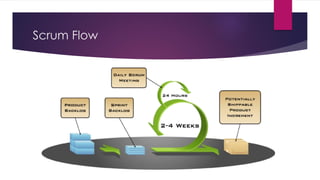
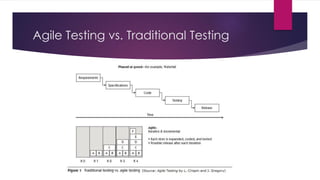
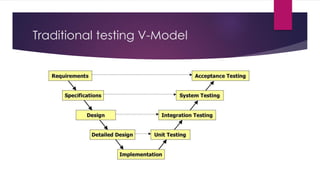
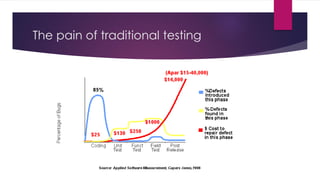
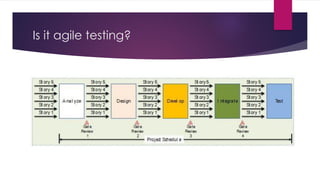
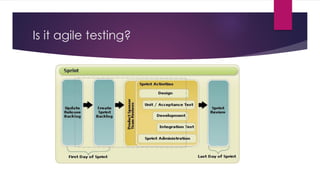
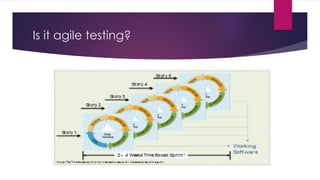
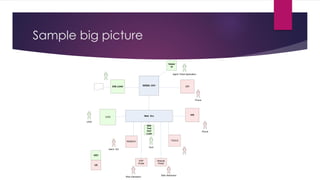
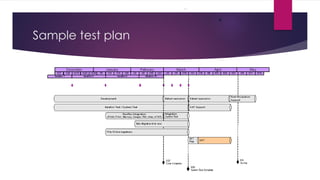
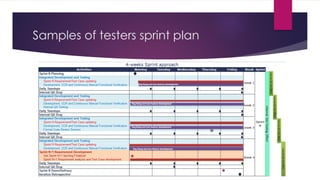
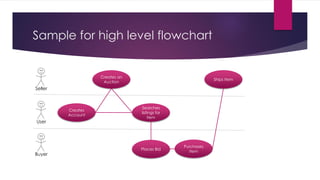
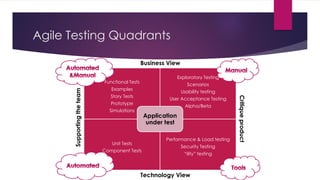
The document provides an overview of agile testing principles and practices. It discusses that agile testing involves the entire cross-functional team working together to test software iteratively. Key aspects of agile testing covered include continuous feedback, delivering value to customers, enabling face-to-face communication, and keeping testing simple. The document also outlines typical testing activities in an agile project such as test planning, driving development, facilitating communication, and completing testing tasks within each sprint.