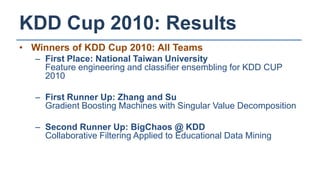
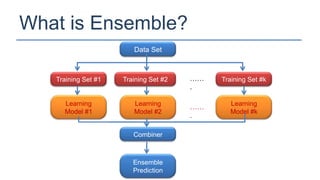
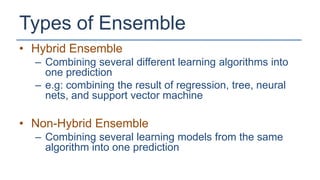
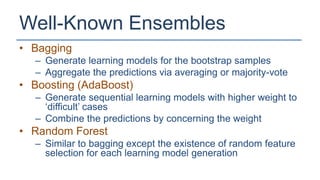
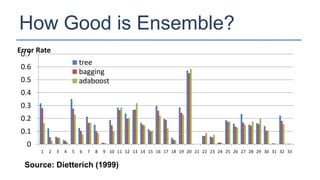
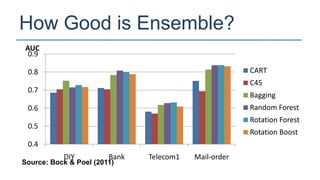
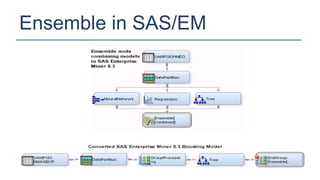
The KDD Cup 2010 challenged participants to predict student performance in mathematical problems based on interaction logs from intelligent tutoring systems. The winners employed various ensemble learning techniques, demonstrating the effectiveness of combining multiple models for improved prediction accuracy. Future efforts should focus on robust and class-imbalance models, advancing the capabilities of ensemble predictive modeling.