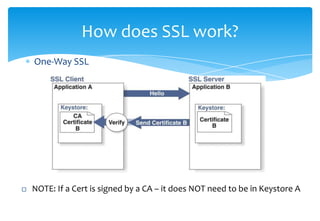
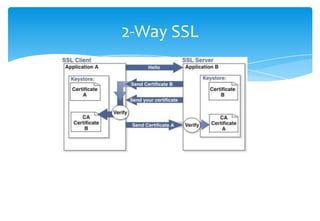
SSL provides encryption and authentication for secure communication over networks. It uses certificates signed by a certificate authority to authenticate servers and establish an encrypted connection. The SSL handshake process involves the client sending a pre-master secret encrypted with the server's public key, both sides then derive encryption keys to encrypt the connection. Debugging SSL issues may require using tools like tcpdump to monitor network traffic or adding debug flags to examine the SSL handshake.





![Creation date: Jul 28, 2010Entry type: PrivateKeyEntryCertificate chain length: 1Certificate[1]:Owner: CN=some.url, OU=Services, O=Nokia, L=Burlington, ST=Massachusetts, C=USIssuer: OU=www.verisign.com/CPS Incorp.by Ref. LIABILITY LTD.(c)97 VeriSign, OU=VeriSign International Server CA - Class 3, OU="VeriSign, Inc.", O=VeriSign Trust NetworkSerial number: 7c391cdfaf10822ce338c3eb925f77bcValid from: Mon Apr 12 00:00:00 UTC 2010 until: Tue Apr 12 23:59:59 UTC 2011Certificate fingerprints: MD5: 06:5C:45:66:C5:28:77:48:E6:58:D9:FB:C5:06:41:1C SHA1: 74:4B:A8:3D:A7:BF:57:30:4E:23:B5:21:4C:2E:9B:8B:27:5F:9E:A5 Signature algorithm name: SHA1withRSA Version: 3And more stuff . . . .What does a cert look like? Ours.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sslforslideshare-110810134615-phpapp02/85/Ssl-in-a-nutshell-6-320.jpg)