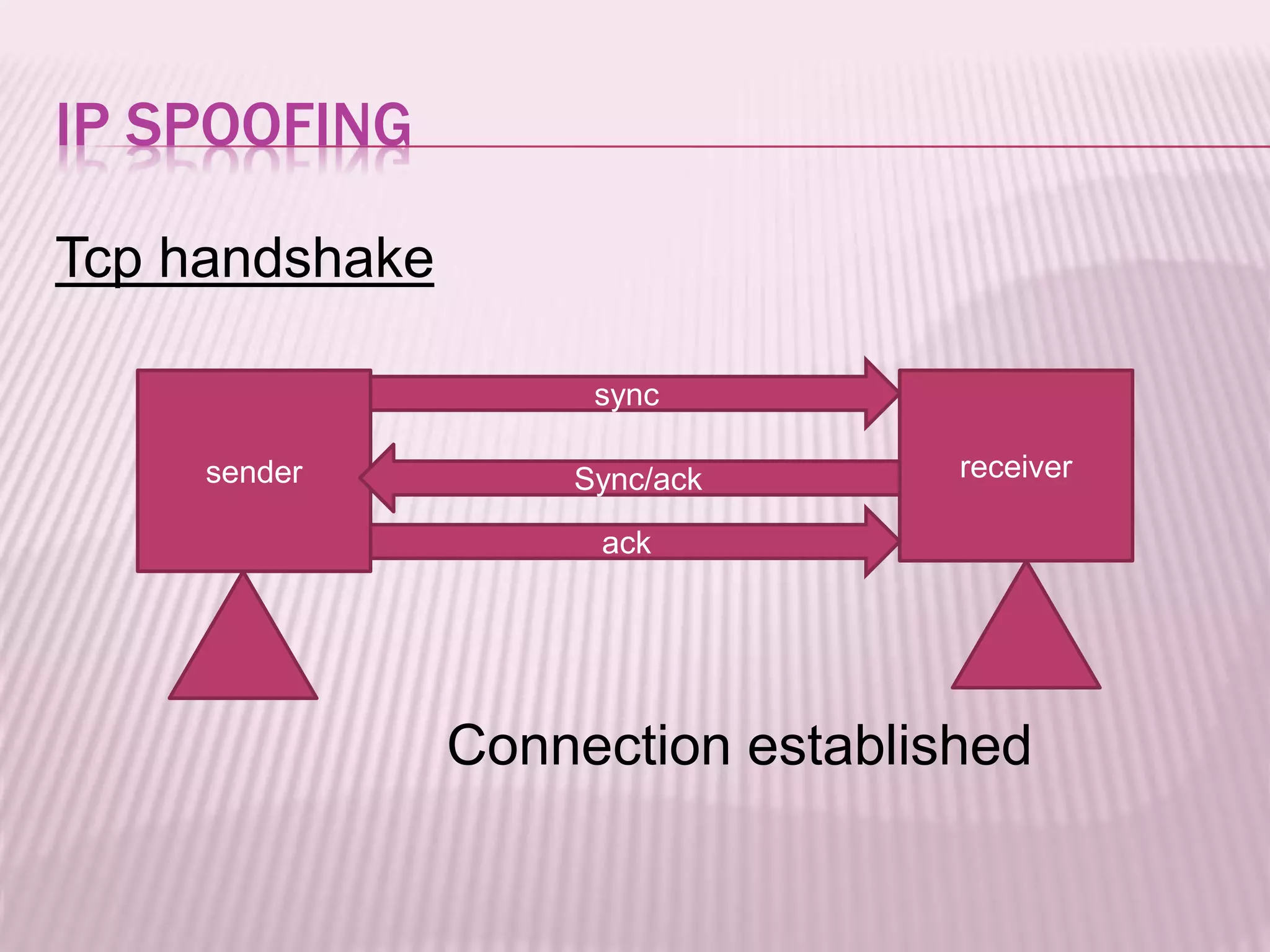
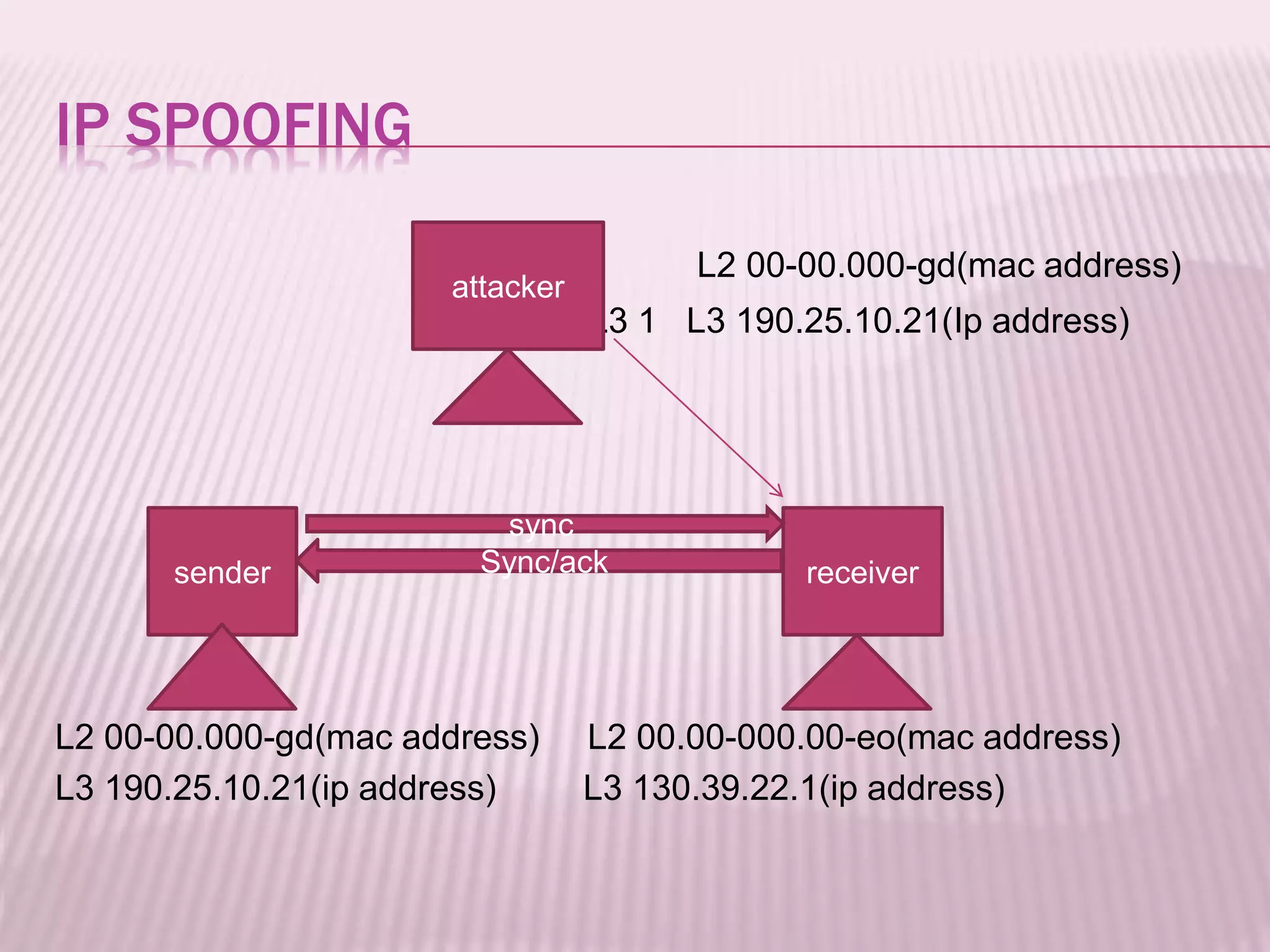
The document discusses IP spoofing, a technique where an attacker manipulates the source IP address to commit cybercrime, such as spamming and denial of service attacks. It covers the mechanics of how IP spoofing works, its historical context, and its applications, including various attack types and the advantages and disadvantages of using this method. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of understanding IP spoofing and implementing preventive measures to protect networks from such threats.