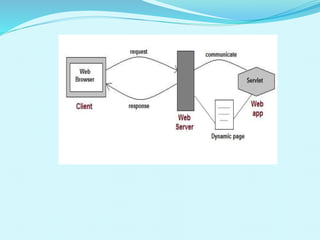
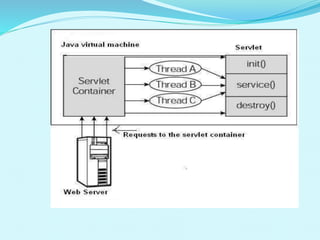
The document provides an overview of Java servlets, covering their history, architecture, life cycle, advantages, and disadvantages. Servlets are Java programs that enhance server capabilities to create dynamic web applications, offering security, scalability, and robustness. The servlet life cycle involves initialization, processing requests, and destruction, with security being a significant focus for applications handling sensitive data.