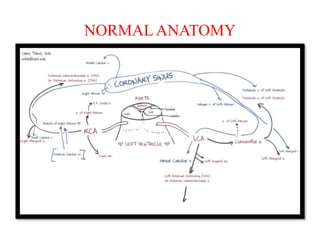
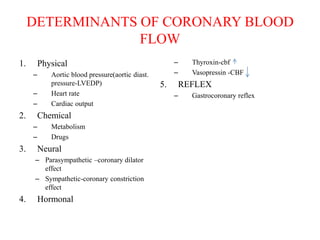
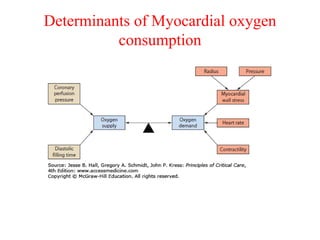
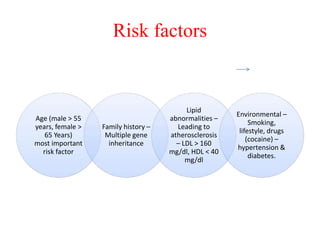
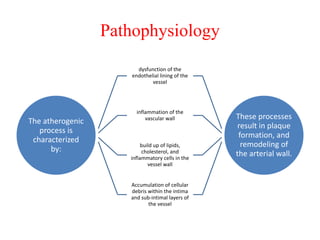
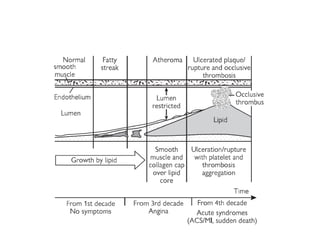
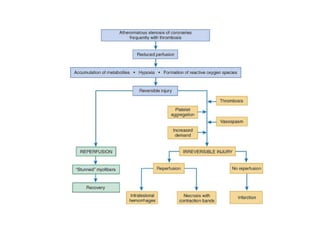
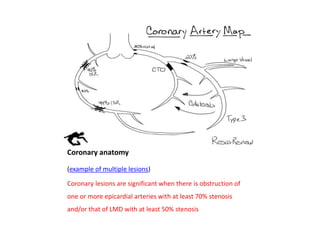
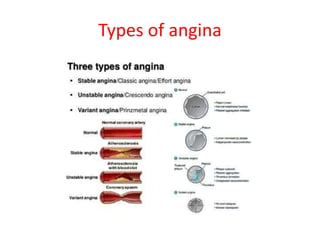
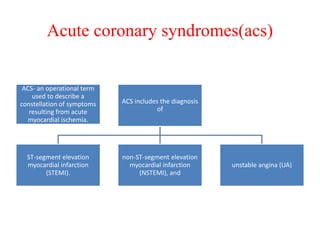
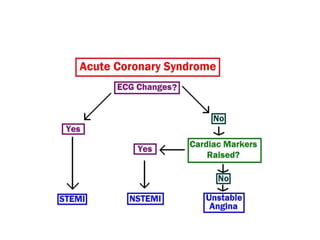
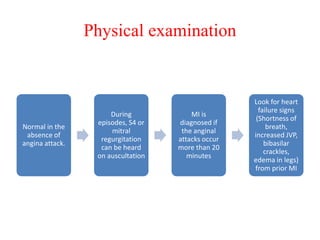
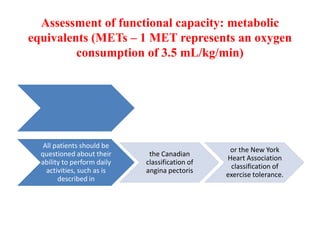
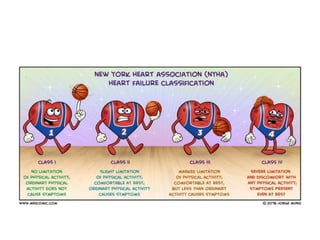
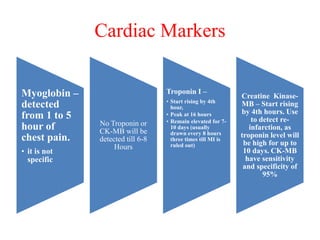
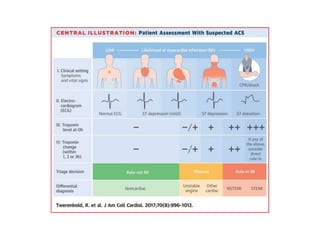
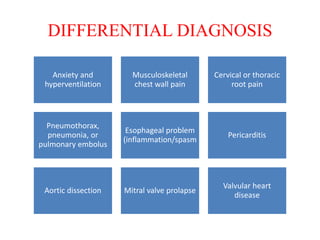
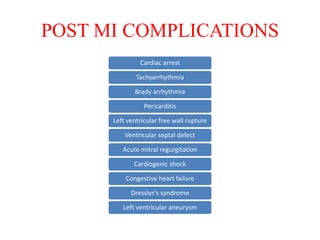
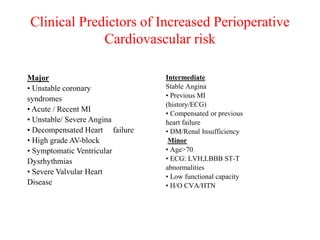
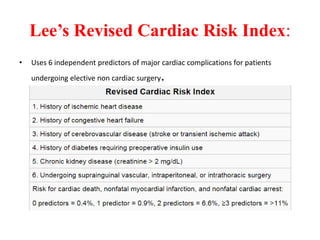
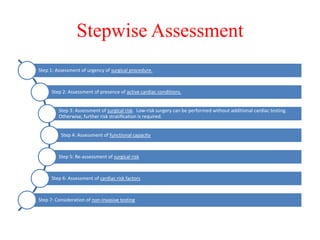
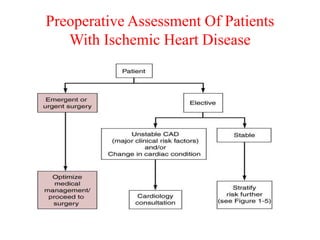
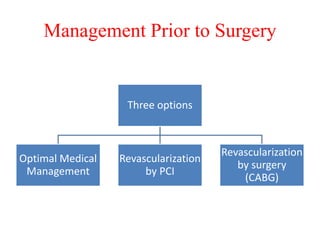
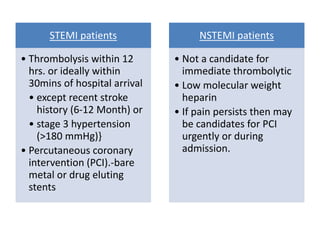
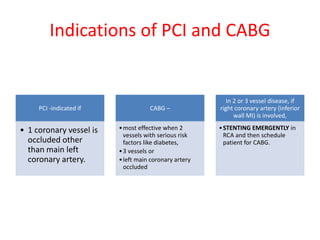
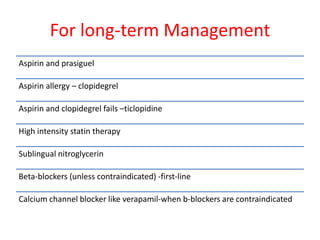
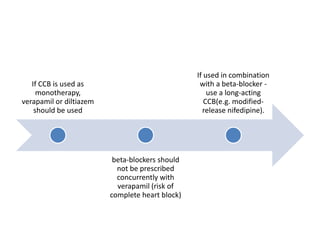
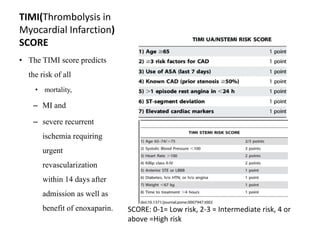
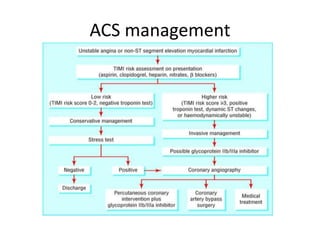
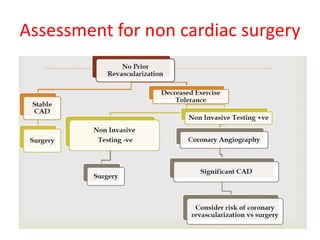
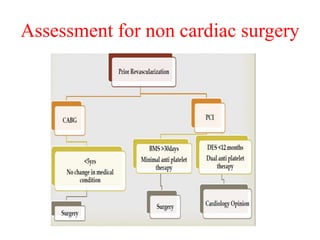
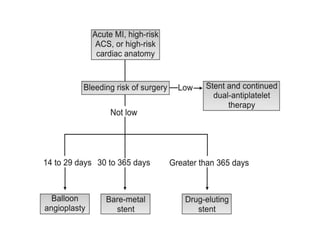
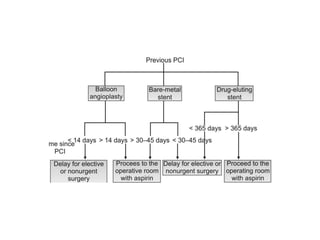
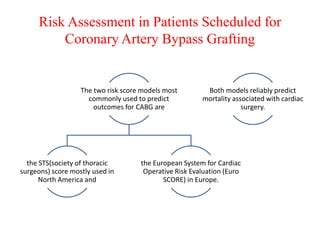
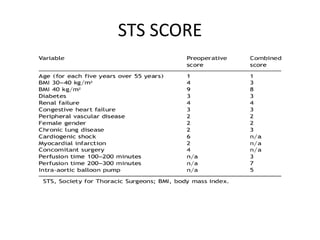
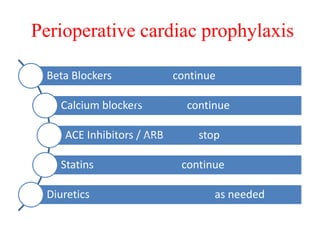
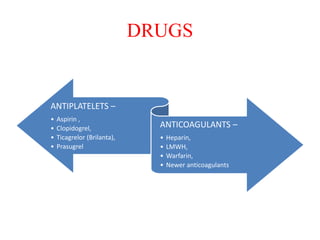
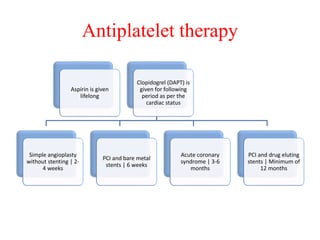
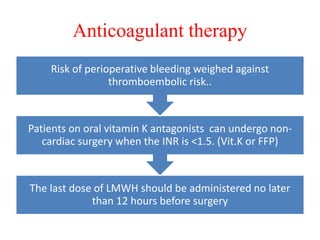
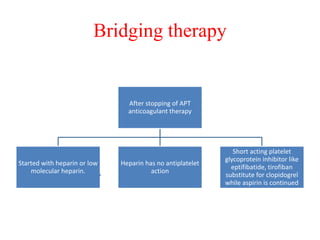
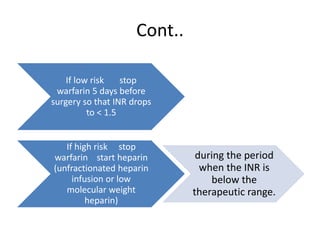
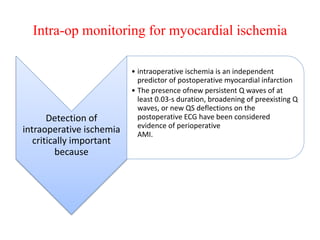
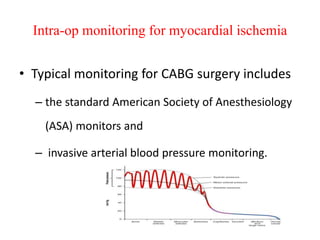
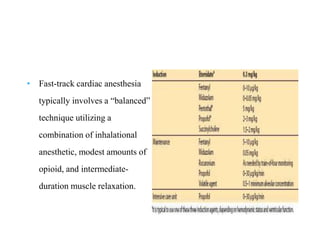
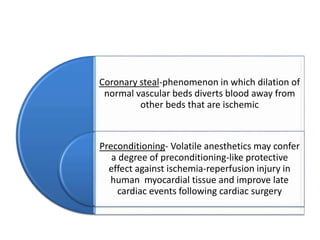
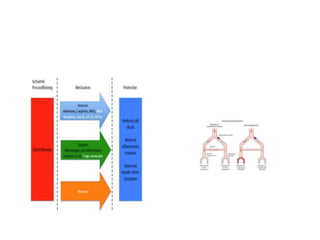
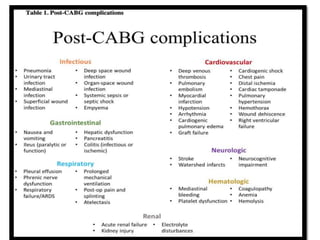
Ischaemic heart disease (IHD) is primarily caused by coronary artery disease (CAD), leading to an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply, with significant risk factors including age, family history, and lifestyle choices. Clinical manifestations include angina and acute coronary syndromes, while diagnostics involve ECG, stress tests, and angiography. Management strategies encompass optimal medical therapy, revascularization methods, and careful preoperative assessments tailored to patient risk profiles.