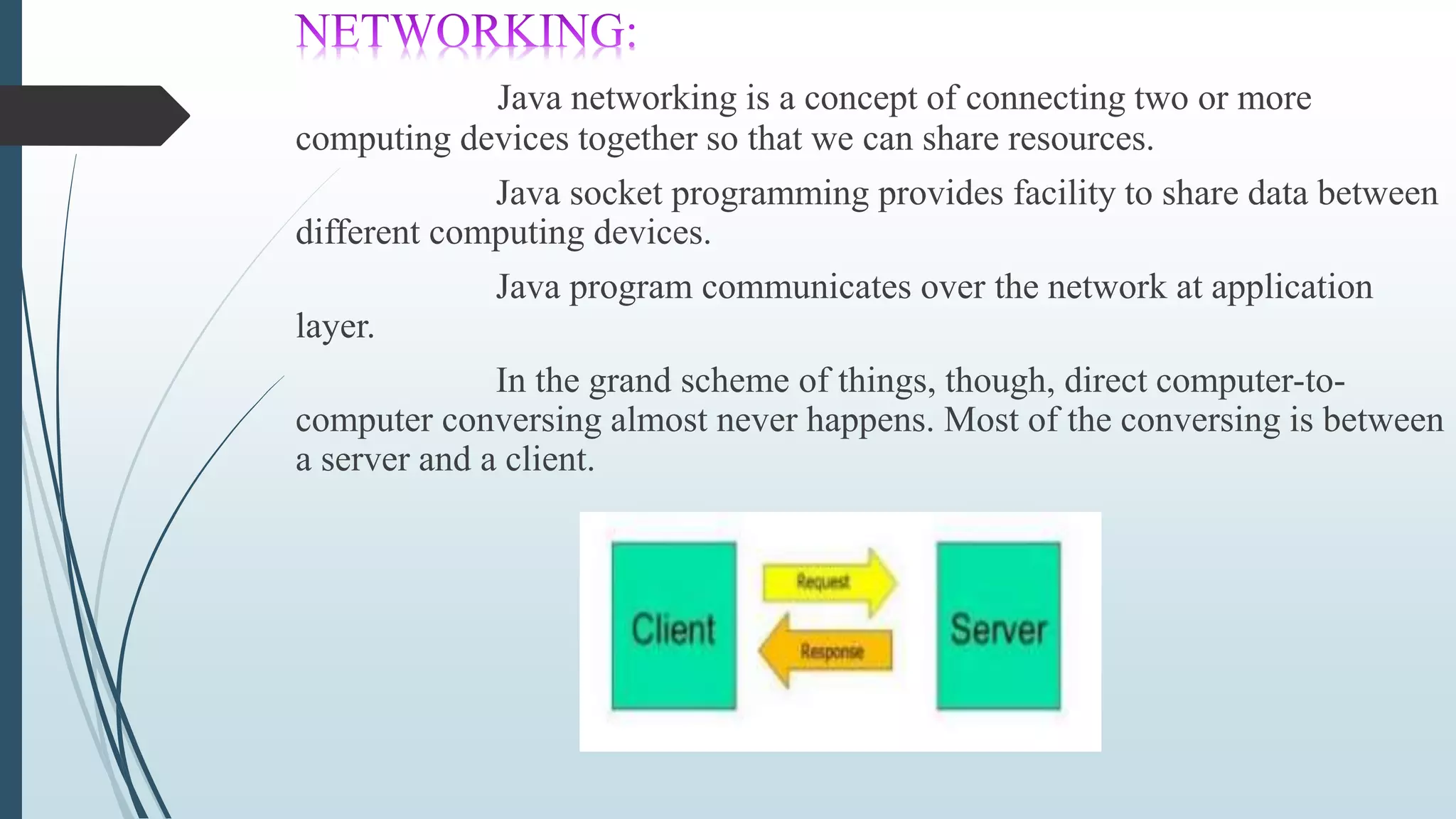
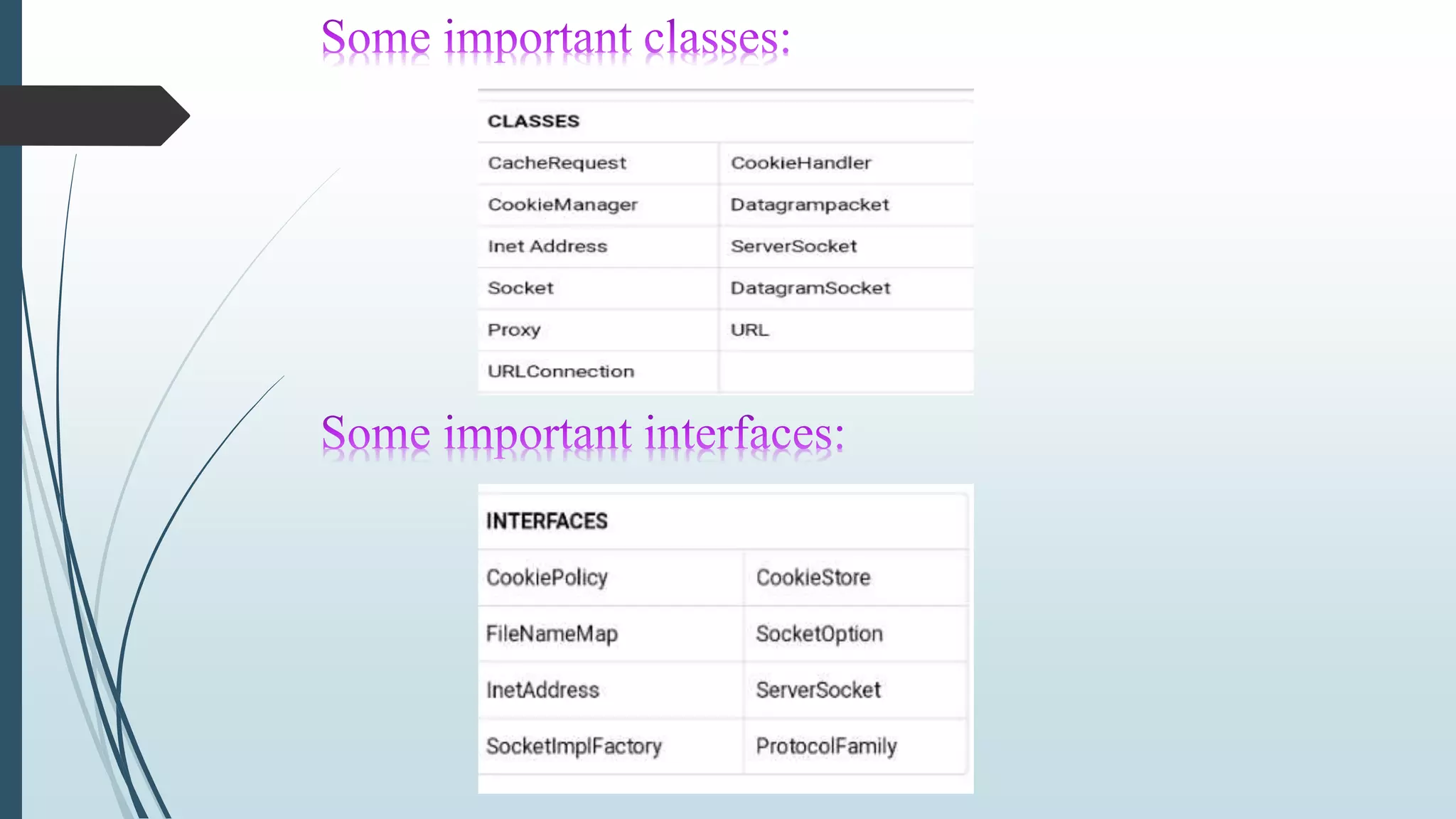
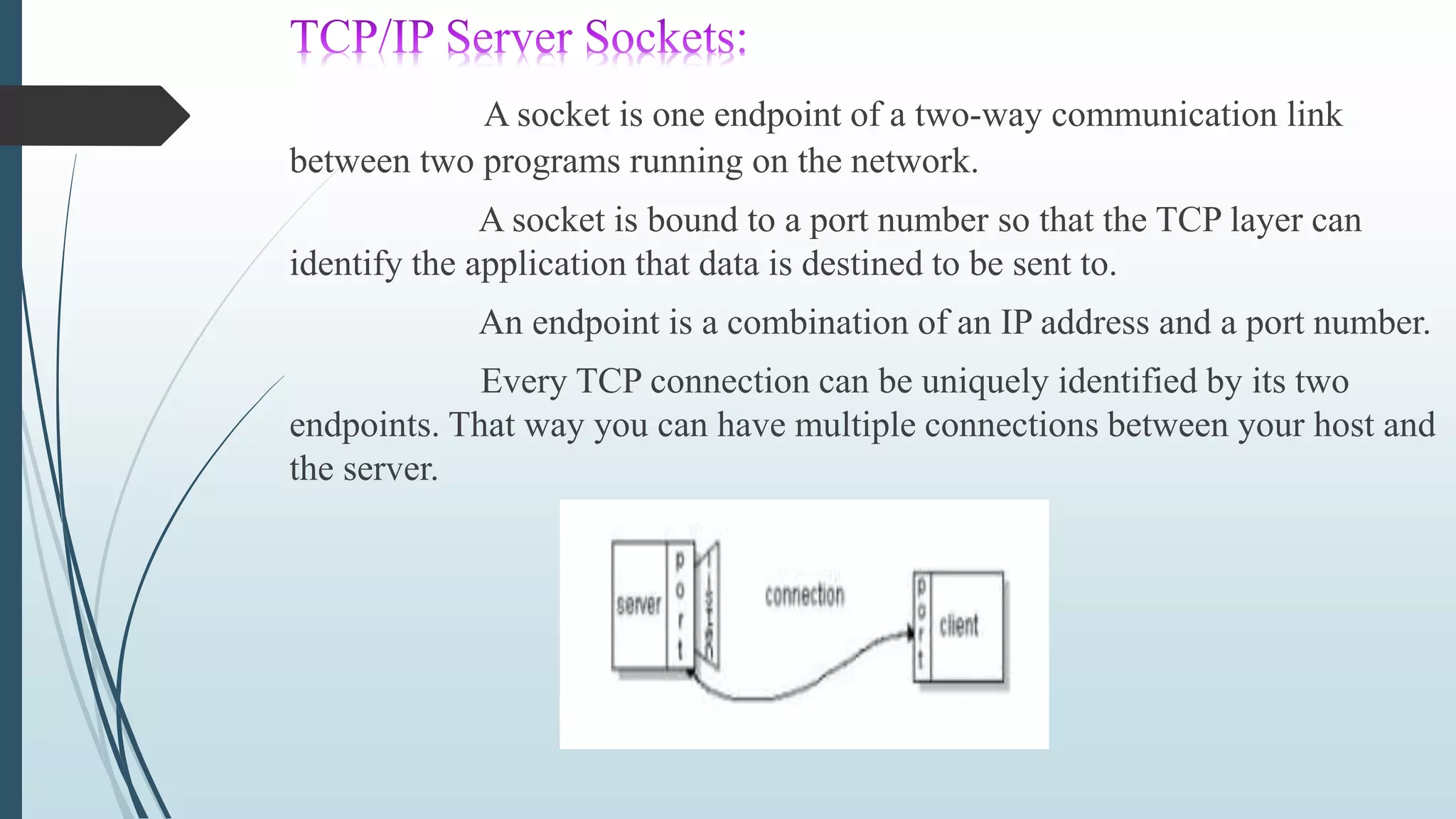
This document discusses networking in Java. It covers networking classes and interfaces in Java's java.net package that provide system-independent network communication functionality. It describes how Java supports both TCP and UDP protocols for reliable stream-based and simpler datagram-oriented communication across networks. It also discusses key classes like InetAddress for representing IP addresses, sockets for identifying communication endpoints, and datagrams for connectionless transfer of data packets over UDP.


![The InetAddress is used to encapsulate both the numerical IP
address and the domain name for that address.
InetAddress class has no visible constructor.To create an Inet
Address object, you have to use Factory methods.
Three commonly used Inet Address factory methods are:
1.static InetAddress getLocalHost() throws
UnknownHostException.
2.static InetAddress getByName(String hostname) throws
UnknownHostException.
3.static InetAddress [] getAllByName(String hostname) throws
UnknownHostException.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-181002151229/75/Java-6-2048.jpg)


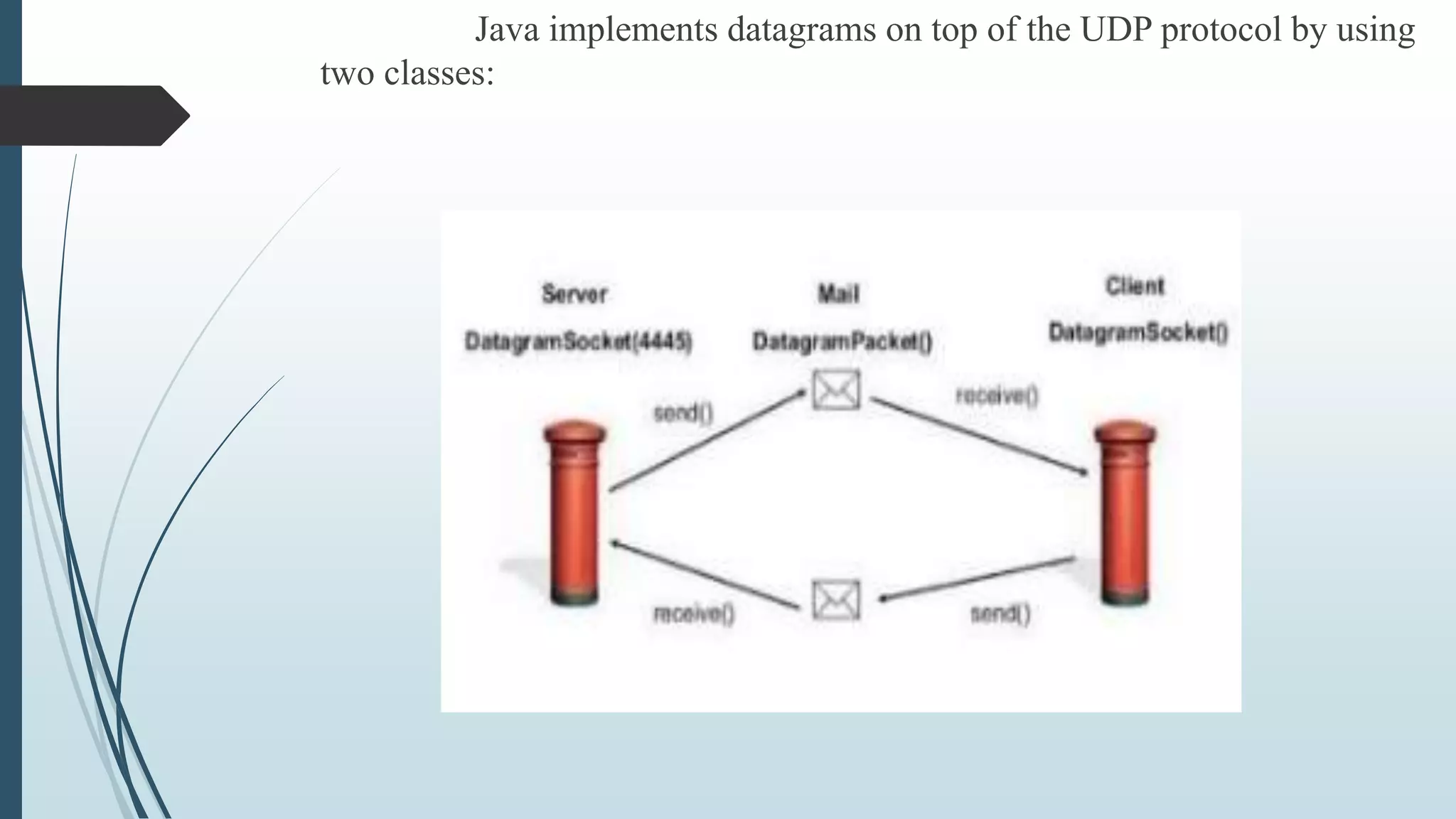

![Java DatagramPacket is a message that can be send or
received.If you send multiple packet,it may arrive in any
order.Additionally,packetdelivery is not guaranteed.
DatagramPacket(byte[] barr, int length):it creates a datagram
packet.This constructor is used to receive the packets.
DatagramPacket(byte[] barr,int length,InetAddress address,int
port):it creates a datagram packet.This constructor is used to send the
packets.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-181002151229/75/Java-13-2048.jpg)
