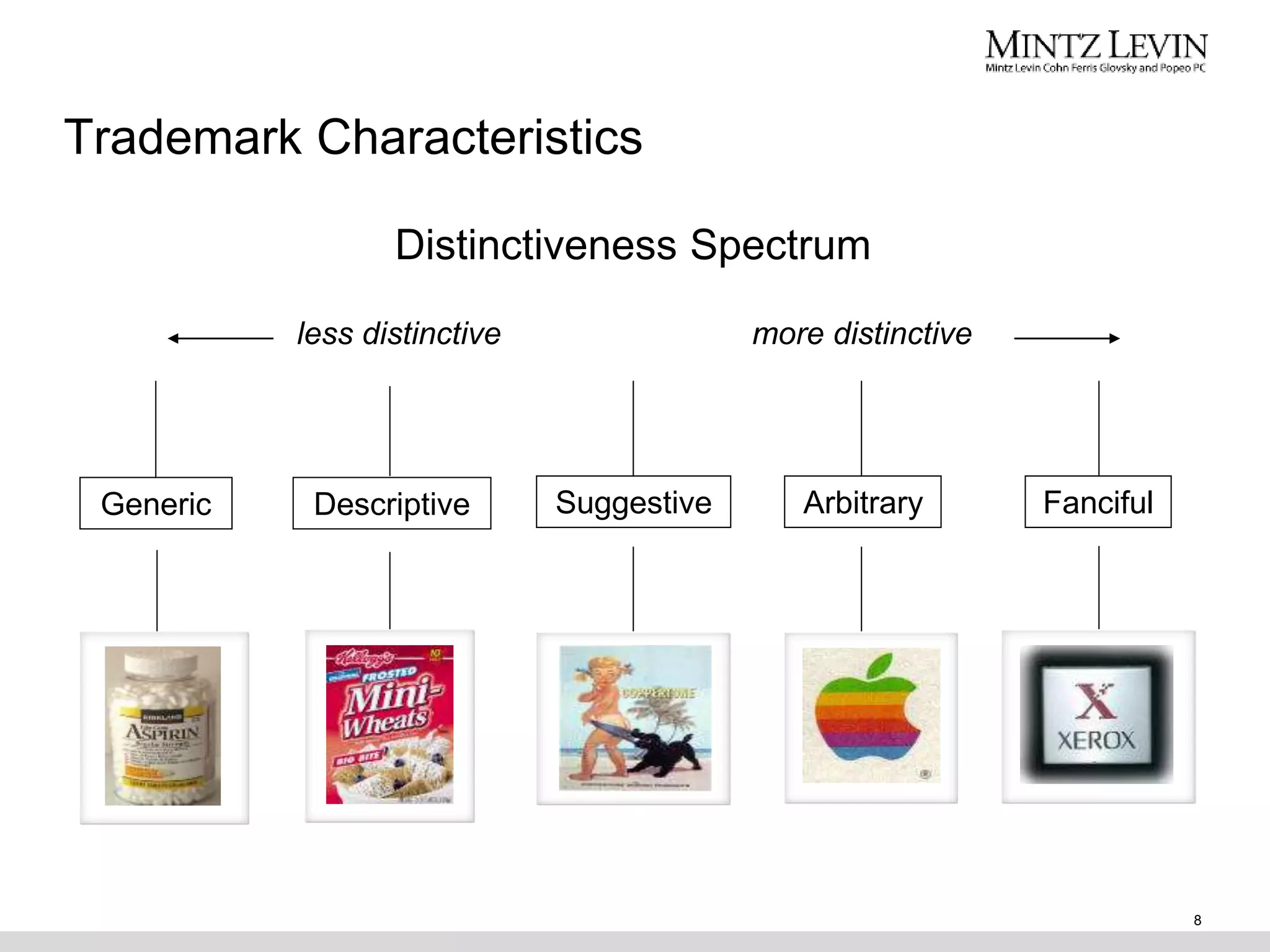
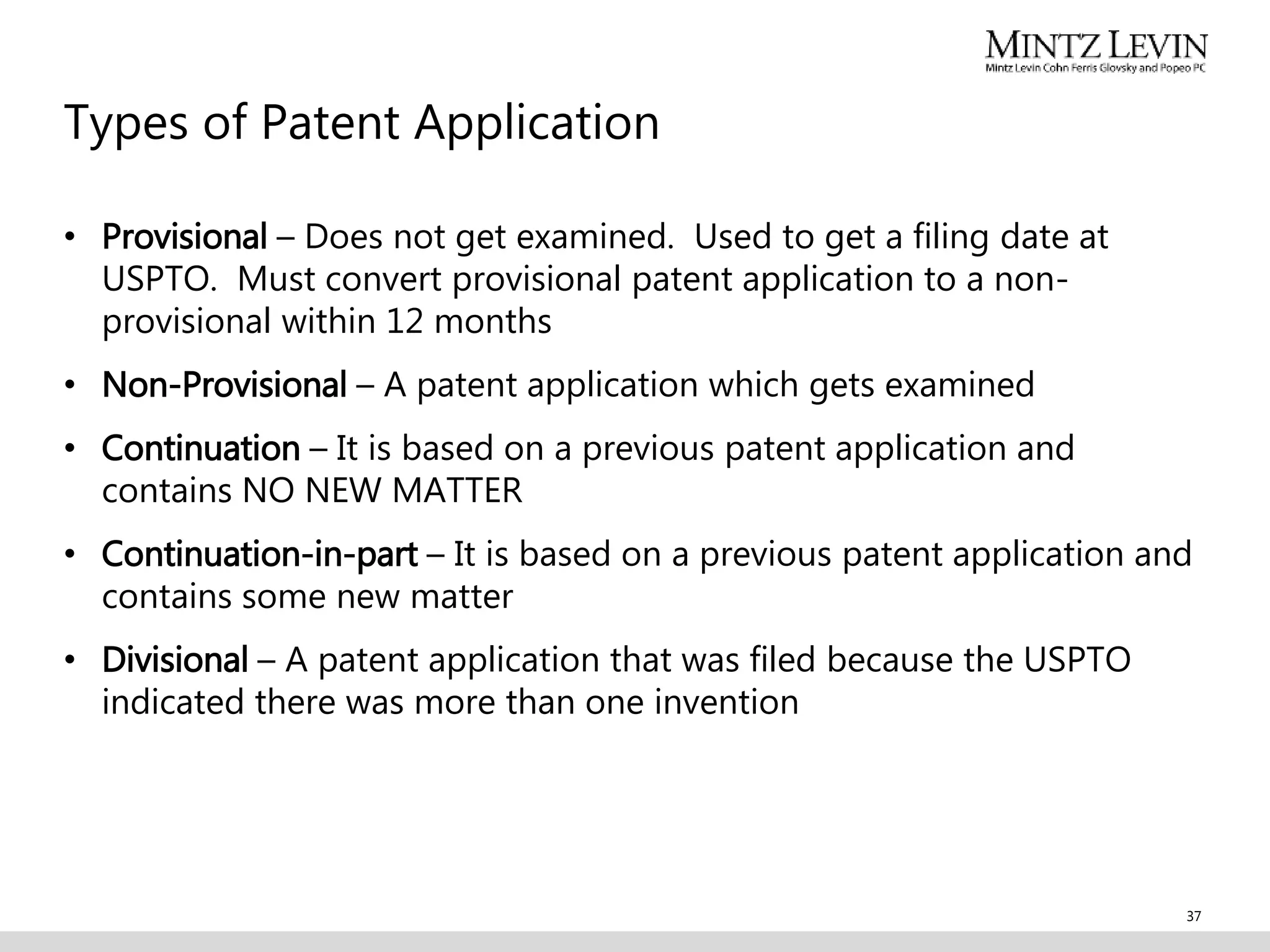
This document provides an overview of various forms of intellectual property including trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and patents. It discusses what each type of intellectual property protects, how to obtain protection, duration of protection, benefits of protection, and common issues to consider. The document covers topics such as trademark clearance searches, federal registration of trademarks and copyrights, requirements for patents including novelty and non-obviousness, international protection, and types of patent applications.