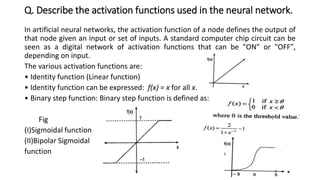
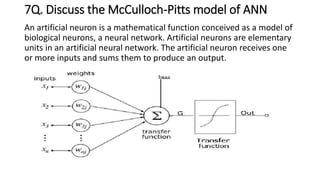
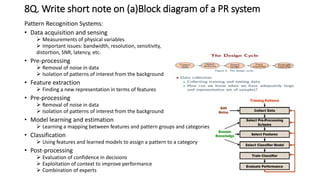
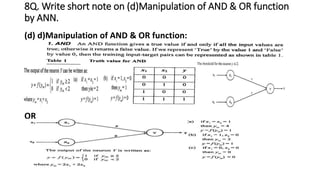
The document discusses various topics related to pattern recognition including:
1. Pattern recognition is the automated recognition of patterns and regularities in data through techniques like machine learning. It has applications in areas like optical character recognition, diagnosis systems, and security.
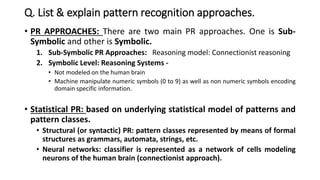
2. There are two main approaches to pattern recognition - sub-symbolic and symbolic. Sub-symbolic uses connectionist models like neural networks while symbolic uses formal structures like strings and automata to represent patterns.
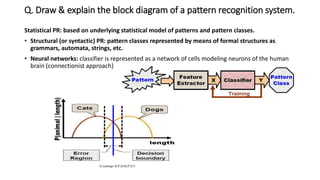
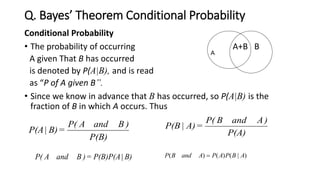
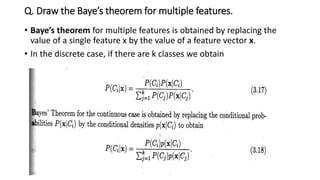
3. A pattern recognition system consists of steps like data acquisition, pre-processing, feature extraction, model learning, classification, and post-processing to classify patterns. Bayesian decision making and Bayes' theorem are statistical techniques used in classification.