Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times
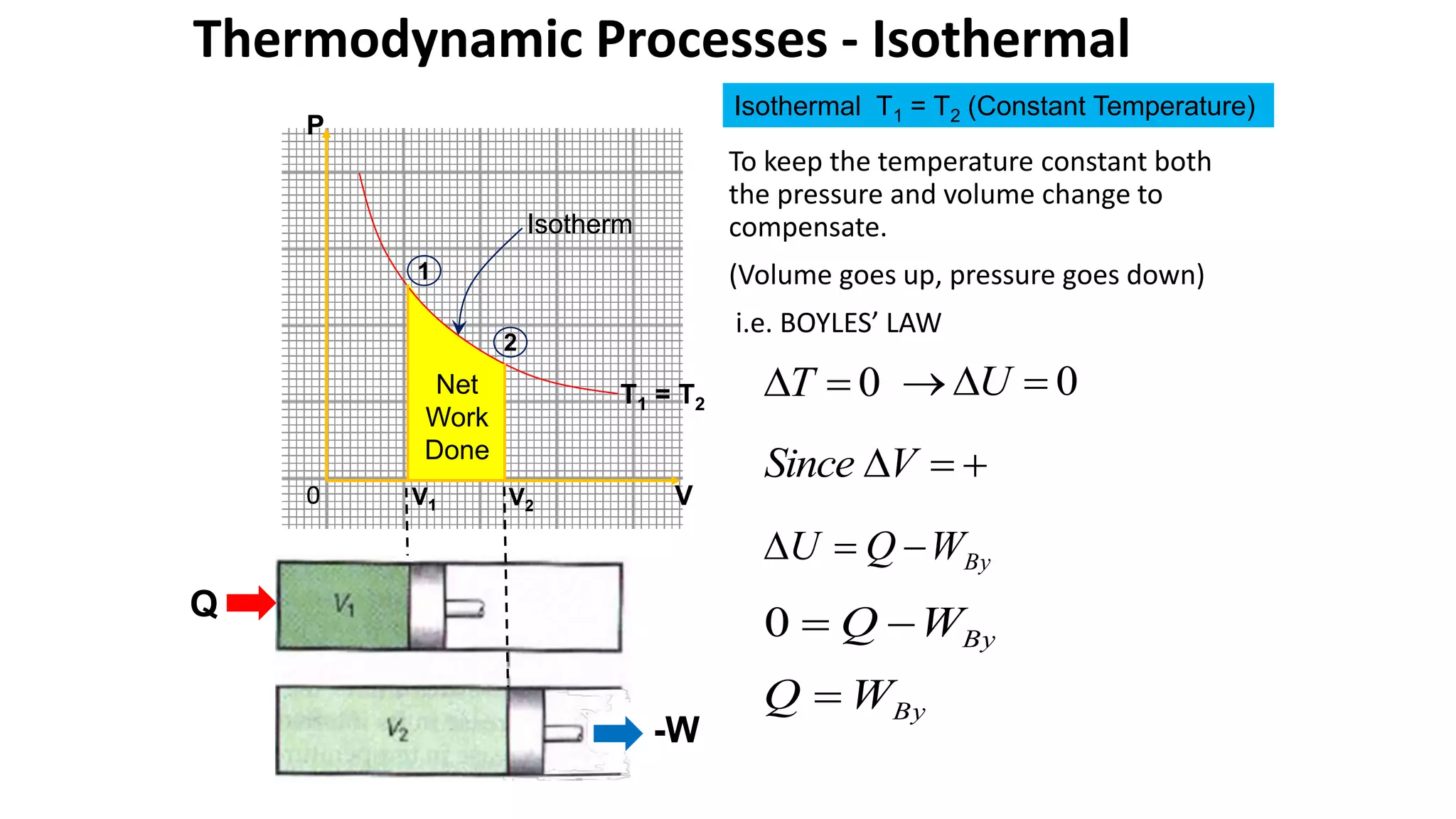
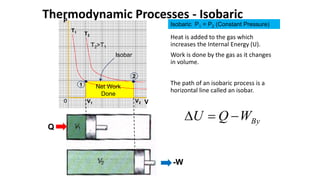
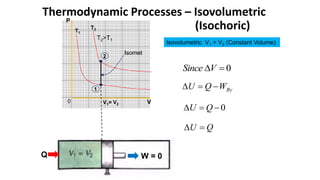
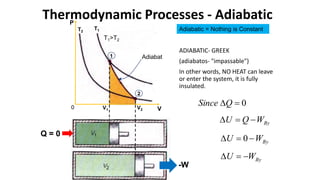
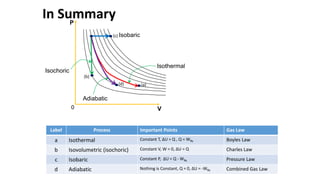
An isothermal process keeps temperature constant by changing both pressure and volume simultaneously and oppositely, according to Boyle's law. An isobaric process keeps pressure constant by adding heat which increases the gas's internal energy and does work as its volume changes. An isovolumetric or isochoric process keeps volume constant, so no work is done and internal energy changes solely from heat. An adiabatic process is fully insulated so no heat enters or leaves; nothing is constant and internal energy changes result only from work done.




