Embed presentation
Download to read offline
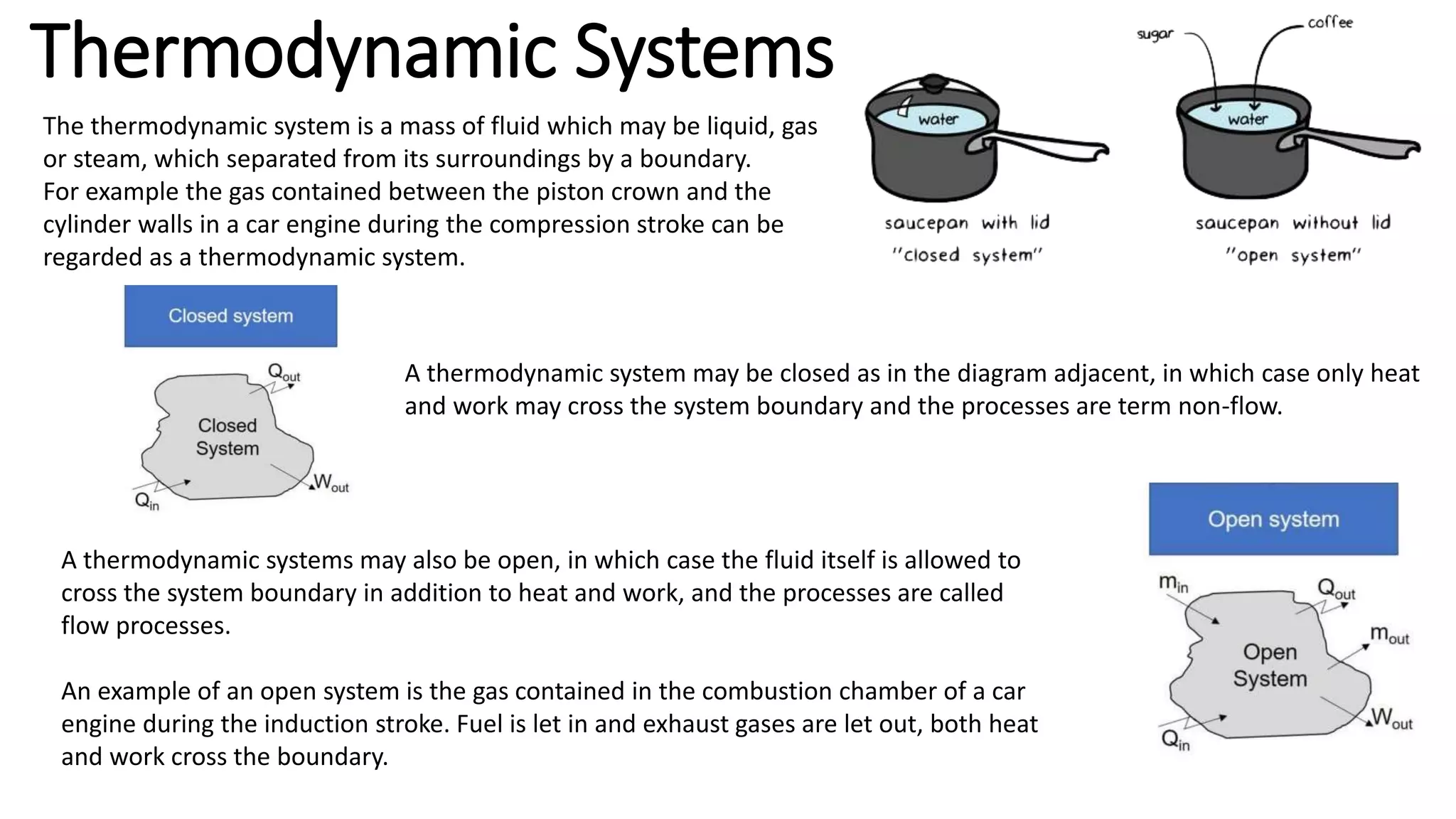
A thermodynamic system is a mass of fluid separated from its surroundings by a boundary, such as the gas contained in a car engine cylinder during compression. A thermodynamic system can be closed, with only heat and work crossing the boundary during non-flow processes, or open, allowing the fluid itself to cross the boundary along with heat and work during flow processes like the gas in a combustion chamber during induction.
