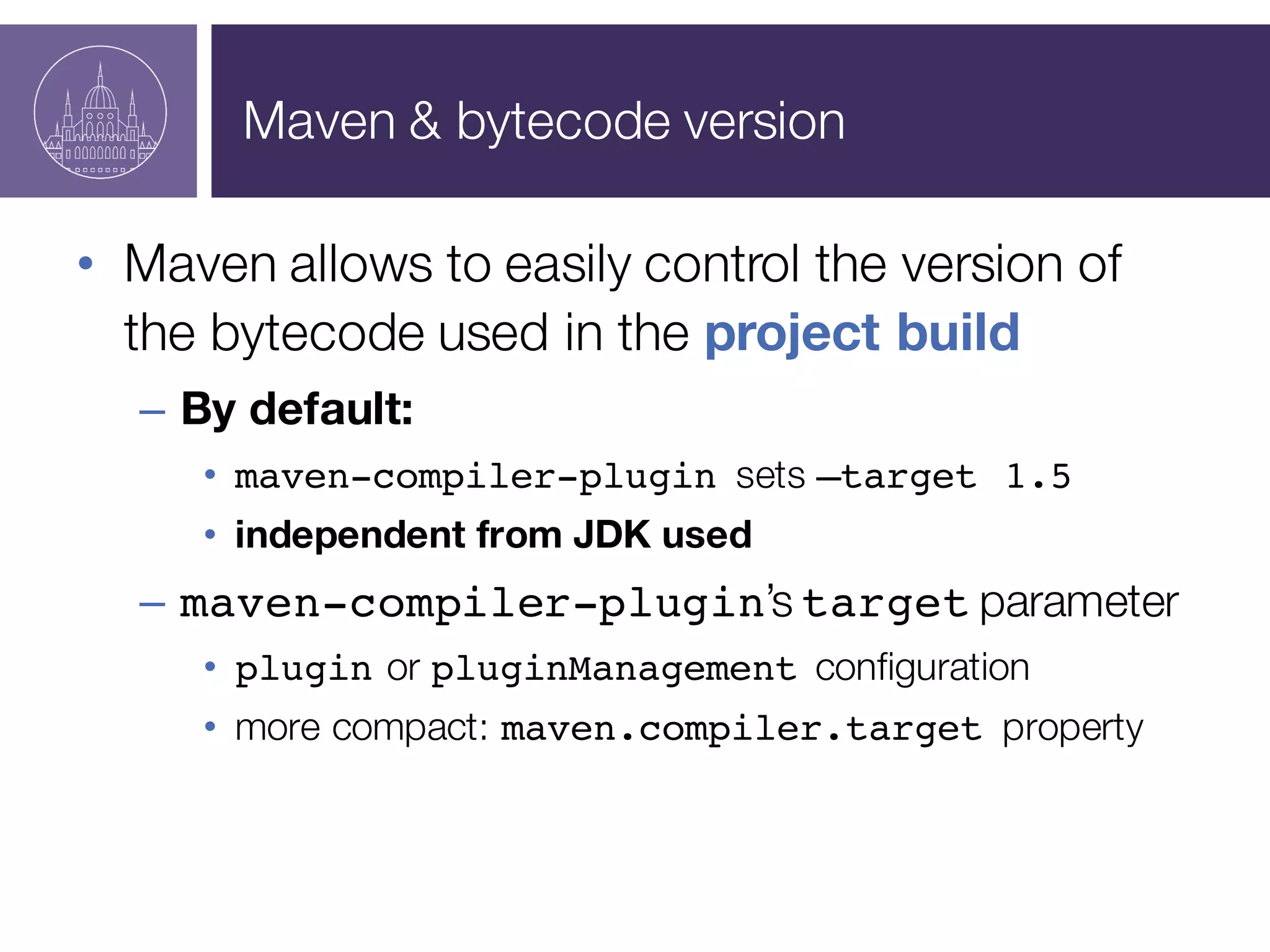
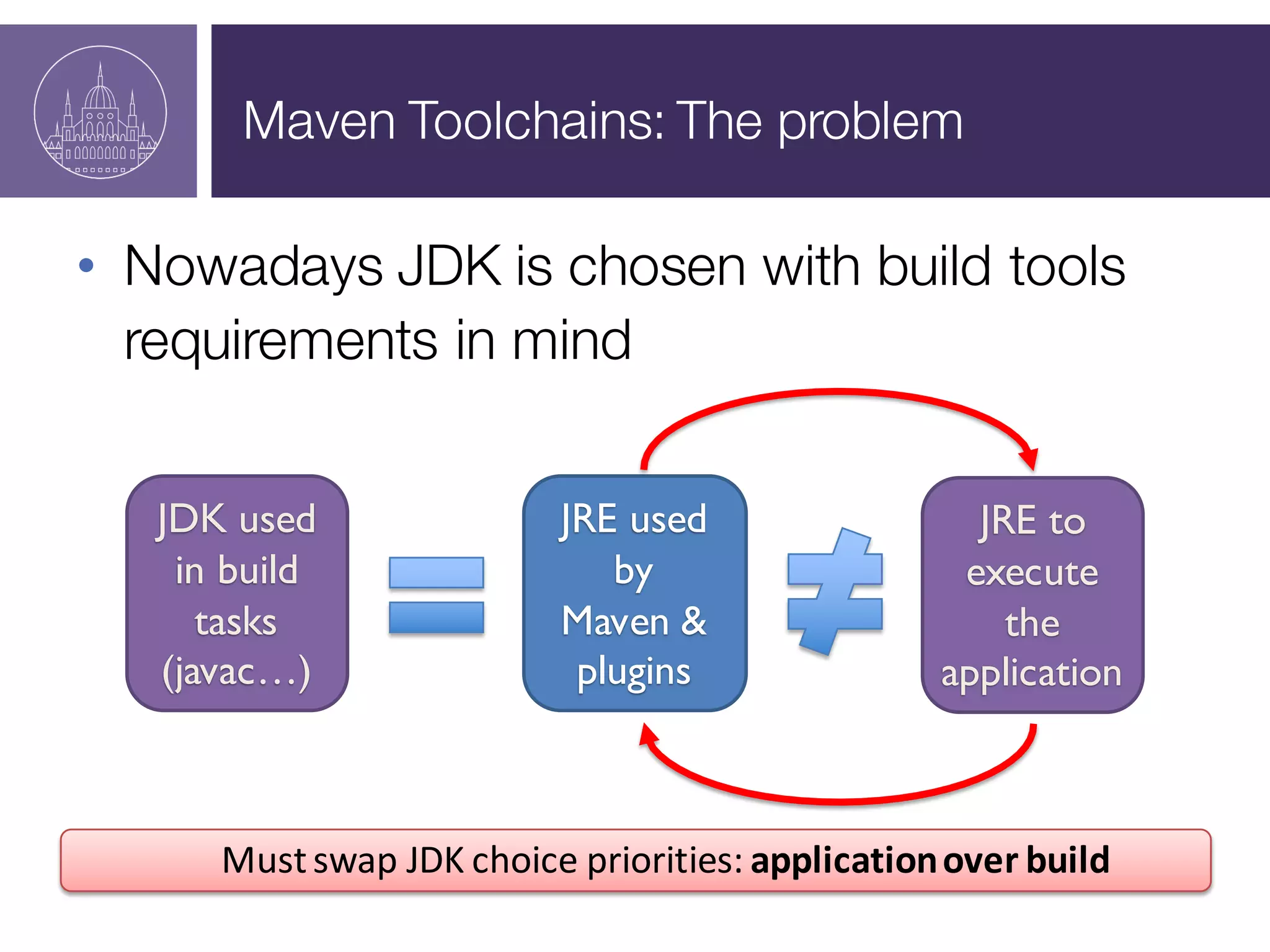
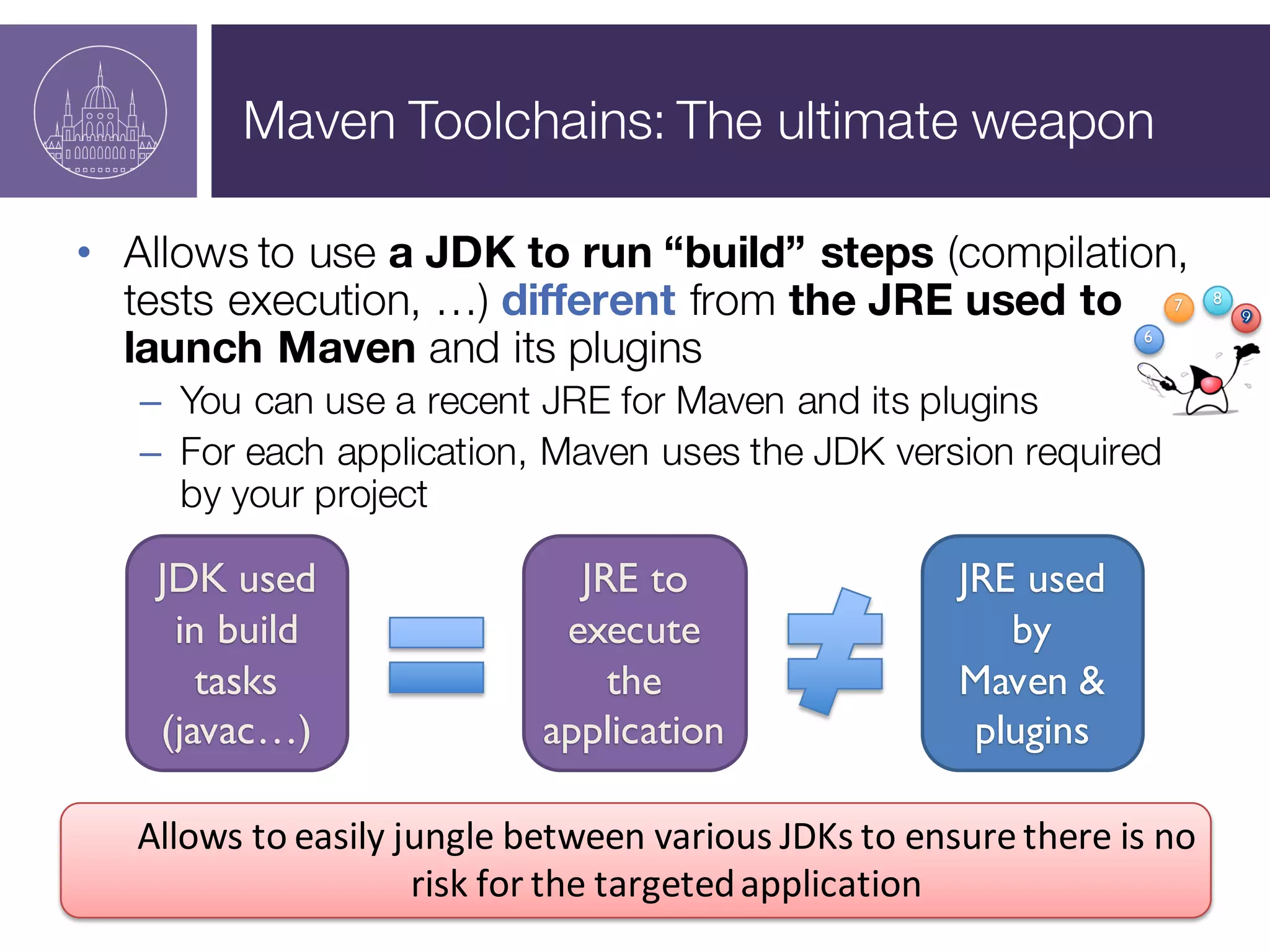
The document presents a session on managing Java evolutions using Apache Maven, highlighting its importance for developers facing compatibility challenges with various Java versions. It discusses toolchains as a solution for using different JDKs for building applications and the significance of bytecode version control. The session also emphasizes the role of tools like Animal Sniffer for ensuring compatibility with targeted JDK APIs.