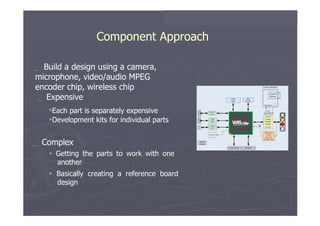
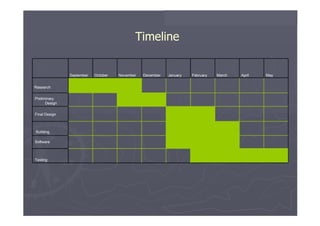
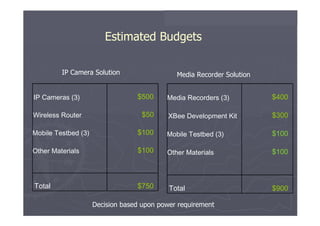
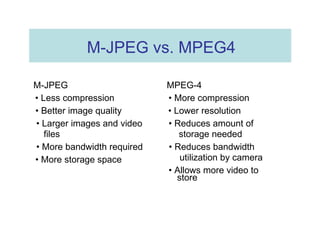
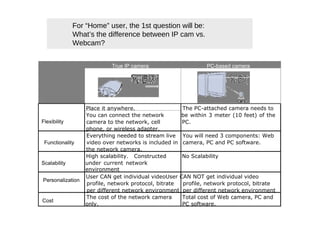
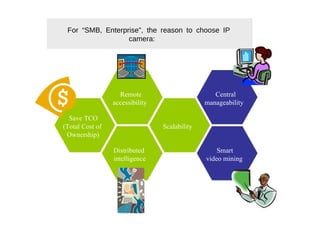
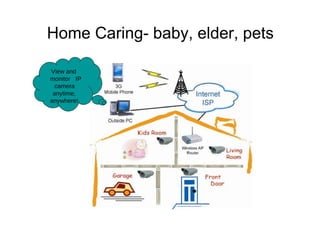
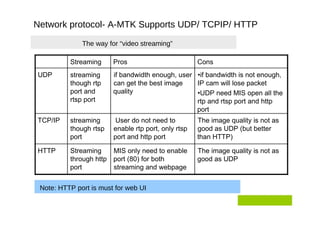
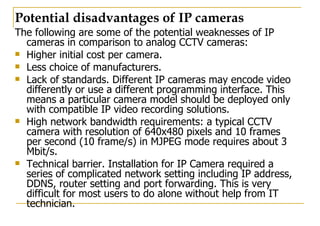
The document outlines different approaches to building a wireless video sensor network, including using existing IP cameras or media recorders with wireless transmission. It discusses the pros and cons of each approach, as well as specifications, components, protocols, and estimated budgets. The timeline shows research and development phases from September to May.