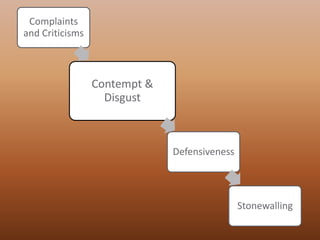
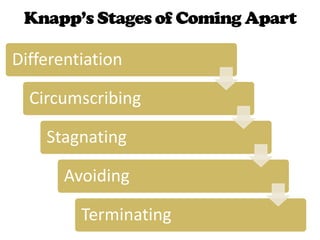
The document discusses reasons for divorce such as infidelity, incompatibility, substance abuse, growing apart, personality issues, lack of communication, and abuse. It also examines how finances, immaturity, lack of financial resources, and poor reasons for marriage can contribute to high divorce rates among young marriages. Additionally, it explores whether opposites attract and identifies the "Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse" relationship issues. Methods for saving marriages through improved communication are presented, as well as stages of breaking up relationships and their effects on children. Maintaining a positive co-parenting relationship after divorce can help reduce negative impacts on kids.