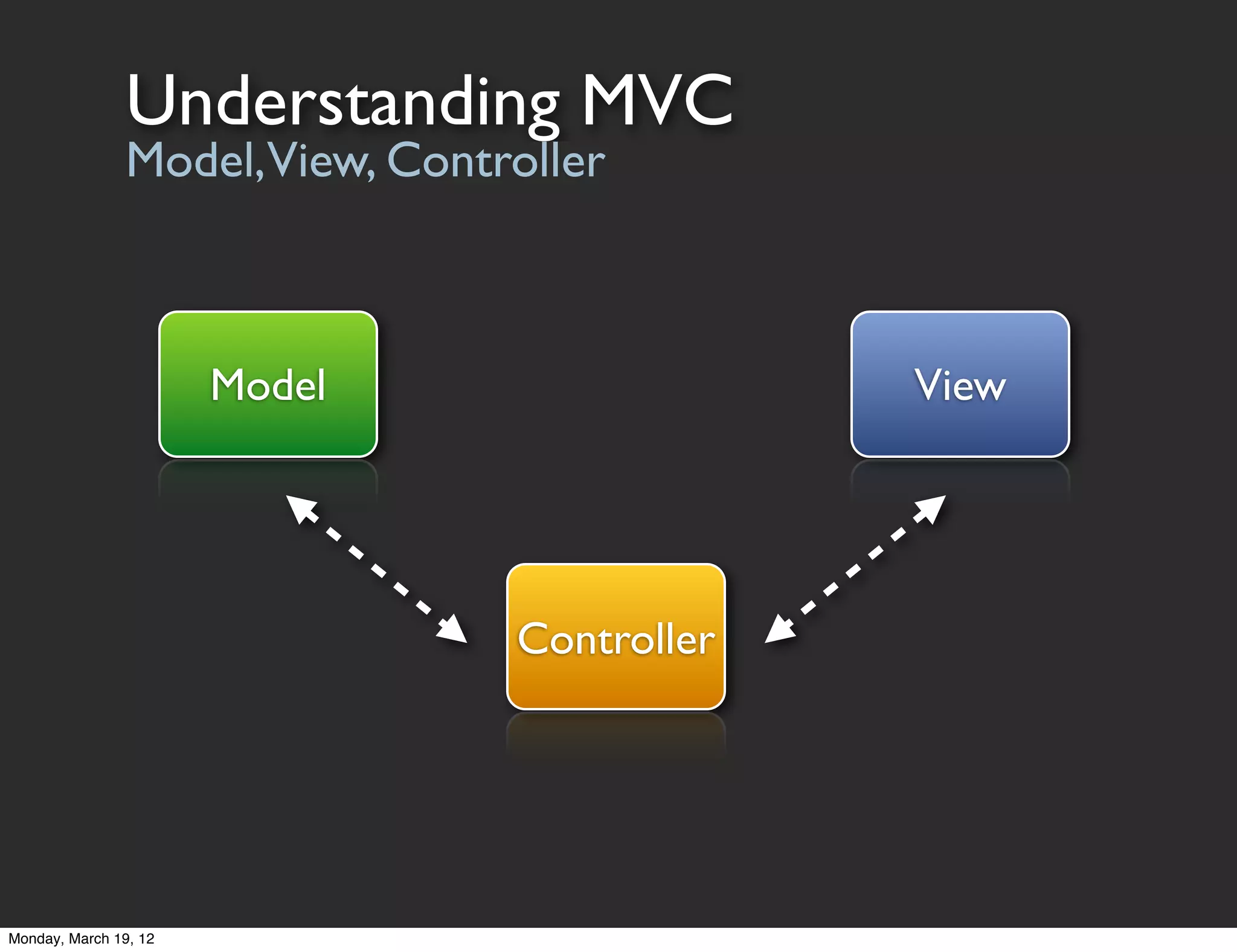
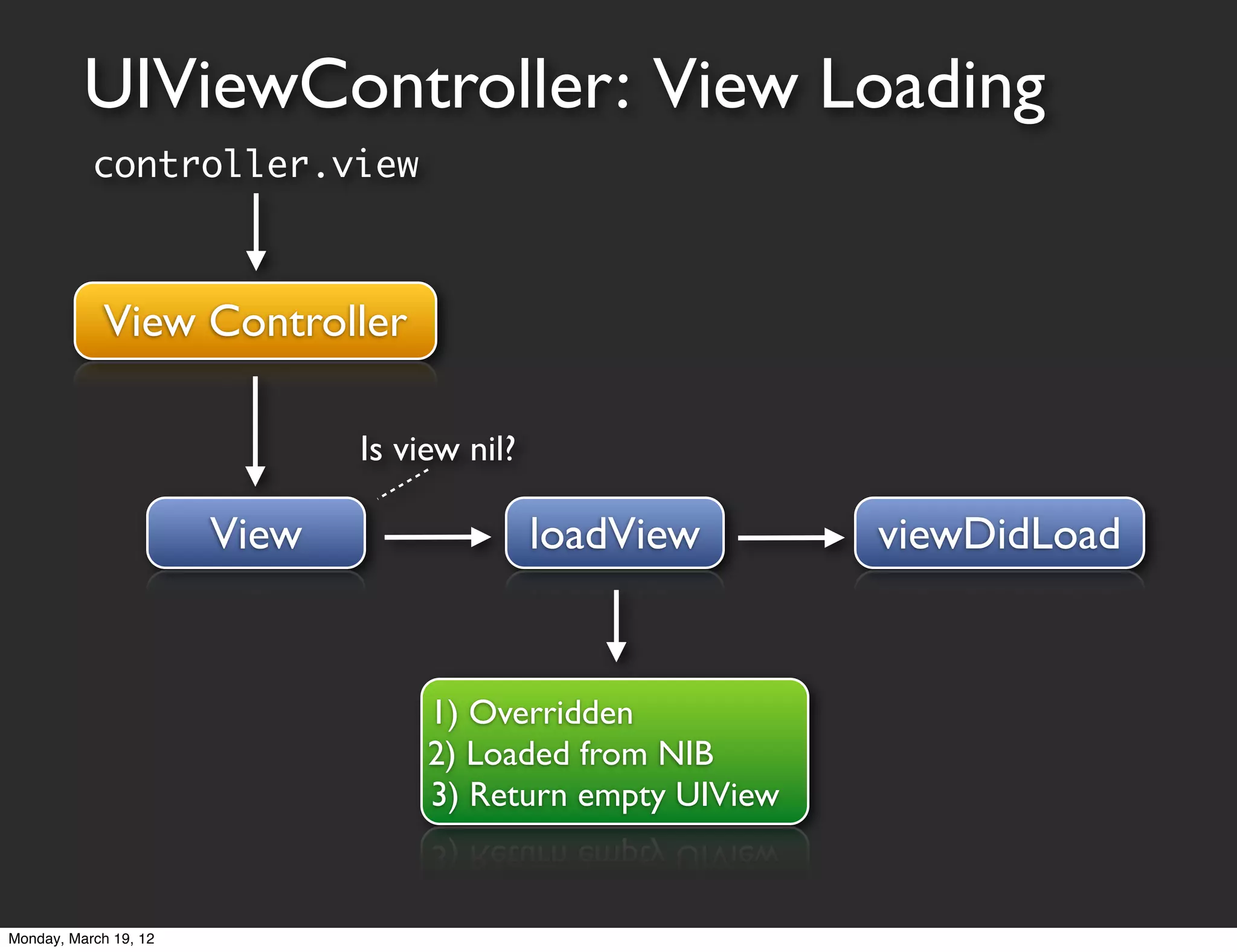
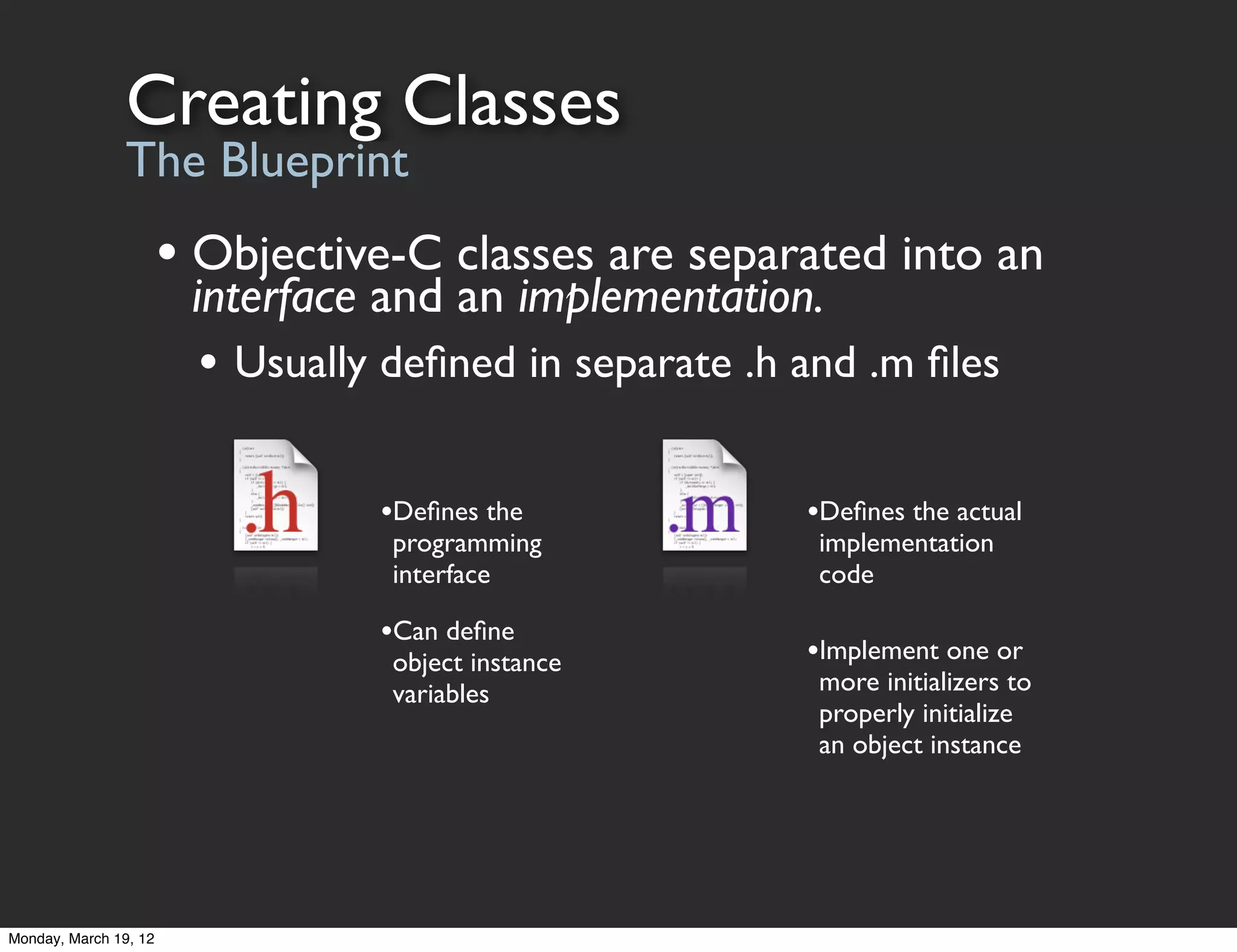
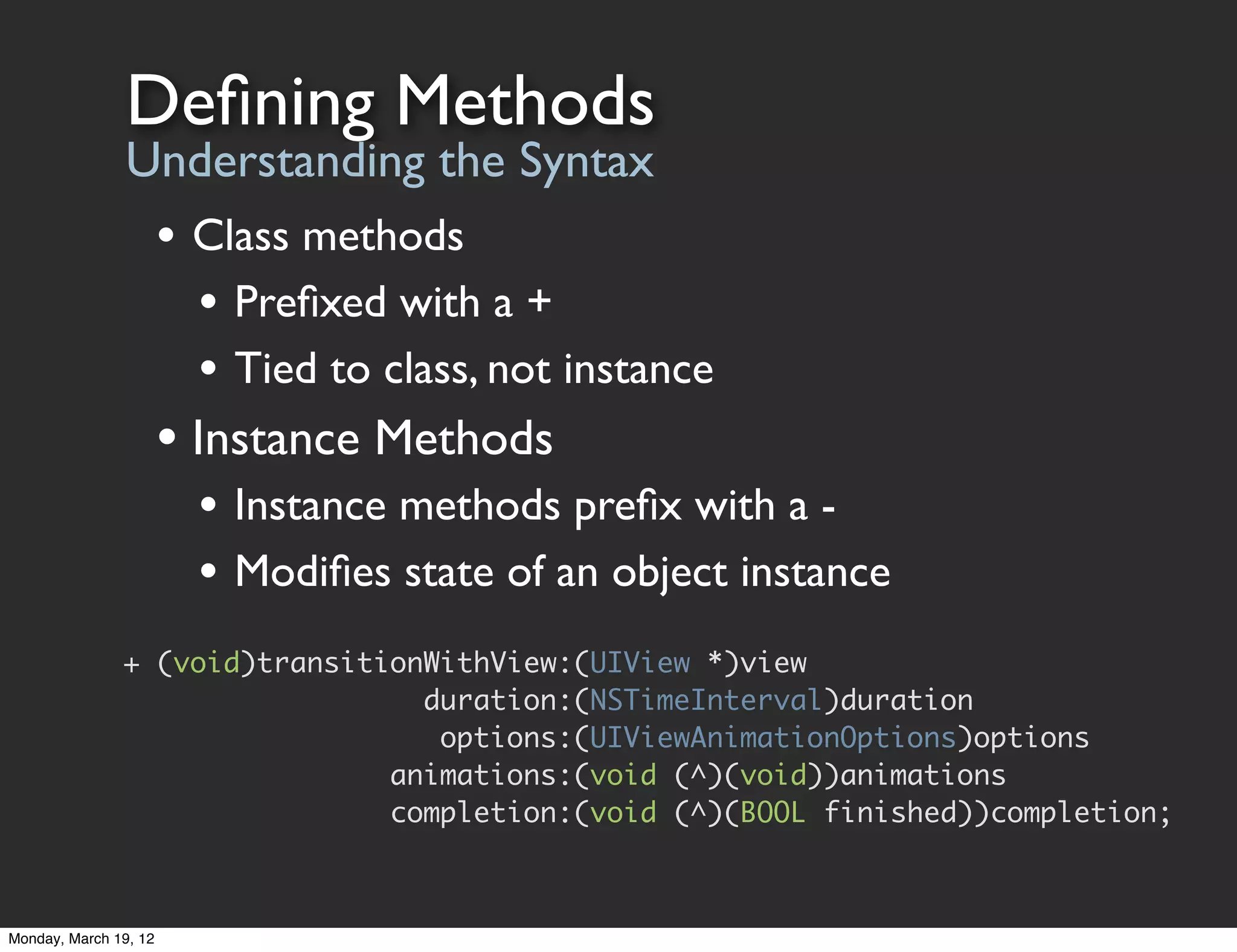
The document provides an overview of tools and concepts for beginning iOS development. It discusses Xcode, the iOS simulator, and Instruments - tools for developing, testing, and profiling iOS apps. It then covers Objective-C concepts like classes, objects, methods, and properties. The document explains how to define classes, work with objects by sending messages, and use properties to simplify accessor code. It also discusses protocols as a way to define interfaces and delegate callbacks. The document concludes by discussing Cocoa Touch frameworks for building iOS UIs and working with views, view controllers, and the MVC design pattern.




















![Defining the Implementation
#import "BankAccount.h"
@implementation BankAccount
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
return self;
}
- (float)withdraw:(float)amount {
// calculate valid withdrawal
return amount;
}
- (void)deposit:(float)amount {
// record transaction
}
@end
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-22-2048.jpg)
![Defining the Implementation
#import "BankAccount.h"
@implementation BankAccount
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
return self;
}
- (float)withdraw:(float)amount {
// calculate valid withdrawal
return amount;
}
- (void)deposit:(float)amount {
// record transaction
}
@end
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-23-2048.jpg)
![Defining the Implementation
#import "BankAccount.h"
@implementation BankAccount
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
return self;
}
- (float)withdraw:(float)amount {
// calculate valid withdrawal
return amount;
}
- (void)deposit:(float)amount {
// record transaction
}
@end
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-24-2048.jpg)
![Defining the Implementation
#import "BankAccount.h"
@implementation BankAccount
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
return self;
}
- (float)withdraw:(float)amount {
// calculate valid withdrawal
return amount;
}
- (void)deposit:(float)amount {
// record transaction
}
@end
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-25-2048.jpg)


![self and super
Talking to yourself
• Methods have implicit reference to owning
object called self
• Additionally have access to superclass
methods using super
-(id)init {
self = [super init];
if (self) {
// do initialization
}
return self;
}
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-29-2048.jpg)

![Two-Stage Creation
• NSObject defines class method called alloc
• Dynamically allocates memory for object
• Returns new instance of receiving class
BankAccount *account = [BankAccount alloc];
• NSObject defines instance method init
• Implemented by subclasses to initialize instance after memory
for it has been allocated
• Subclasses commonly define several initializers
account = [account init];
• alloc and init calls should always nested into single line
BankAccount *account = [[BankAccount alloc] init];
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-31-2048.jpg)
![Messages
Communicating with Objects
• Methods are invoked by passing messages
• Methods are never directly invoked
• Messages dynamically bound to method
implementations at runtime
• Simple messages take the form:
•
[object message];
• Can pass one or more arguments:
•
[object methodWithArg1:arg1 arg2:arg2];
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-32-2048.jpg)
![Messaging an Object
NSMutableDictionary *person =
[NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
[person setObject:@"Joe Smith" forKey:@"name"];
NSString *address = @"123 Street";
NSString *house =
[address substringWithRange:NSMakeRange(0, 3)];
[person setObject:house forKey:@"houseNumber"];
NSArray *children =
[NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"Jack", @"Susie", nil];
[person setObject:children forKey:@"children"];
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-33-2048.jpg)


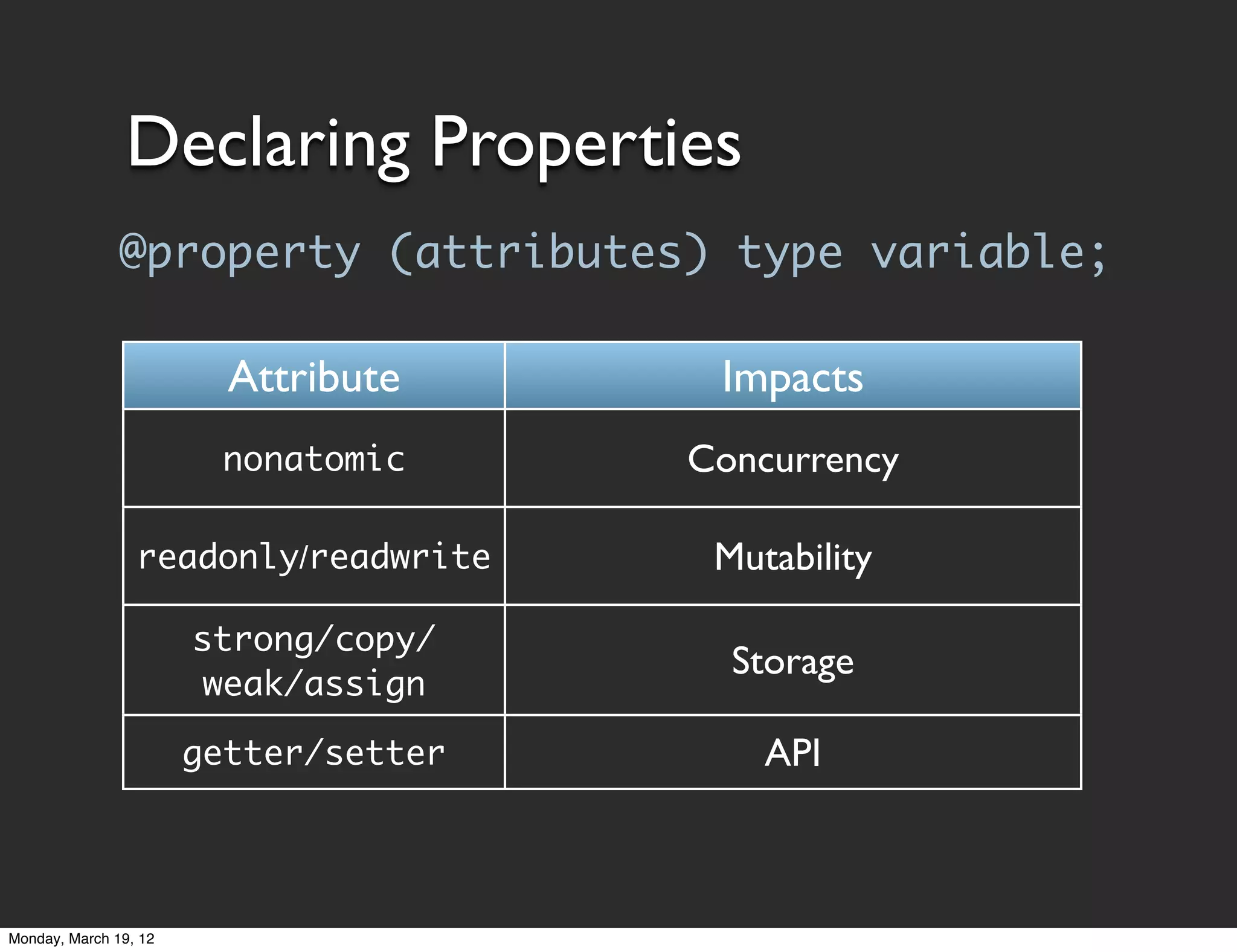
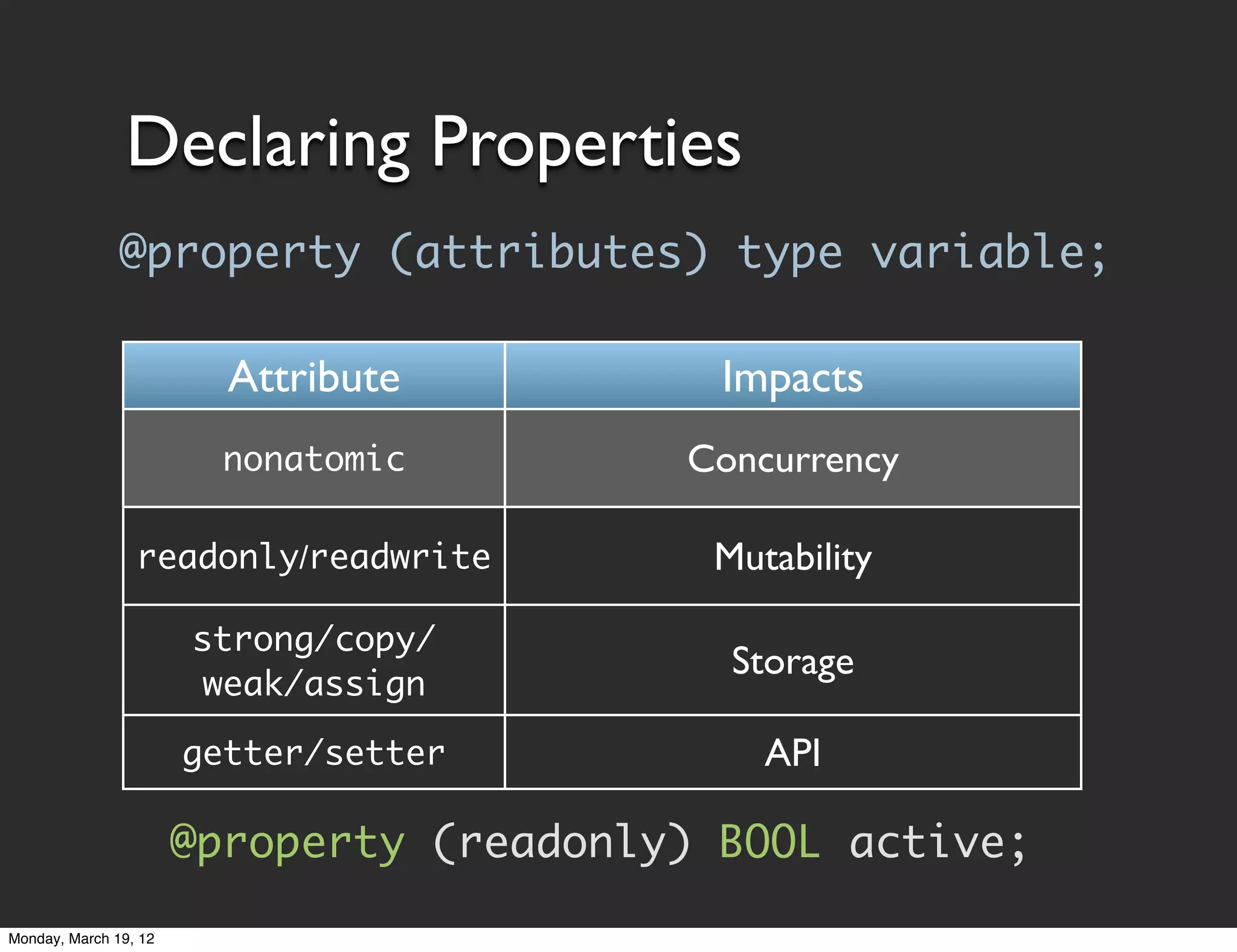
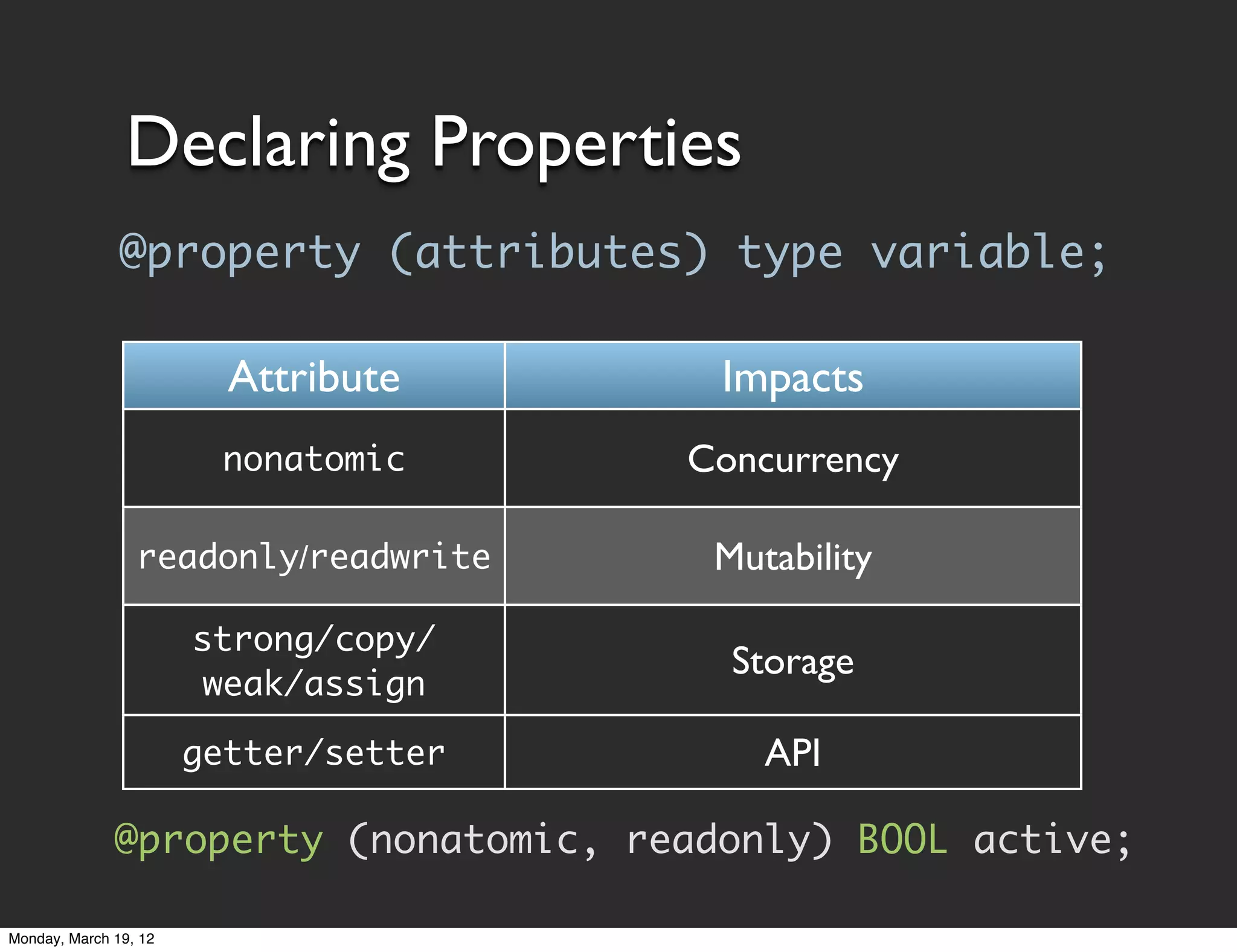
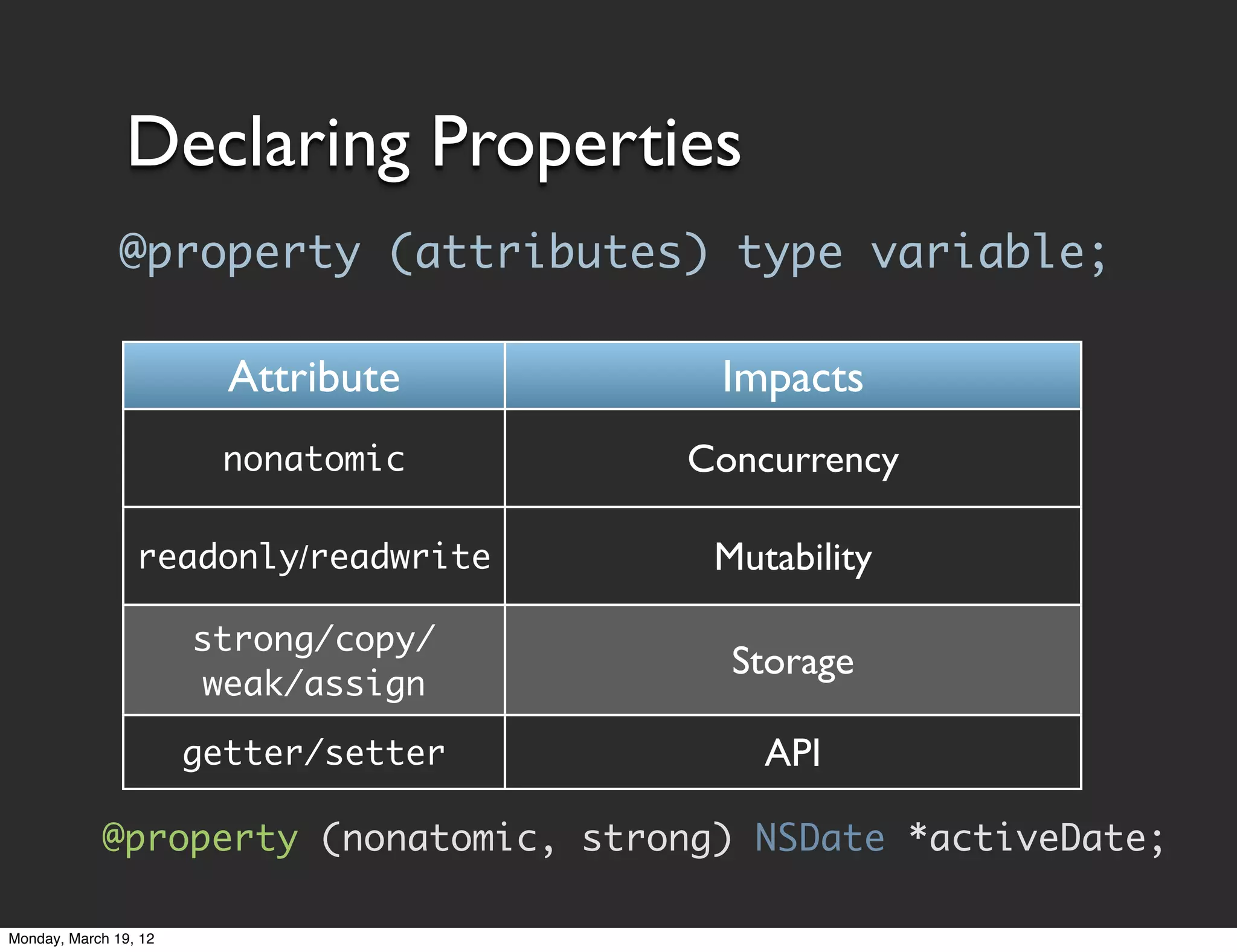
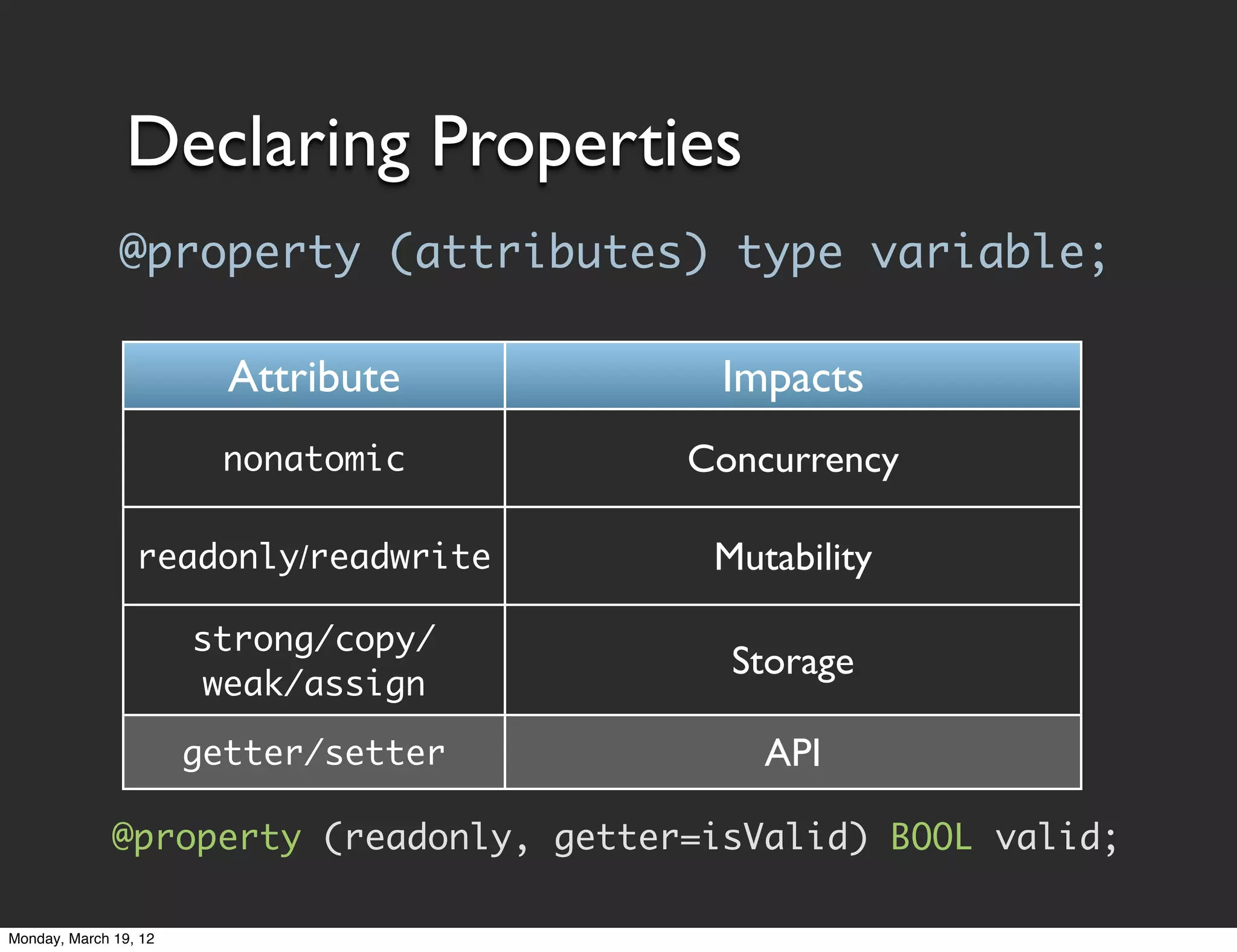

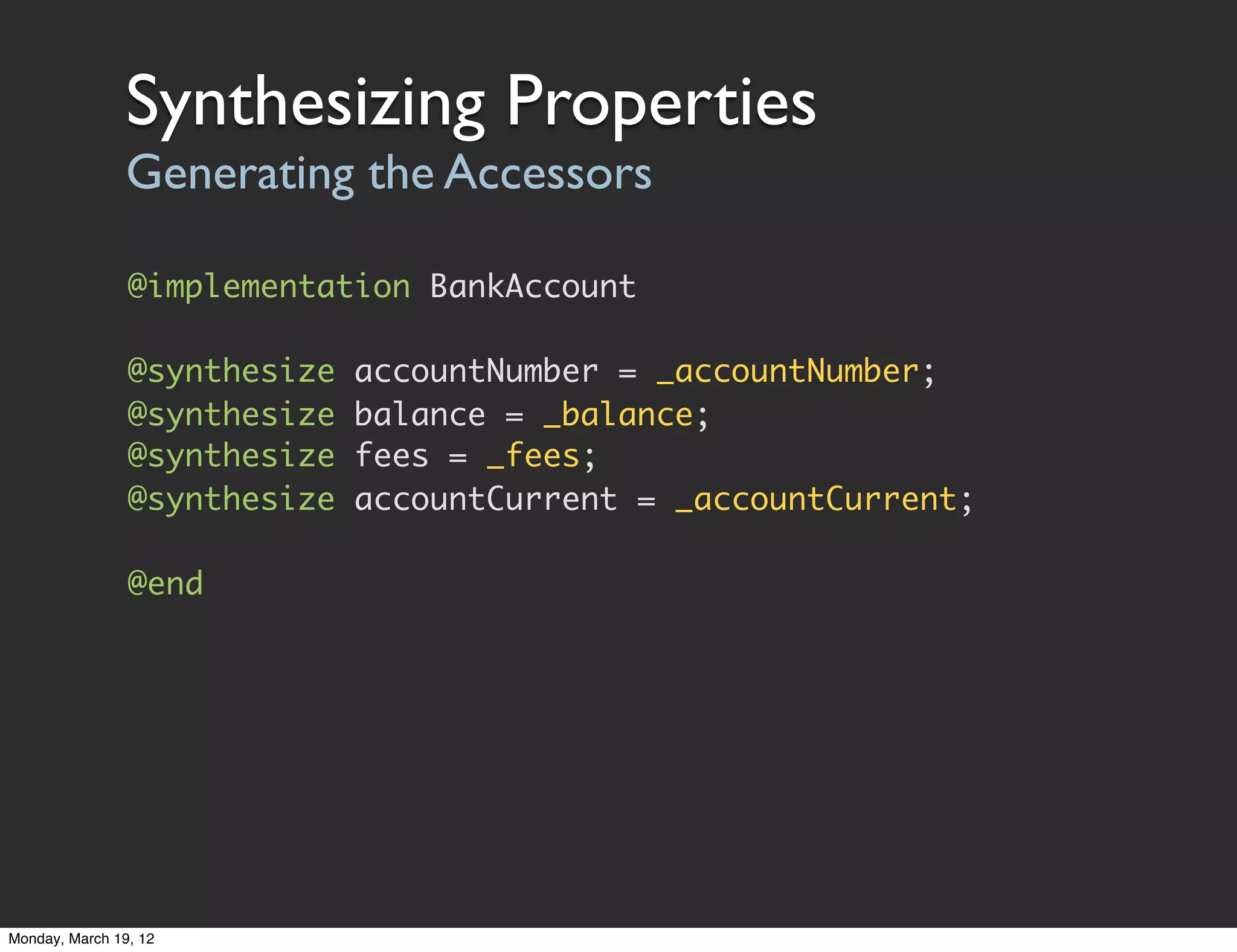
![Accessing Properties
• Generated properties are standard methods
• Accessed through normal messaging syntax
[object property];
[object setProperty:newValue];
• Objective-C property access via dot notation
object.property;
object.property = newValue;
Dot notation is just syntactic sugar. Still uses accessor
methods. Doesn't get/set values directly.
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-43-2048.jpg)





![Adopting a Protocol
Conforming to the Contract
@implementation User
-(id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)coder {
if (self = [super init]) {
self.username = [coder decodeObjectForKey:@"username"];
self.password = [coder decodeObjectForKey:@"password"];
}
return self;
}
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)coder {
[coder encodeObject:self.username forKey:@"username"];
[coder encodeObject:self.username forKey:@"password"];
}
@end
Monday, March 19, 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beginningiospart1-bobmccune-120321111754-phpapp02/75/Beginningi-os-part1-bobmccune-49-2048.jpg)