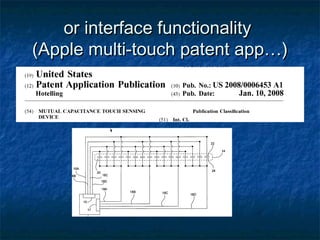
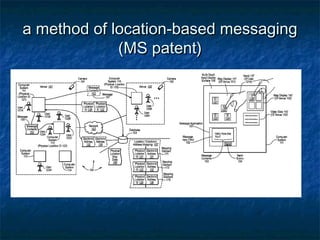
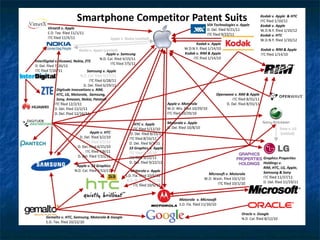
The document provides an overview of intellectual property (IP) types including patents, trade secrets, trademarks, and copyrights that are relevant for mobile startups. It discusses what each type of IP is, why it is useful, examples, processes for obtaining protection, typical timelines and costs, duration of protection, enforcement considerations, and best practices. Key takeaways are that patents, trademarks, and copyrights can be formally registered while trade secrets rely on maintaining confidentiality, and IP planning and protection are important for startups.