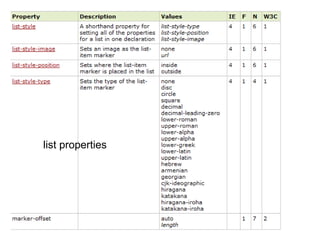
This document provides an overview of Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) including what CSS is, the different levels at which CSS can be defined, CSS syntax, using colors in CSS, and examples of how to style text, lists, padding, margins, and tables using CSS. It recommends defining styles in external CSS files and linking to them via HTML for maintenance purposes. It also provides resources for learning more about CSS properties and values.