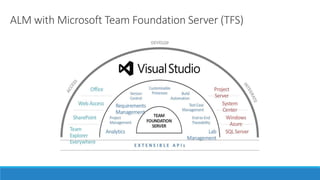
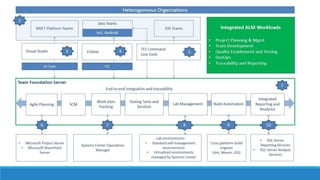
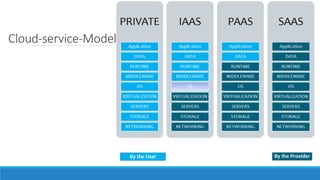
This document discusses Agile testing tools. It covers task management tools, software build tools, configuration management tools, test design tools, communication tools, and cloud/virtualization tools. Task management tools help track user stories and tasks throughout sprints. Build tools enable daily builds. Configuration management tools store code and tests. Test design tools help automate testing. Communication tools like wikis and chat support collaboration. Cloud/virtualization tools provide flexible testing environments.