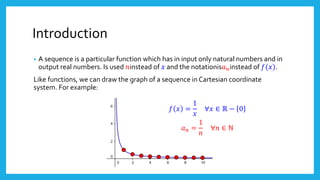
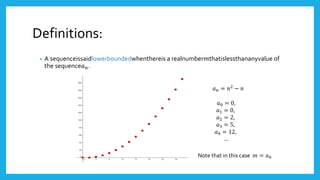
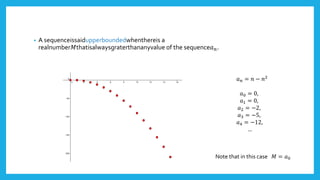
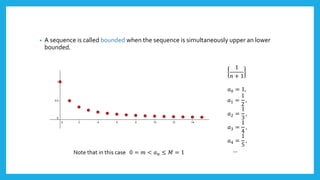
The document defines key concepts related to sequences:
- A sequence is a function with natural numbers as inputs and real numbers as outputs. Sequences can be bounded, meaning all terms fall within a certain range, or unbounded.
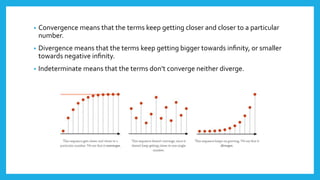
- Sequences can converge, meaning the terms get closer to a limit, or diverge, meaning the terms approach positive or negative infinity.
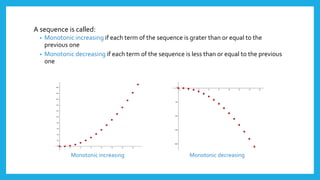
- A sequence is monotonically increasing if each term is greater than or equal to the previous one, and monotonically decreasing if each term is less than or equal to the previous one.
- A sequence converges to a value L if, given any small positive number ε, there exists an N such that all terms after N are within