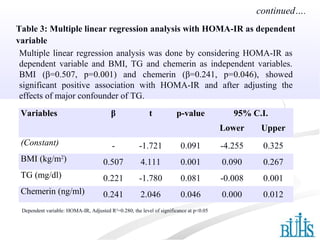
Elevated levels of circulating chemerin have an association with insulin resistance among Bangladeshi subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. The study measured levels of serum chemerin, insulin, and insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in 34 subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and 46 control subjects. Serum chemerin and HOMA-IR levels were significantly higher in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance compared to controls. There was a significant positive association found between serum chemerin levels and HOMA-IR among all subjects. Logistic regression also found serum chemerin to be a significant determinant of impaired glucose tolerance after adjusting for confounding factors.















![Table 2: Binary logistic regression to evaluate the contribution of
HOMA-IR and serum chemerin on IGT group after adjusting the effects
of major confounders
Dependent variable: Group (IGT vs. Control); Adjusted R2
=0.164 the level of significance at p<0.05..
Variables Coefficient S. E.
p-value Odds
Ratio
95% C.I.
Lower Upper
(Constant) -7.424 3.358 0.027 0.001 - -
BMI (kg/m2
) 0.186 0.146 0.202 1.205 0.905 1.604
TG (mg/dl) 0.006 0.007 0.340 1.006 0.993 1.019
HOMA-IR 0.143 0.373 0.701 1.154 0.555 2.400
Chemerin (ng/ml) 0.112 0.009 0.035 1.012 0.995 1.030
continued….
On Binary logistic regression analysis, serum chemerin [odds ratio (OR)
1.012, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.995-1.030, p=0.035] was found to be
significant determinant of IGT group (IGT considered as dichotomous
variable) after adjusting the effects of BMI, TG and HOMA-IR respectively](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isratarahossain-nst17-18-180810154252/85/Israt-ara-hossain-nst-17-18-16-320.jpg)