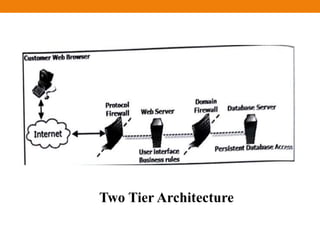
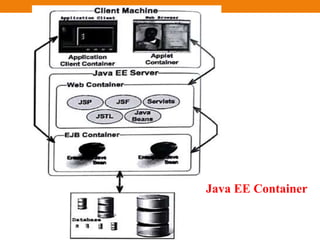
The document discusses Java EE architecture, including the Java EE server and containers. It describes the Java EE server as implementing the Java EE platform APIs and providing standard services. Java EE containers provide an interface between components (like servlets, EJBs) and platform functionality/services. There are three main containers: the web container, application client container, and EJB container. The document also discusses single, two, three and multitier architectures.