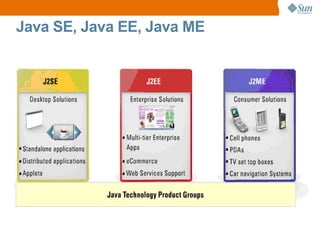
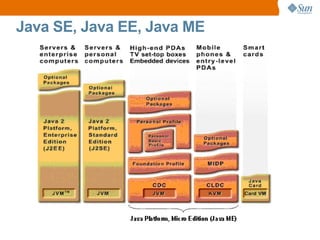
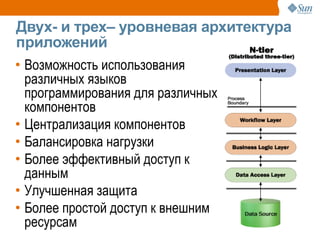
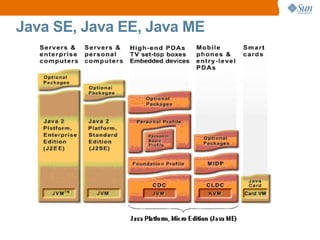
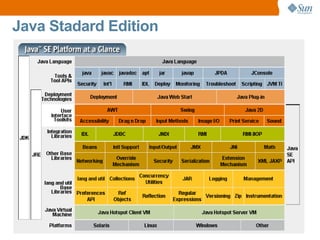
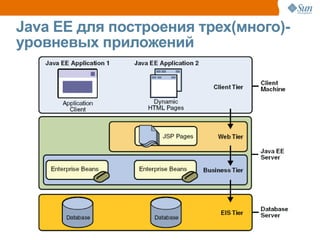
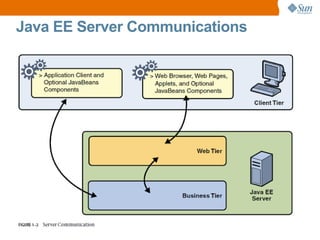
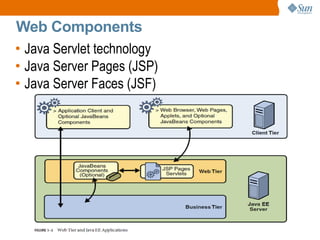
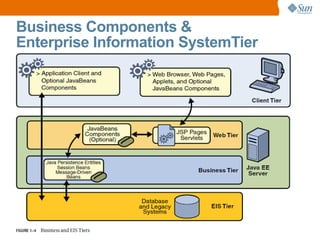
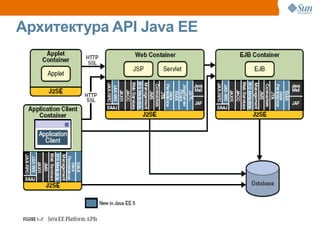
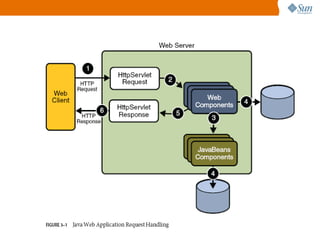
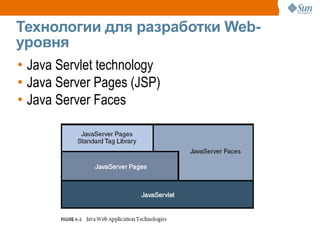
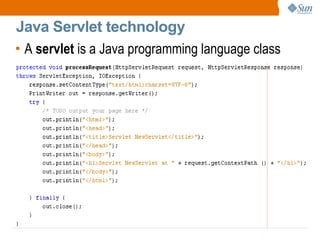
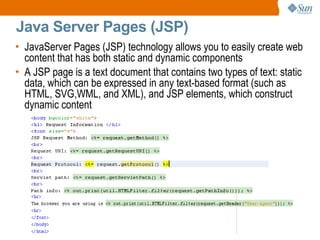
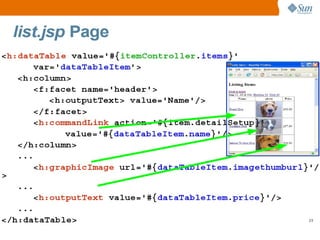
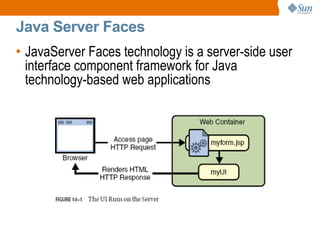
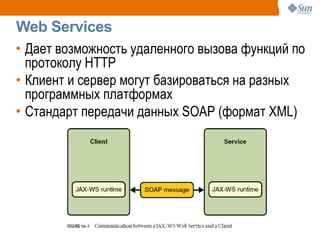
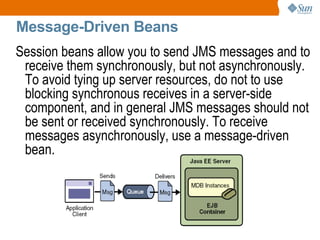
The document discusses the use of Java platform and NetBeans IDE 6.7 for developing enterprise and web applications, including the architecture, and technologies involved. It provides an overview of Java SE, EE, ME, and the capabilities offered for building multi-tier applications using components such as servlets, JSP, and EJBs. Additionally, it highlights the types of web applications and the significance of enterprise beans in scalable, distributed applications.