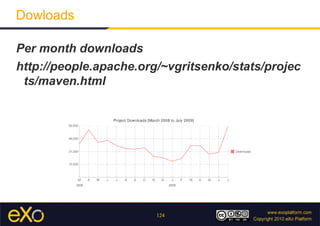
This document provides an overview of Apache Maven, including its history, key concepts, and ecosystem. Maven is a software project management tool that uses conventions for builds and dependencies. It manages a project's build process through a Project Object Model (POM) file and standardizes directory layout and build lifecycles. Maven allows for modular projects through a reactor and dependency management. Its ecosystem includes plugins, repository managers, and tools for testing, reporting and continuous integration.











![Conventions1 project = 1 artifact (pom, jar, war, ear, …)Standardized project descriptor (POM)build lifecycledirectories layout*.java to compile in src/[main|test]/java*.xml, *.properties needed in classpath and to bundle in archive in src/[main|test]/resourcestarget directory for generated stuffs (sources, classes, …)…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110303-exovn-apachemaven-110302213637-phpapp01/85/Apache-Maven-eXo-VN-office-presentation-12-320.jpg)














































































![Using Reactor Optionsarnaud@mbp-arnaud:~$ mvn install[INFO] ------------------------------------------------[INFO] Reactor Summary:[INFO][INFO] Project ....................... SUCCESS [2.132s][INFO] ModuleA ....................... SUCCESS [5.574s][INFO] ModuleB ....................... SUCCESS [0.455s][INFO] ModuleC ....................... SUCCESS [0.396s][INFO] ModuleD ....................... SUCCESS [0.462s][INFO] ModuleE ....................... SUCCESS [0.723s][INFO] ModuleF ....................... SUCCESS [0.404s]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110303-exovn-apachemaven-110302213637-phpapp01/85/Apache-Maven-eXo-VN-office-presentation-94-320.jpg)
![Builds everything from A to FUsing Reactor Optionsarnaud@mbp-arnaud:~$ mvn install –pl moduleE,moduleB[INFO] -------------------------------------------[INFO] Reactor Summary:[INFO][INFO] ModuleB .................. SUCCESS [2.774s][INFO] ModuleE .................. SUCCESS [1.008s]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110303-exovn-apachemaven-110302213637-phpapp01/85/Apache-Maven-eXo-VN-office-presentation-95-320.jpg)


![-pl --project-list: Build the specified reactor projects instead of all projectsUsing Reactor Optionsarnaud@mbp-arnaud:~$ mvn install –pl moduleD -am[INFO] ------------------------------------------[INFO] Reactor Summary:[INFO][INFO] ModuleA ................. SUCCESS [4.075s][INFO] ModuleB ................. SUCCESS [0.468s][INFO] ModuleC ................. SUCCESS [0.354s][INFO] ModuleD ................. SUCCESS [0.384s]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110303-exovn-apachemaven-110302213637-phpapp01/85/Apache-Maven-eXo-VN-office-presentation-98-320.jpg)


![Usecase : Build all modules required for a war, ear, …Using Reactor Optionsarnaud@mbp-arnaud:~$ mvn install –pl moduleD -amd[INFO] ------------------------------------------[INFO] Reactor Summary:[INFO][INFO] ModuleD ................. SUCCESS [4.881s][INFO] ModuleE ................. SUCCESS [0.478s][INFO] ModuleF ................. SUCCESS [0.427s]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110303-exovn-apachemaven-110302213637-phpapp01/85/Apache-Maven-eXo-VN-office-presentation-101-320.jpg)


![Usecase : Check that a change in a module didn’t break others which are using itUsing Reactor Optionsarnaud@mbp-arnaud:~$ mvn install –rf moduleD[INFO] ------------------------------------------[INFO] Reactor Summary:[INFO][INFO] ModuleD ................. SUCCESS [9.707s][INFO] ModuleE ................. SUCCESS [0.625s][INFO] ModuleF ................. SUCCESS [0.679s] [INFO] Project ................. SUCCESS [2.467s]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20110303-exovn-apachemaven-110302213637-phpapp01/85/Apache-Maven-eXo-VN-office-presentation-104-320.jpg)