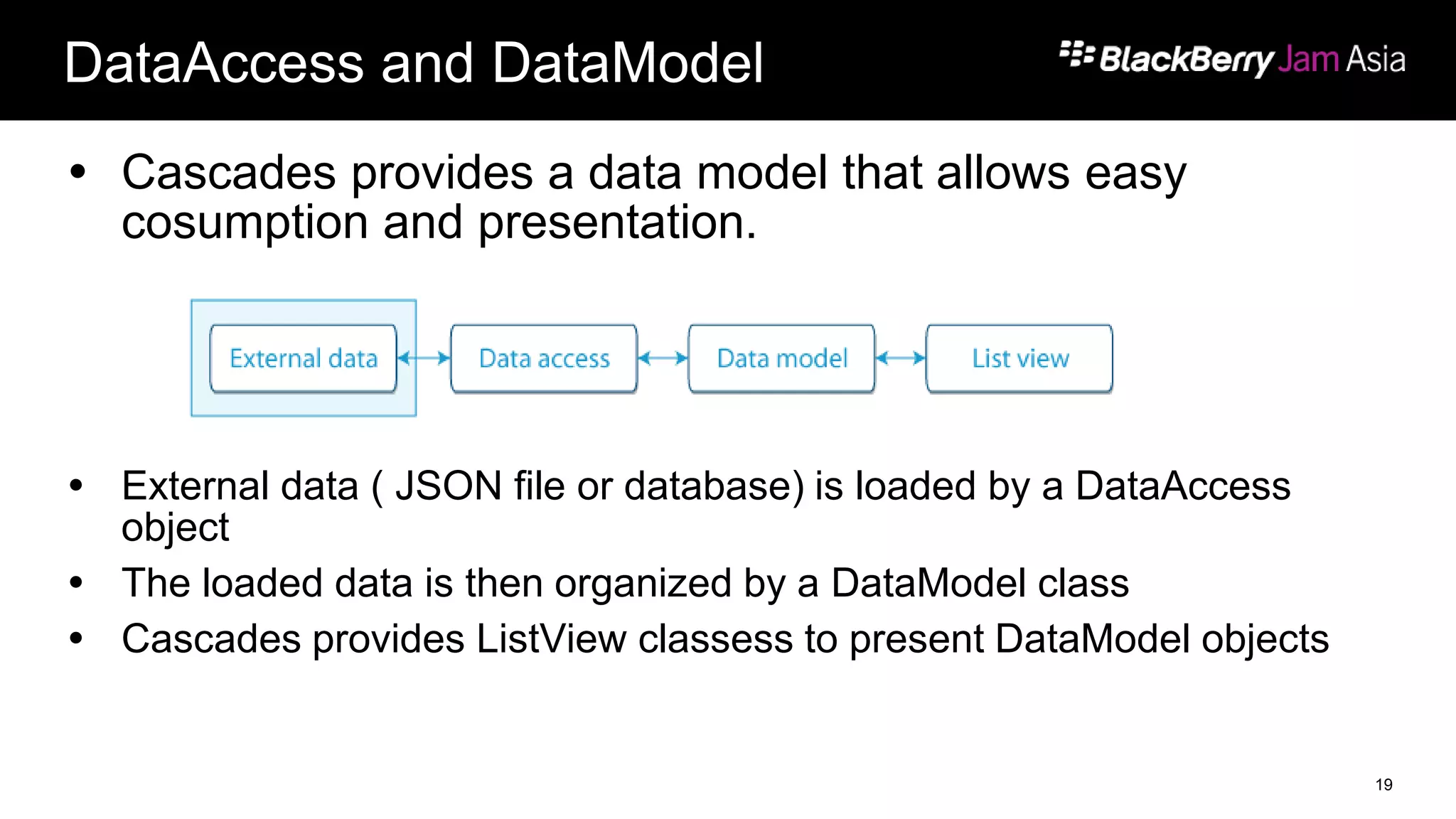
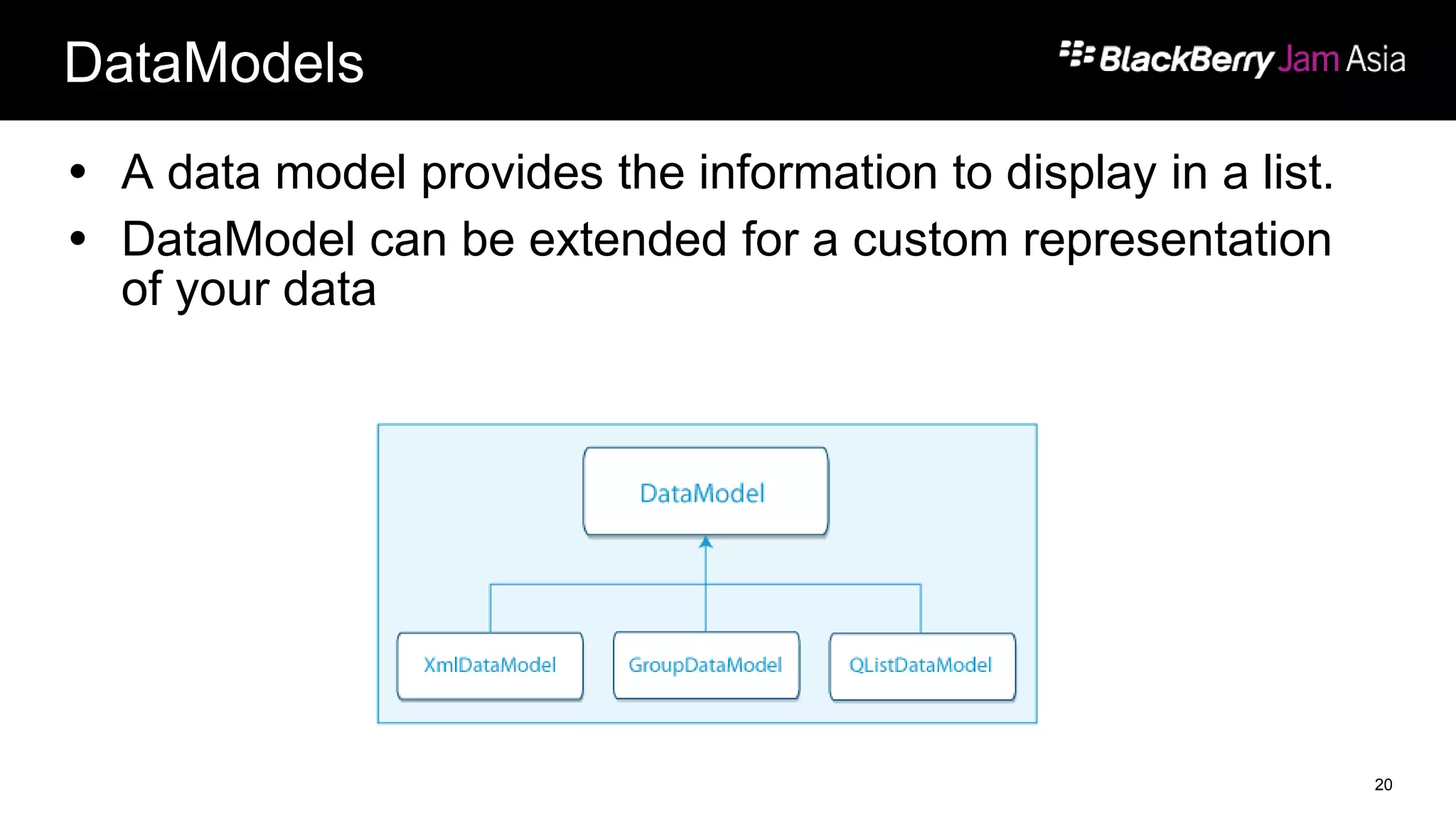
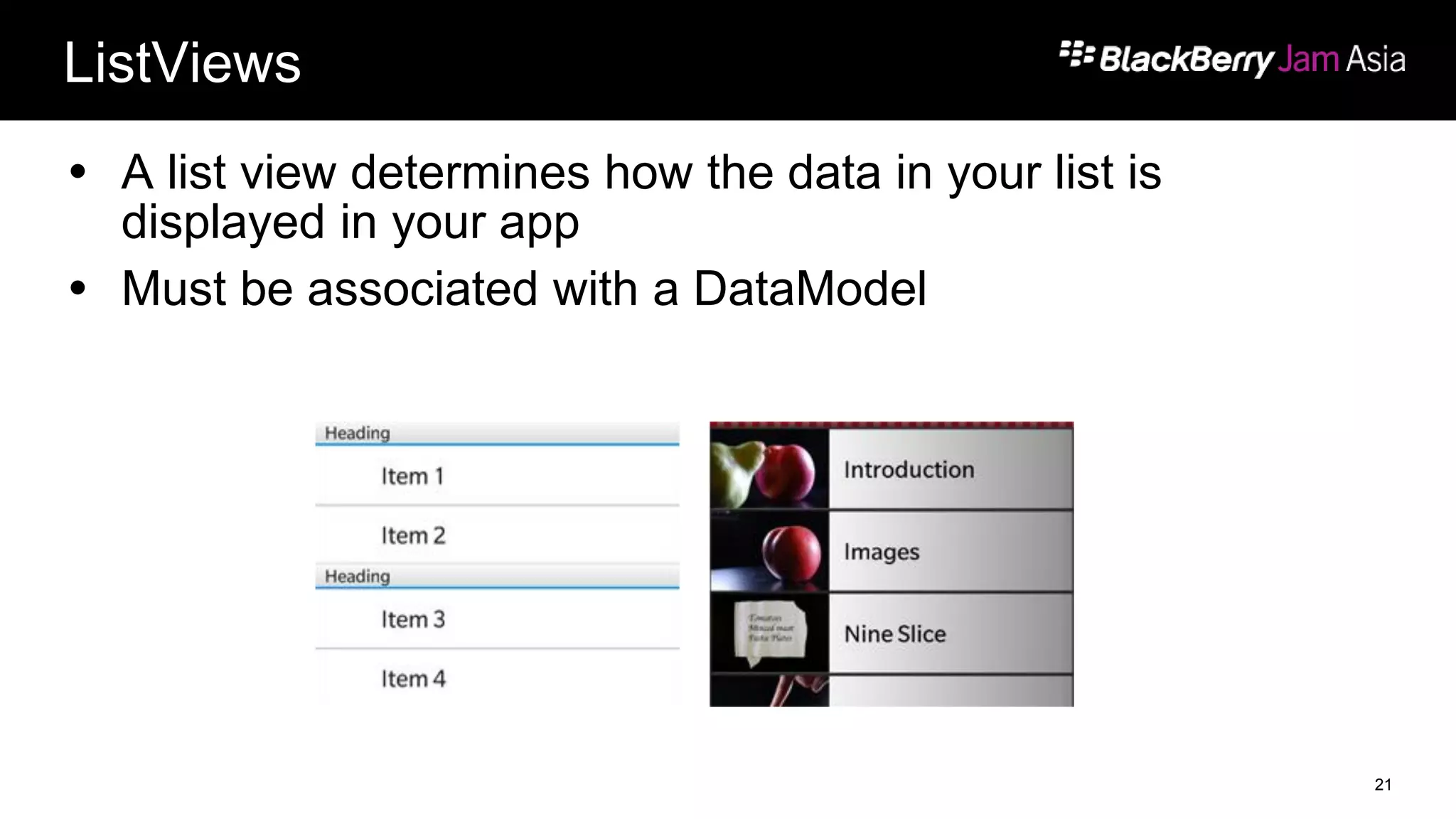
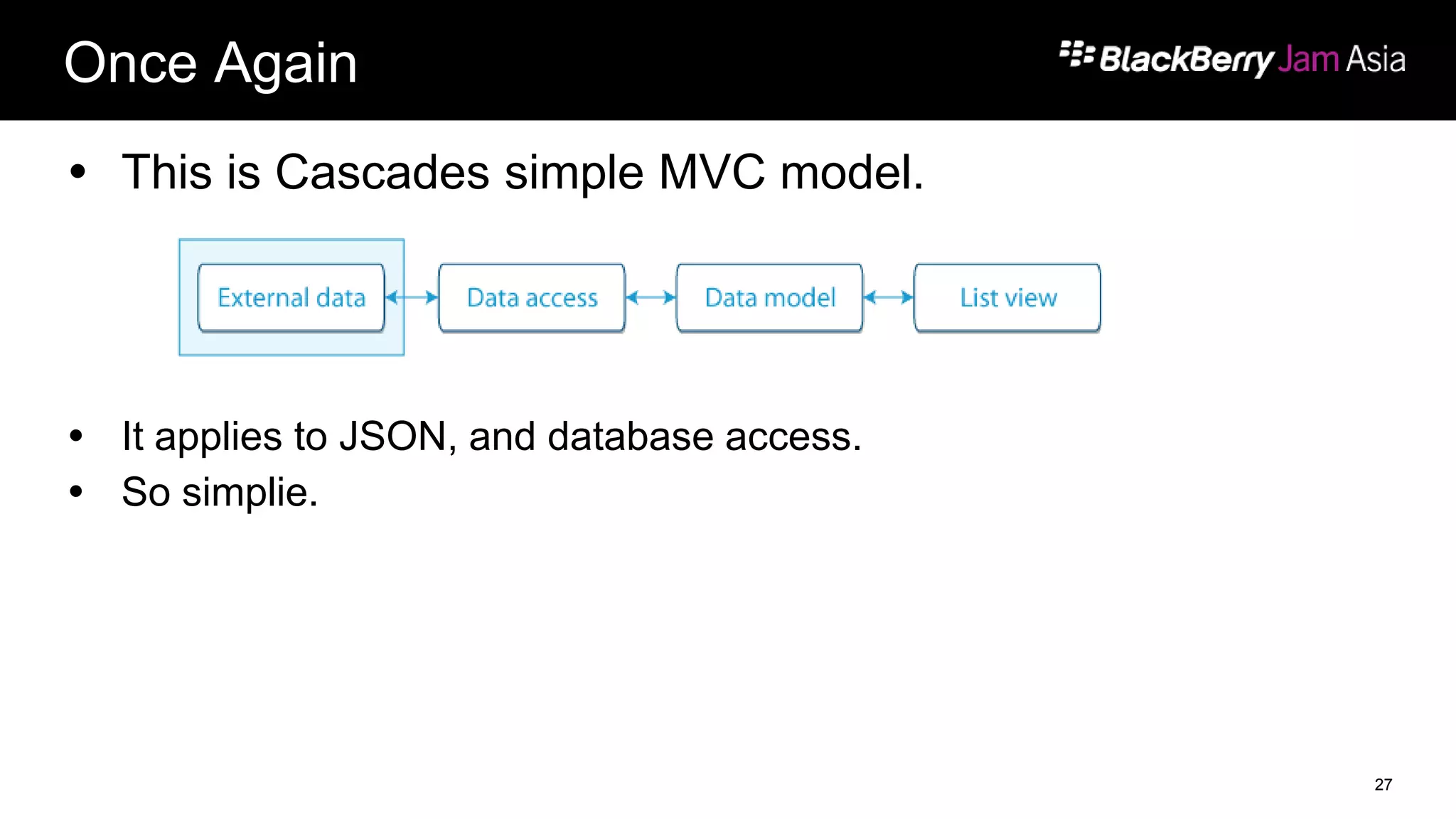
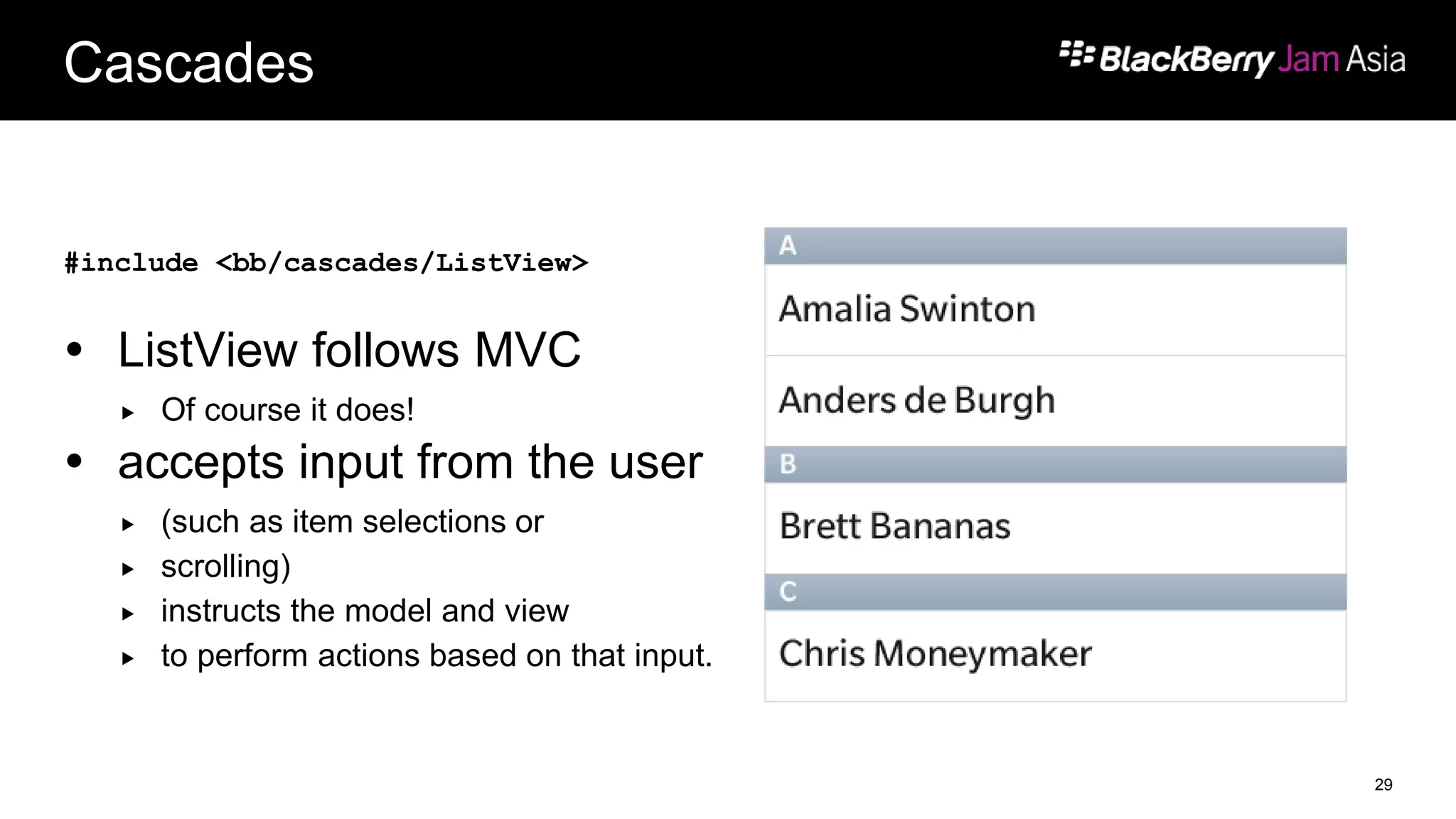
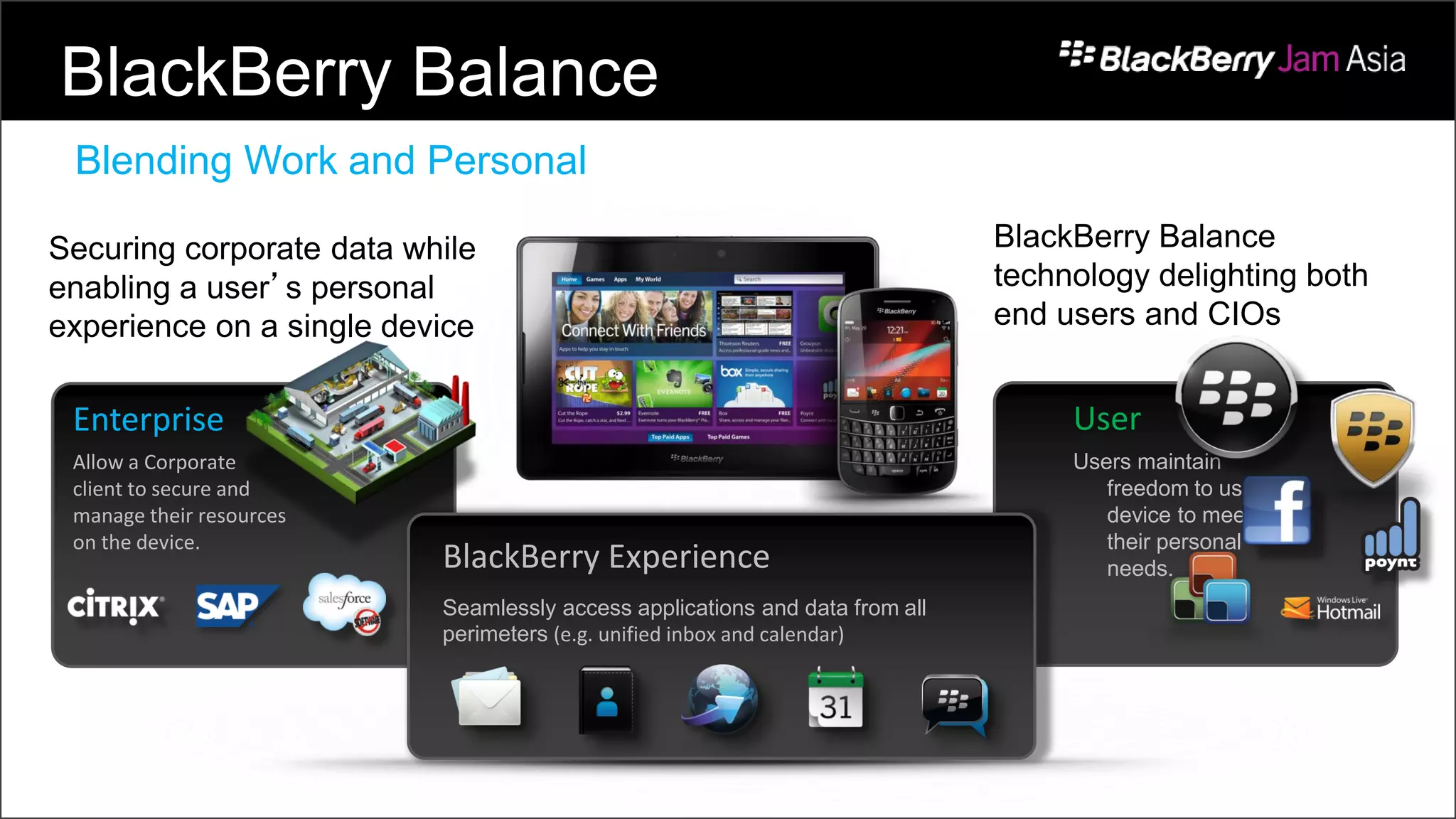
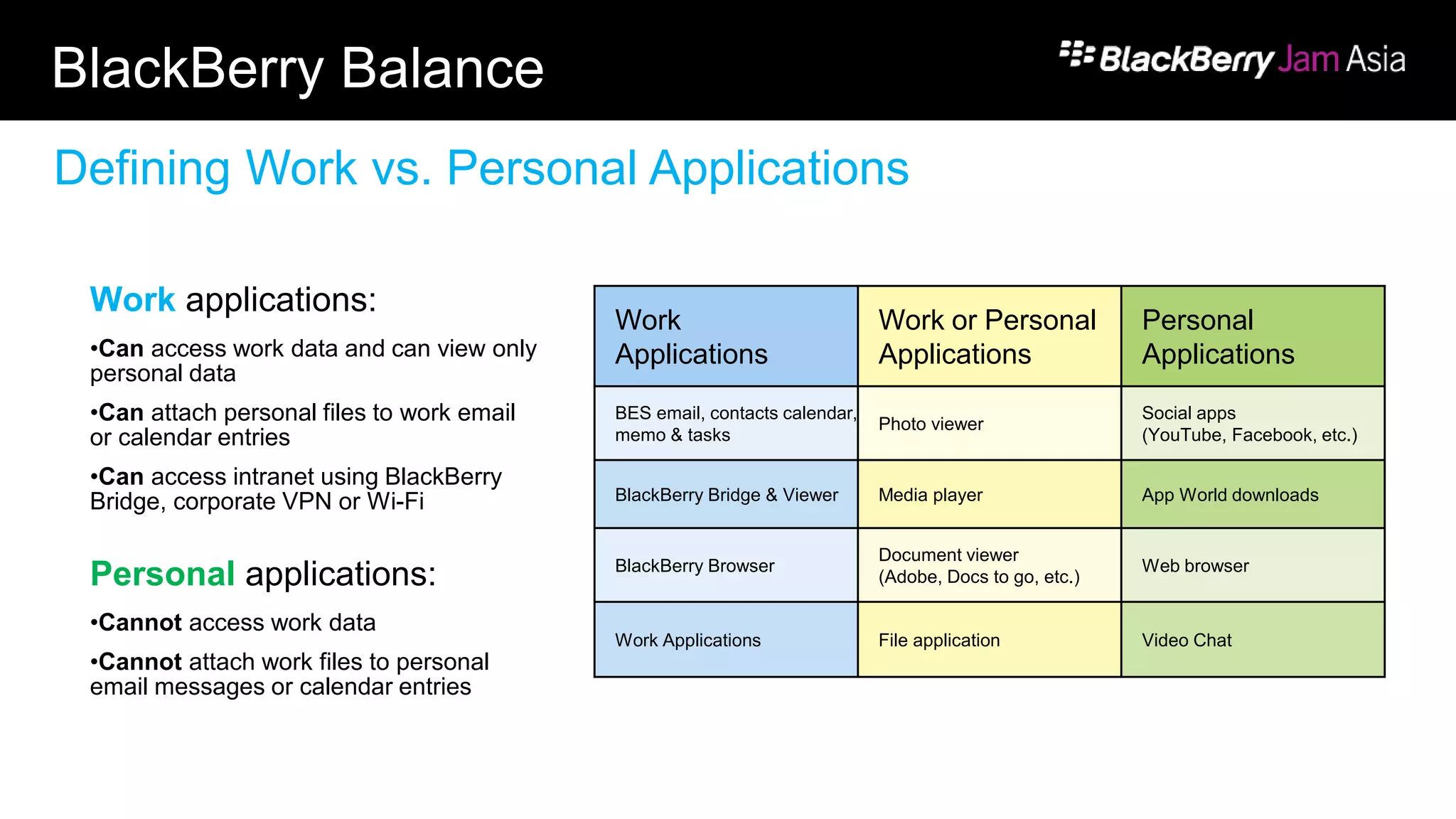
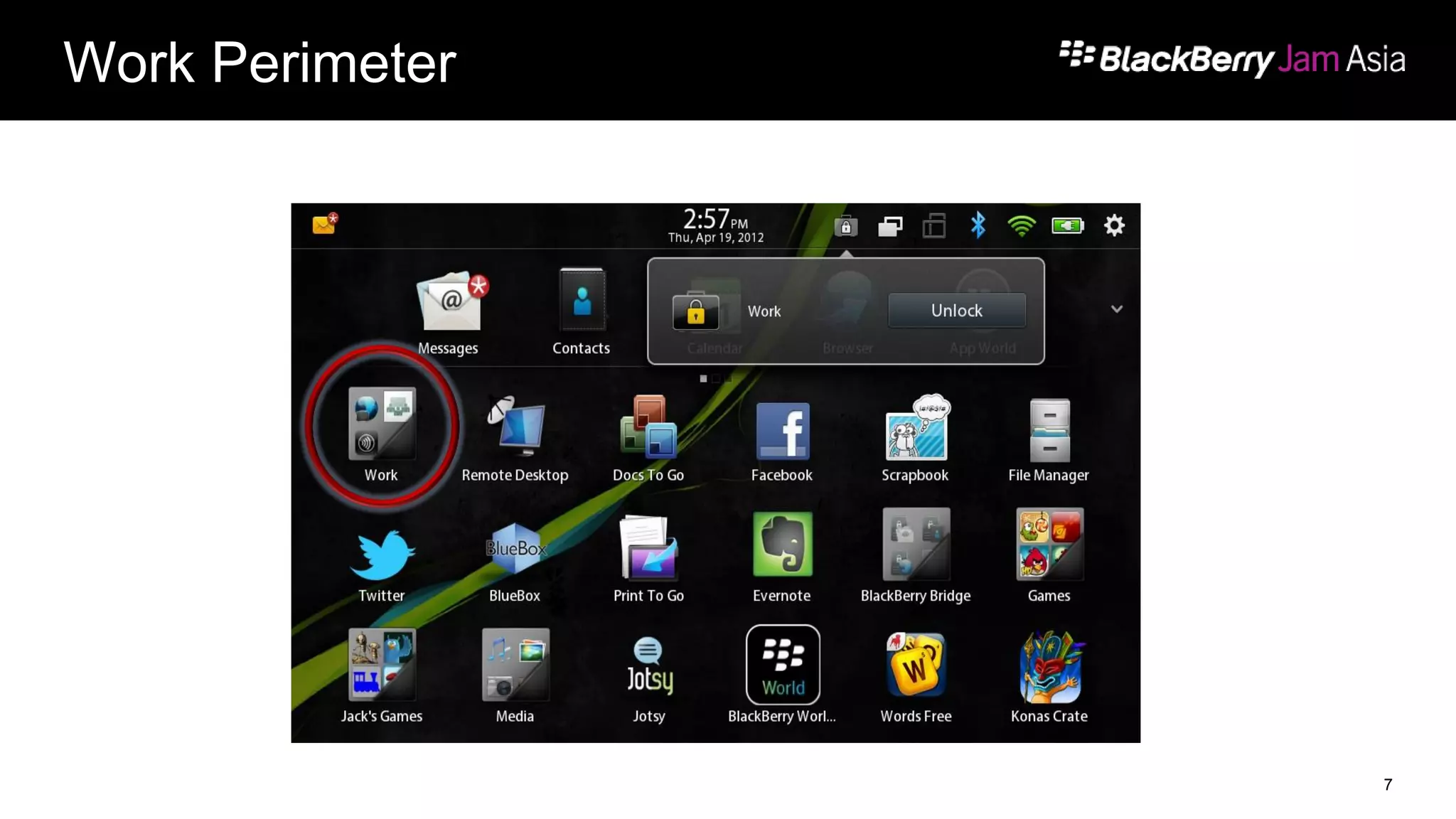
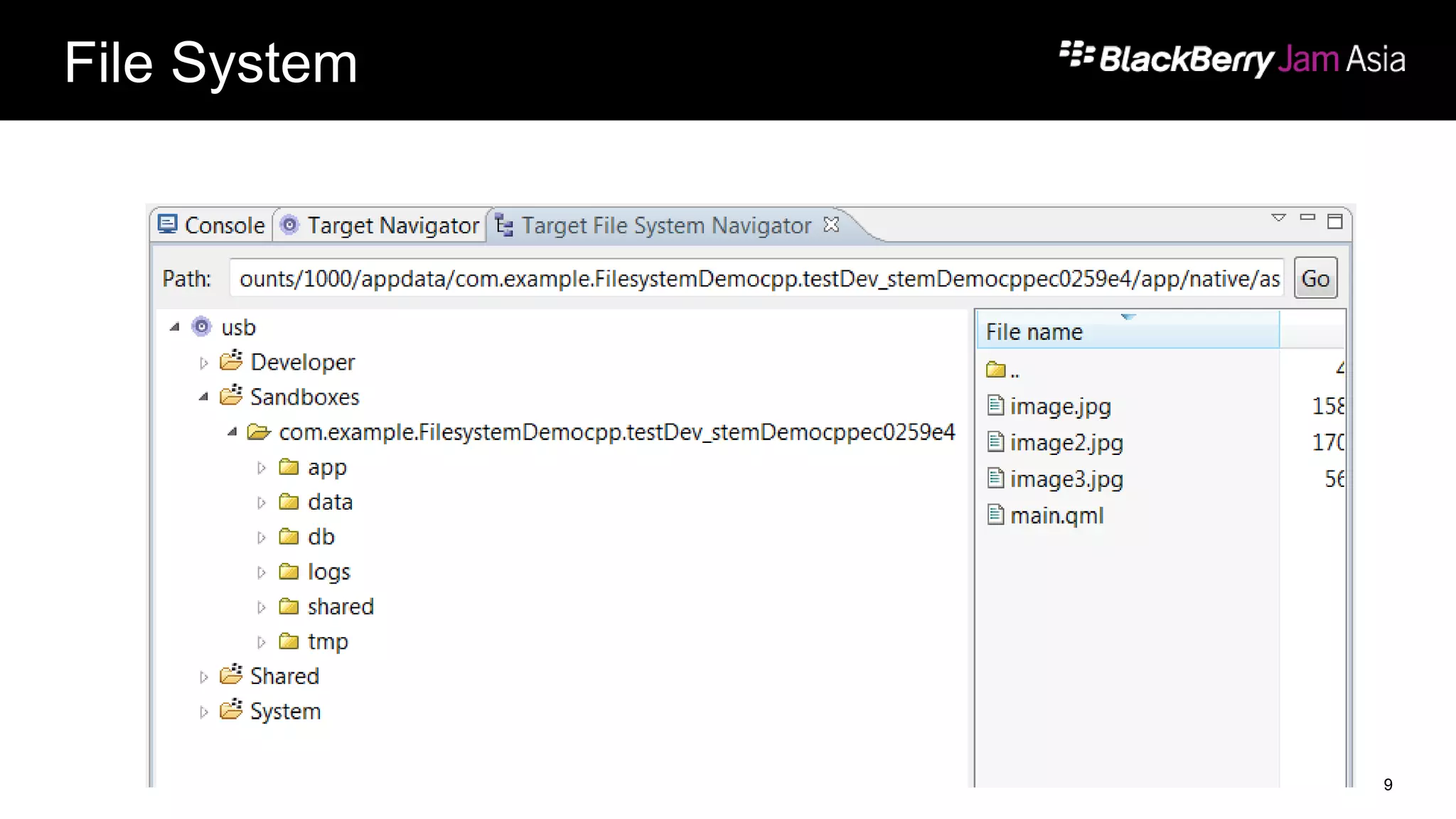
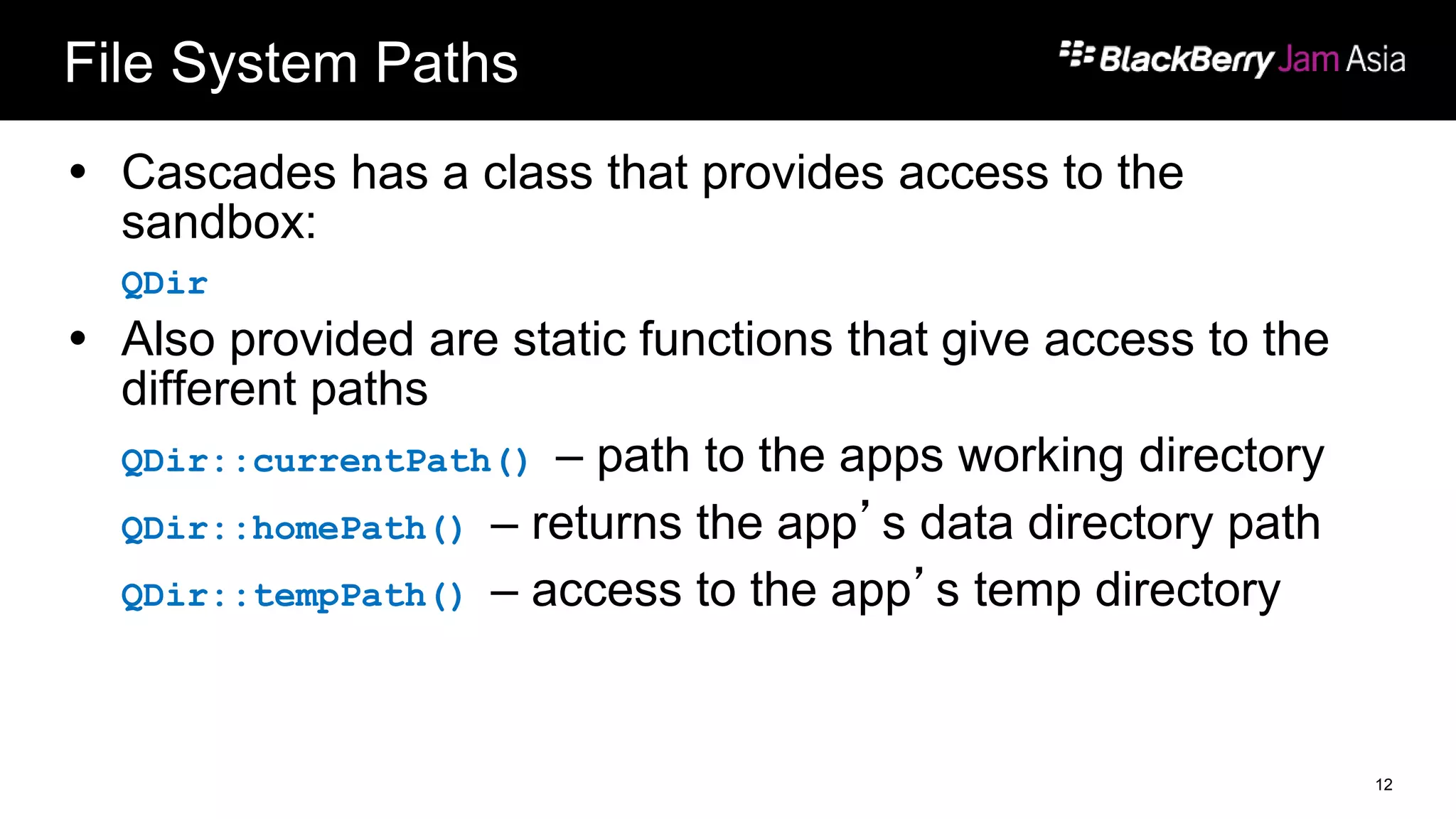
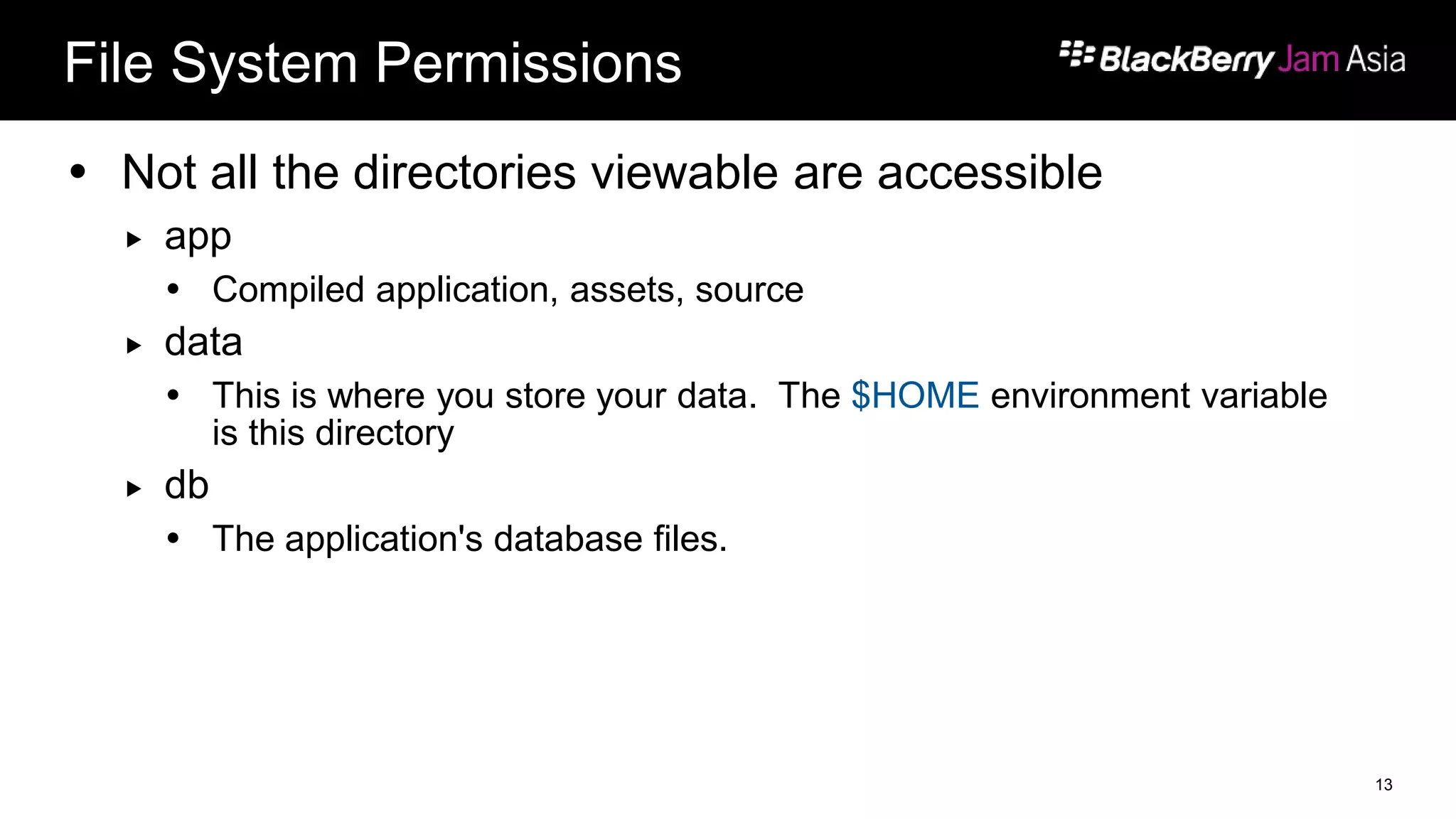
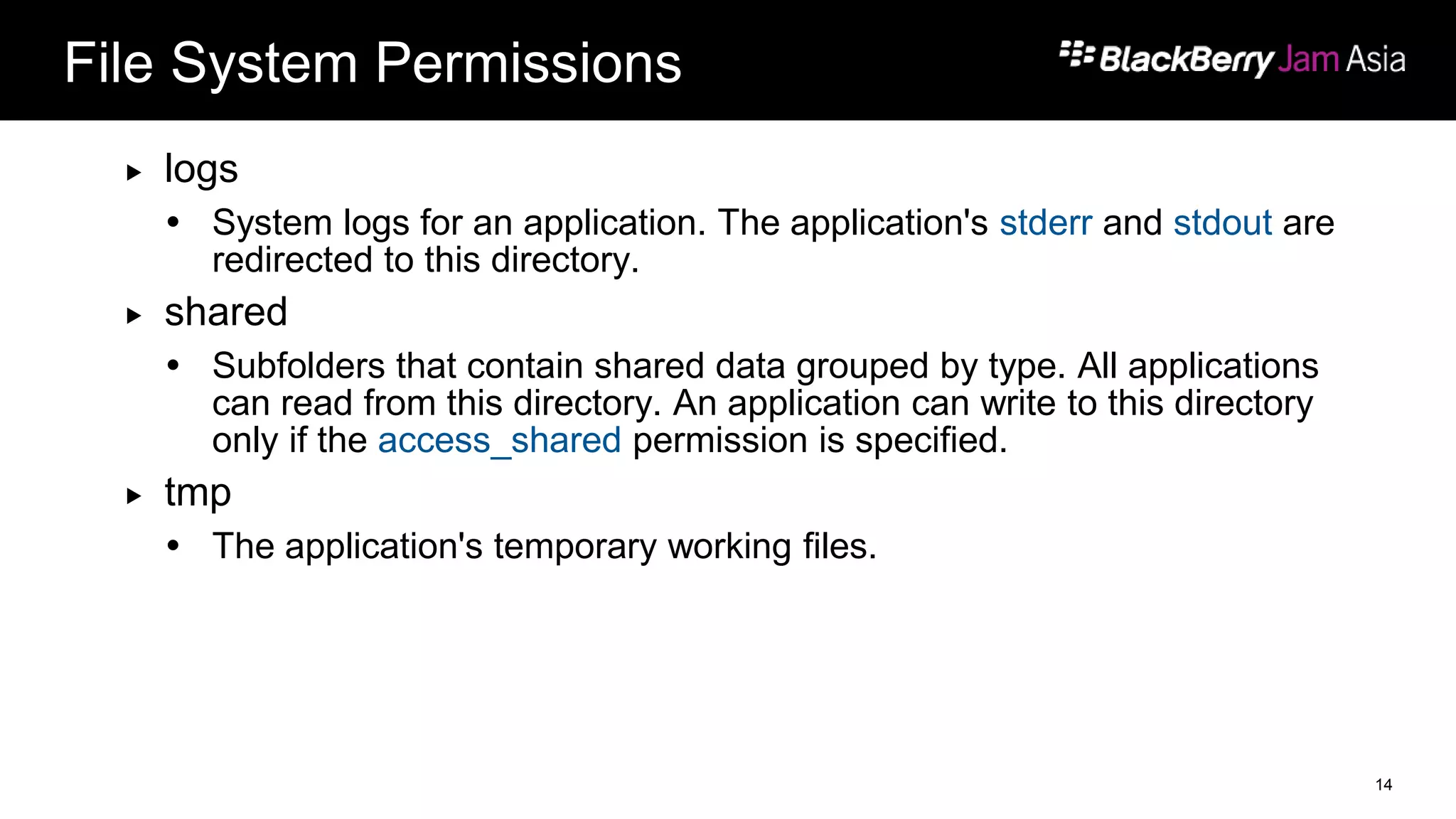
This document presents a deep dive into data storage and retrieval for mobile applications, specifically focusing on native APIs and the use of files and databases. It discusses various methods for accessing and managing data, including the use of JSON for data distribution, and highlights the importance of security for corporate and personal data on devices. Furthermore, it covers the MVC architectural model utilized in the Cascades framework for organizing data access and presentation.







![What does JSON look like?
[
{
"firstName" : "Mike",
"lastName" : "Chepesky",
"employeeNumber" : 01840192
},
{
"firstName" : "Westlee",
"lastName" : "Barichak",
"employeeNumber" : 47901927
}
]
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-1415-mtg03-jam819wong-160106071053/75/JAM819-Native-API-Deep-Dive-Data-Storage-and-Retrieval-17-2048.jpg)